fractions a plenty - Biblical Christian World View
... The median3 of a group of n numbers is the number such that just as many numbers are greater than it as are less than it. For example, in the set of numbers {1, 2, 3}, the median is 2. The median of {1, 1, 1, 2, 10, 15, 16, 20, 100, 105, 110} is 15. You can find the median from a list of numbers as ...
... The median3 of a group of n numbers is the number such that just as many numbers are greater than it as are less than it. For example, in the set of numbers {1, 2, 3}, the median is 2. The median of {1, 1, 1, 2, 10, 15, 16, 20, 100, 105, 110} is 15. You can find the median from a list of numbers as ...
DOC - Rose
... Additionally, we want as tight a bound on x as possible with our choices. To do this, it is easiest to think of the process of picking the digits as an algorithm where you pick the largest c1 available under the FGCE definition to satisfy c1*P(1) ≤ x ≤ (c1+1)*P(1), then pick the largest c2 available ...
... Additionally, we want as tight a bound on x as possible with our choices. To do this, it is easiest to think of the process of picking the digits as an algorithm where you pick the largest c1 available under the FGCE definition to satisfy c1*P(1) ≤ x ≤ (c1+1)*P(1), then pick the largest c2 available ...
PROBLEM SET 7
... The pigeonhole principle is the following observation: Theorem 1. Suppose that > kn marbles are distributed over n jars, then one jar will contain at least ≥ k + 1 marbles. (It can also be formulated in terms of pigeons and pigeonholes, hence the name.) The proof of this pigeonhole principle is easy ...
... The pigeonhole principle is the following observation: Theorem 1. Suppose that > kn marbles are distributed over n jars, then one jar will contain at least ≥ k + 1 marbles. (It can also be formulated in terms of pigeons and pigeonholes, hence the name.) The proof of this pigeonhole principle is easy ...
Supplemental Reading (Kunen)
... A Finitist believes only in finite objects; one is not justified in forming the set of rational numbers, let alone the set of real numbers, so CH is a meaningless statement. There is some merit in the Finitist’s position, since all objects in known physical reality are finite, so that infinite sets ...
... A Finitist believes only in finite objects; one is not justified in forming the set of rational numbers, let alone the set of real numbers, so CH is a meaningless statement. There is some merit in the Finitist’s position, since all objects in known physical reality are finite, so that infinite sets ...
Sequence Notes
... Recursive Definition or Formula: In a recursive definition or formula, the first term in a sequence is given and subsequent terms are defined by the terms before it. If an is the term we are looking for, an-1 is the term before it. To find a specific term, terms prior to it must be found. Ex: Find t ...
... Recursive Definition or Formula: In a recursive definition or formula, the first term in a sequence is given and subsequent terms are defined by the terms before it. If an is the term we are looking for, an-1 is the term before it. To find a specific term, terms prior to it must be found. Ex: Find t ...
Teachers` Notes
... The Tower of Hanoi is a puzzle consisting of three rods, and a number of hoops of different sizes. The hoops are set up on one rod, from largest at the bottom to smallest at the top. The idea is to move all the hoops across to a different rod, using the smallest number of moves possible. But you can ...
... The Tower of Hanoi is a puzzle consisting of three rods, and a number of hoops of different sizes. The hoops are set up on one rod, from largest at the bottom to smallest at the top. The idea is to move all the hoops across to a different rod, using the smallest number of moves possible. But you can ...
4 The Natural Numbers
... The next topic we consider is the set-theoretic reconstruction of the theory of natural numbers. This is a key part of the general program to reduce mathematics to set theory. The basic strategy is to reduce classical arithmetic (thought of as the theory of the natural numbers) to set theory, and ha ...
... The next topic we consider is the set-theoretic reconstruction of the theory of natural numbers. This is a key part of the general program to reduce mathematics to set theory. The basic strategy is to reduce classical arithmetic (thought of as the theory of the natural numbers) to set theory, and ha ...
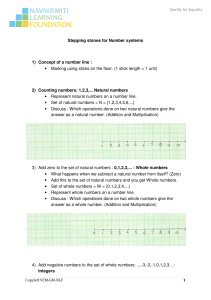
Number System – Natural numbers to Real numbers
... You get a point which is representing √2 It means √2 exists on a number line. What is special about numbers like √2, √3, √5 ? When we try to write them in the form of decimal, they neither terminate, nor repeat. It means they cannot be expressed as p/q where p and q both are integers and q is non-ze ...
... You get a point which is representing √2 It means √2 exists on a number line. What is special about numbers like √2, √3, √5 ? When we try to write them in the form of decimal, they neither terminate, nor repeat. It means they cannot be expressed as p/q where p and q both are integers and q is non-ze ...