Document
... The solar system is made from quarks (baryons) and leptons, interacting via weak, electro-magnetic and strong color forces. This are the only forms of matter we have been able to create in accelerators at energies up 1 TeV ...
... The solar system is made from quarks (baryons) and leptons, interacting via weak, electro-magnetic and strong color forces. This are the only forms of matter we have been able to create in accelerators at energies up 1 TeV ...
INTRODUCTION TO ELEMENTARY PARTICLE PHYSICS
... elementary particles are extremely small, of course, an typically they are also very fast. So elementary particle physics naturally falls under the dominion of quantum field theory. The goal of elementary particle dynamics, then, is to guess a set of force laws which, within the context of quantum f ...
... elementary particles are extremely small, of course, an typically they are also very fast. So elementary particle physics naturally falls under the dominion of quantum field theory. The goal of elementary particle dynamics, then, is to guess a set of force laws which, within the context of quantum f ...
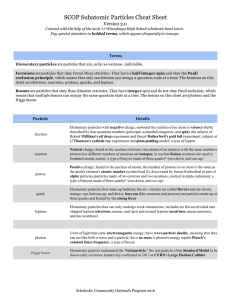
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
... Elementary particles are particles that are, as far as we know, indivisible. Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fe ...
... Elementary particles are particles that are, as far as we know, indivisible. Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fe ...
The Higgs Boson and Electroweak Symmetry Breaking
... The Standard Model contains many fermions fields, a separate one for each left- or right-handed quark or lepton. A supersymmetric extension of the Standard Model therefore contains a huge number of elementary scalar fields. The mass terms for all of these fields are forbidden by the combination of t ...
... The Standard Model contains many fermions fields, a separate one for each left- or right-handed quark or lepton. A supersymmetric extension of the Standard Model therefore contains a huge number of elementary scalar fields. The mass terms for all of these fields are forbidden by the combination of t ...
Tutorial material for weak interactions and more
... new particles predicted by such theories have an masses above the reach of our experiments, one can search for new physics in a more general framework of Effective Field Theory. One assumes that the new particles are too heavy to be produced, but that at high enough energies, sizable corrections to ...
... new particles predicted by such theories have an masses above the reach of our experiments, one can search for new physics in a more general framework of Effective Field Theory. One assumes that the new particles are too heavy to be produced, but that at high enough energies, sizable corrections to ...
An Overview of the Field of High Energy Physics
... photons using relativistic quantum mechanics. • In quantum mechanics, observable quantities are calculated using the “wavefunction” for a particle. • The definition of the wavefunction is not unique... it could be arbitrarily re-defined at each point in space without changing any observables. • This ...
... photons using relativistic quantum mechanics. • In quantum mechanics, observable quantities are calculated using the “wavefunction” for a particle. • The definition of the wavefunction is not unique... it could be arbitrarily re-defined at each point in space without changing any observables. • This ...
Supersymmetry and Lorentz Invariance as Low-Energy
... (1) A Euclidean path integral in quantum physics is equivalent to a partition function in statistical physics. This suggests that a fundamental description of Nature should start with some sort of statistical picture. The true picture is likely to be richer than the one presented here, which may be ...
... (1) A Euclidean path integral in quantum physics is equivalent to a partition function in statistical physics. This suggests that a fundamental description of Nature should start with some sort of statistical picture. The true picture is likely to be richer than the one presented here, which may be ...
Outline Summary
... ending with the standard models for cosmology and particle structure as we understand them now. A brief discussion of the consequences of the special relativity for the structure of space and time introduced by Einstein in 1905 is presented, to be followed by Einstein’s interpretation of the force o ...
... ending with the standard models for cosmology and particle structure as we understand them now. A brief discussion of the consequences of the special relativity for the structure of space and time introduced by Einstein in 1905 is presented, to be followed by Einstein’s interpretation of the force o ...
Monday, September 10 - Long Island University
... • Spectrum depended only on temp, not material • Higher temp meant more intensity & higher average frequency ...
... • Spectrum depended only on temp, not material • Higher temp meant more intensity & higher average frequency ...
Monday, October 15 Agenda
... • Spectrum depended only on temp, not material • Higher temp meant more intensity & higher average frequency ...
... • Spectrum depended only on temp, not material • Higher temp meant more intensity & higher average frequency ...
CLASSICAL FIELD THEORY AND ELECTRODYNAMICS
... approach of the charge, assumed fixed on the x02 axis. 2. An alternative Lagrangian density for the electromagnetic field due to Enrico Fermi is ...
... approach of the charge, assumed fixed on the x02 axis. 2. An alternative Lagrangian density for the electromagnetic field due to Enrico Fermi is ...
The Fine Structure Constant and Electron (g‐2) Factor: Questions
... mass (respectively), these terms are very small compared to the QED expansion. ...
... mass (respectively), these terms are very small compared to the QED expansion. ...
File - AMS02 BOLOGNA
... assures that any particle species there exists the antiparticle with exactly the same mass and decay width and eventually opposite charges. This striking symmetry would naturally lead us to conclude that the Universe contains particles and antiparticles in equal number densities. The observed Univer ...
... assures that any particle species there exists the antiparticle with exactly the same mass and decay width and eventually opposite charges. This striking symmetry would naturally lead us to conclude that the Universe contains particles and antiparticles in equal number densities. The observed Univer ...
What`s common these things
... form the atoms. Its messenger is the photon, the quantum of light Weak interaction It affects both quarks and leptons and it is the only kind of interaction neutrinos can have. It is responsible of weird processes as, for instance, to transform a neutron in a proton (by transforming a down-quark in ...
... form the atoms. Its messenger is the photon, the quantum of light Weak interaction It affects both quarks and leptons and it is the only kind of interaction neutrinos can have. It is responsible of weird processes as, for instance, to transform a neutron in a proton (by transforming a down-quark in ...
Intro to particle physics 1. Particles, Fields
... There are 3 gauge bosons for called corresponding to generators These only interact with L-handed fermions. So this interaction distinguishes L and R helicity, so violates Parity. (Weak interaction parity violation discovered in ~1956) The other gauge group has a gauge boson B, coupling to the quant ...
... There are 3 gauge bosons for called corresponding to generators These only interact with L-handed fermions. So this interaction distinguishes L and R helicity, so violates Parity. (Weak interaction parity violation discovered in ~1956) The other gauge group has a gauge boson B, coupling to the quant ...
Special Issue on Neutrino Research
... gravity, which is relatively weak on the subatomic scale. Therefore a typical neutrino passes through normal matter unimpeded. Neutrinos’ low mass and neutral charge mean they interact exceedingly weakly with other particles and fields. This feature of weak interaction interests scientists because i ...
... gravity, which is relatively weak on the subatomic scale. Therefore a typical neutrino passes through normal matter unimpeded. Neutrinos’ low mass and neutral charge mean they interact exceedingly weakly with other particles and fields. This feature of weak interaction interests scientists because i ...
Slides - Antimatter
... Unified field theory of e and w forces Salaam, Weinberg, Glashow Single interaction above 100 GeV Mediated by W,Z bosons Predictions • Weak neutral currents (1973) • W and Z gauge bosons (CERN, 1983) ...
... Unified field theory of e and w forces Salaam, Weinberg, Glashow Single interaction above 100 GeV Mediated by W,Z bosons Predictions • Weak neutral currents (1973) • W and Z gauge bosons (CERN, 1983) ...
Supercomputing in High Energy Physics
... Particle Physics “Everything in the universe seems to be made of simple, small objects which like to stick together” • Modern realization of this: The Standard Model – A quantum field theory in which point-like, spin-1/2 fermions interact through the exchange of spin-1 vector bosons – Electroweak i ...
... Particle Physics “Everything in the universe seems to be made of simple, small objects which like to stick together” • Modern realization of this: The Standard Model – A quantum field theory in which point-like, spin-1/2 fermions interact through the exchange of spin-1 vector bosons – Electroweak i ...
Standard Model history (2008)
... e-, p, n, ν, μ-, π±, π0, Λ0, Σ+ , Σ0 , Ξ,…. question: Can nature be so messy? are all these particles really intrinsically different? or can we recognize patterns or symmetries in their nature (charge, mass, flavor) or the way they behave (decays)? ...
... e-, p, n, ν, μ-, π±, π0, Λ0, Σ+ , Σ0 , Ξ,…. question: Can nature be so messy? are all these particles really intrinsically different? or can we recognize patterns or symmetries in their nature (charge, mass, flavor) or the way they behave (decays)? ...