Abstract
... itself evident by rise in a compound’ distribution coefficient (Kd, i.e., sorbed concentration over solution concentration) at increasing a solute (sorbate) concentration. The phenomenon of the cooperative sorption was additionally validated for simazine on the OMW-treated Revivim soil (from the 0-3 ...
... itself evident by rise in a compound’ distribution coefficient (Kd, i.e., sorbed concentration over solution concentration) at increasing a solute (sorbate) concentration. The phenomenon of the cooperative sorption was additionally validated for simazine on the OMW-treated Revivim soil (from the 0-3 ...
3.3 Procaryotes – Further questions and answers Q1. Bk Ch3 S3.3
... i Nitrogen is a component of protein, including enzymes, and nucleic acids, both complex organic compounds. Proteins make up a large part of living organisms and nucleic acids are contained in the nucleus—they direct the activities of cells and are involved in heredity. ii Plants obtain nitrogen in ...
... i Nitrogen is a component of protein, including enzymes, and nucleic acids, both complex organic compounds. Proteins make up a large part of living organisms and nucleic acids are contained in the nucleus—they direct the activities of cells and are involved in heredity. ii Plants obtain nitrogen in ...
Profit Maximizing Phospherous Fertilization for Commercial Potato
... Phosphorus (P) is a macronutrient element essential for potato growth and development. Due to its unique chemistry, P fertilizer applied to soil is vulnerable to be immobilized or run off in the northeast Florida where sandy soil dominates. Potato growers have to face thin profit margin and eutrophi ...
... Phosphorus (P) is a macronutrient element essential for potato growth and development. Due to its unique chemistry, P fertilizer applied to soil is vulnerable to be immobilized or run off in the northeast Florida where sandy soil dominates. Potato growers have to face thin profit margin and eutrophi ...
7.2E.4 Erosion and Deposition
... I can describe the differences between the various types of mass movements. I can explain why forces erode some materials and deposit others. I can show why the slope of the land effects erosion. I can predict how modifications can effect the results of erosion and deposition. ...
... I can describe the differences between the various types of mass movements. I can explain why forces erode some materials and deposit others. I can show why the slope of the land effects erosion. I can predict how modifications can effect the results of erosion and deposition. ...
Lithosphere Quiz
... Which of these statements is NOT true? A. The mantle is almost 3,000 KM thick. B. The center of the Earth is more than 6,000 degrees Celsius. C. The hardest layer of the Earth is the crust. D. Humans have not drilled all the way through the crust of the Earth. ...
... Which of these statements is NOT true? A. The mantle is almost 3,000 KM thick. B. The center of the Earth is more than 6,000 degrees Celsius. C. The hardest layer of the Earth is the crust. D. Humans have not drilled all the way through the crust of the Earth. ...
Earth and Environmental Science
... Identify the source of ONE named greenhouse gas whose atmospheric concentration has increased since the Industrial Revolution. ...
... Identify the source of ONE named greenhouse gas whose atmospheric concentration has increased since the Industrial Revolution. ...
15. Identify the problems that have resulted from the indiscriminate
... 34. Why is soil considered as a resource? / What is the importance of soil as a resource? Ans. Soil is considered as a resource because it is used to satisfy our needs. It is the most renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth. It supports different types of living organisms on the ...
... 34. Why is soil considered as a resource? / What is the importance of soil as a resource? Ans. Soil is considered as a resource because it is used to satisfy our needs. It is the most renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth. It supports different types of living organisms on the ...
Chapter 1 Introduction - SOIL 4234 Soil Nutrient Management
... water. Once dissolved, the solid NaCl does not reform until the ions, Na+ + Cl-, are present in high concentration. • When water is lost from the solution by evaporation the solid finally reforms as NaCl precipitate. • Iron oxide or rust, represents multiple charged ions forming a relatively insolub ...
... water. Once dissolved, the solid NaCl does not reform until the ions, Na+ + Cl-, are present in high concentration. • When water is lost from the solution by evaporation the solid finally reforms as NaCl precipitate. • Iron oxide or rust, represents multiple charged ions forming a relatively insolub ...
Casa Grande - Soils 4 Teachers
... decompose. They affect the chemical, physical and biological relationships in the soil. The climate is hot and arid where Casa Grande soils were formed. The annual precipitation is only 6 to 10 inches. The average annual air temperature ranges from 67 to 75 degrees F, which means that more than ¾ of ...
... decompose. They affect the chemical, physical and biological relationships in the soil. The climate is hot and arid where Casa Grande soils were formed. The annual precipitation is only 6 to 10 inches. The average annual air temperature ranges from 67 to 75 degrees F, which means that more than ¾ of ...
Chapter 2 Physical Geography: A Living Planet
... rock created by weathering (mud, sand or silt) v. Mechanical Weathering – processes that break rock into smaller pieces (doesn’t change the composition of rock, but the size) example: road construction ...
... rock created by weathering (mud, sand or silt) v. Mechanical Weathering – processes that break rock into smaller pieces (doesn’t change the composition of rock, but the size) example: road construction ...
residual .vs. transported soils(cont)
... LANDFILLS ARE NOT COVERED IN THIS COURSE. HOWEVER, THEY ARE RELEVANT RELATED TOPICS ...
... LANDFILLS ARE NOT COVERED IN THIS COURSE. HOWEVER, THEY ARE RELEVANT RELATED TOPICS ...
Wind erosion intensity determination by airbone capture
... event between 10:00 and 11:00 at an average wind speed of 5.6 ms-1 364.4 grams of eroded soil was trapped equating to 275.0 kg.ha-1.hour-1 of soil loss. A third measurement was performed between 11:00 to 12:00 the same day in the same place at an average speed of 4.3 ms-1. In soil particle catcher 1 ...
... event between 10:00 and 11:00 at an average wind speed of 5.6 ms-1 364.4 grams of eroded soil was trapped equating to 275.0 kg.ha-1.hour-1 of soil loss. A third measurement was performed between 11:00 to 12:00 the same day in the same place at an average speed of 4.3 ms-1. In soil particle catcher 1 ...
Earth History Benchmark Study Guide 2014 Sedimentary Rocks
... Principle of Superposition states that sedimentary rock layers on the bottom formed, or were deposited, first and are older than layers that formed on the top. Those small pieces are then glued together due to compaction and cementation to form a new rock (kind of like cement). Common examples inclu ...
... Principle of Superposition states that sedimentary rock layers on the bottom formed, or were deposited, first and are older than layers that formed on the top. Those small pieces are then glued together due to compaction and cementation to form a new rock (kind of like cement). Common examples inclu ...
Sulfur for Kentucky Grain Crops: A Meta
... mean difference = 4.1 bu/A standard error = ± 0.6 bu/A significant at the 99.9% level of confidence Paul et al, 2011, Phytopathology 101:1122-1132 Department of Plant and Soil Sciences ...
... mean difference = 4.1 bu/A standard error = ± 0.6 bu/A significant at the 99.9% level of confidence Paul et al, 2011, Phytopathology 101:1122-1132 Department of Plant and Soil Sciences ...
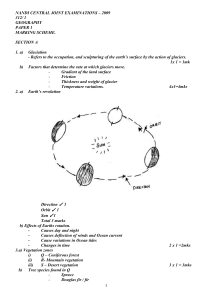
nandi central joint examinations – 2009
... weak carbonic acid. The rainwater dissolves calcium carbonate as it percolates through limestone joints The solution in form of calcium hydrogen carbonate drips to the floor of the cave. Some of the water and carbon dioxide are released leaning behind deposits of calcium carbonate. The calcium carbo ...
... weak carbonic acid. The rainwater dissolves calcium carbonate as it percolates through limestone joints The solution in form of calcium hydrogen carbonate drips to the floor of the cave. Some of the water and carbon dioxide are released leaning behind deposits of calcium carbonate. The calcium carbo ...
Scheck-Diagnosing Strawberry Root and Crown Diseases
... • Isolate from the margin of healthy and discolored tissue • Grows on semi-selective media for fungi amended with antibacterial and antifungal compounds • Identification based on colony size and shape plus on size and shape of conidia ...
... • Isolate from the margin of healthy and discolored tissue • Grows on semi-selective media for fungi amended with antibacterial and antifungal compounds • Identification based on colony size and shape plus on size and shape of conidia ...
Mineral – Naturally formed solids that are not made from living
... Mineral – Naturally formed solids that are not made from living organisms. Have same chemical makeup throughout. Ex: Graphite, Quartz, Magnetite, mica, feldspar Rock – Naturally occurring solid mixture of minerals. Classified by composition and texture Rock Cycle – Process by which new rocks formed ...
... Mineral – Naturally formed solids that are not made from living organisms. Have same chemical makeup throughout. Ex: Graphite, Quartz, Magnetite, mica, feldspar Rock – Naturally occurring solid mixture of minerals. Classified by composition and texture Rock Cycle – Process by which new rocks formed ...
SGN 100 SGN 150 SGN 250 SGN 350 50 pounds (22 kg.) 2,000
... 1. For use as an Aerification Amendment: On golf course greens, tees and fairways, commercial & residential lawns and sports turf: • Aerify surface to be treated. • Broadcast 5 to 10 lbs of NutriSmart B per 1,000 ft2. • Drag NutriSmart B into holes. • Top dress as normal. Note: Apply NutriSmart B at ...
... 1. For use as an Aerification Amendment: On golf course greens, tees and fairways, commercial & residential lawns and sports turf: • Aerify surface to be treated. • Broadcast 5 to 10 lbs of NutriSmart B per 1,000 ft2. • Drag NutriSmart B into holes. • Top dress as normal. Note: Apply NutriSmart B at ...
Chapter 3 – Erosion and Deposition
... Deposition can add to a river’s flood plain. Alluvial fan – a wide, sloping deposit of sediment formed where a stream leaves a mountain range. Deposit is shaped like a fan. Deltas - sediment deposited where a river flows into the ocean – variety of shapes Soil of the flood plains – deposition of new ...
... Deposition can add to a river’s flood plain. Alluvial fan – a wide, sloping deposit of sediment formed where a stream leaves a mountain range. Deposit is shaped like a fan. Deltas - sediment deposited where a river flows into the ocean – variety of shapes Soil of the flood plains – deposition of new ...
How can I determine watershed patterns and their divides on a map?
... Affected by the permeability of the land cover. Permeability is determined size of the pores in the land cover. The smaller the pores the more impermeable the land cover. The larger the pores the more permeable the land cover. Water is pulled into the ground by gravity. Some of the water is ab ...
... Affected by the permeability of the land cover. Permeability is determined size of the pores in the land cover. The smaller the pores the more impermeable the land cover. The larger the pores the more permeable the land cover. Water is pulled into the ground by gravity. Some of the water is ab ...
Conservation Agriculture under different Agro Eco
... almost 1 billion still do not have enough to eat. I want to see an end to hunger everywhere within my lifetime.” – Ban Ki-moon, United ...
... almost 1 billion still do not have enough to eat. I want to see an end to hunger everywhere within my lifetime.” – Ban Ki-moon, United ...