The Global Hydrological Cycle
... • 77.2% of this is in cold storage. • 22.4% is in groundwater storage. • 0.35% in lakes and swamps. • 0.01% in rivers and streams. ...
... • 77.2% of this is in cold storage. • 22.4% is in groundwater storage. • 0.35% in lakes and swamps. • 0.01% in rivers and streams. ...
Michigan Groundwater Stewardship Program
... identifying groundwater risks coordinate resources to reduce those risks pollution prevention through education, not regulation! ...
... identifying groundwater risks coordinate resources to reduce those risks pollution prevention through education, not regulation! ...
Hydrologic Cycle Note
... leaves behind salts and other impurities as it evaporates. As the evaporated moisture rises, it declines in temperature at the average rate of 1°C/100m. Moving air masses carry the vapour over the land. Condensation: Water vapour is changed to a liquid (or solid). A critical temperature called “dewp ...
... leaves behind salts and other impurities as it evaporates. As the evaporated moisture rises, it declines in temperature at the average rate of 1°C/100m. Moving air masses carry the vapour over the land. Condensation: Water vapour is changed to a liquid (or solid). A critical temperature called “dewp ...
Protecting Resources
... ◦ sand- biggest grains; most space ◦ Silt- grains just large enough to see ◦ Clay- the grains too small to see; least space between particles- holds water ...
... ◦ sand- biggest grains; most space ◦ Silt- grains just large enough to see ◦ Clay- the grains too small to see; least space between particles- holds water ...
Strand 17: Review
... SC.L17.20 IMPACT OF INDIVIDUALS ON ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS Human activities may be increasingly harmful to ecosystems. However unlike other organisms, humans can recognize their impact on natural systems and change their behavior to minimize those effects 1. Use of resources (renewable and nonrenewab ...
... SC.L17.20 IMPACT OF INDIVIDUALS ON ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS Human activities may be increasingly harmful to ecosystems. However unlike other organisms, humans can recognize their impact on natural systems and change their behavior to minimize those effects 1. Use of resources (renewable and nonrenewab ...
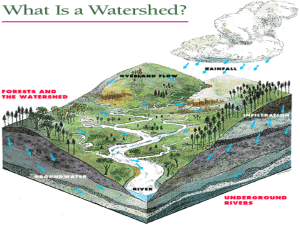
What is a watershed?
... pavement •Irrigate efficiently to avoid runoff from your yard •Minimize pavement to allow water to soak into the ground •Pick up feces that your animal deposits on you lawn ...
... pavement •Irrigate efficiently to avoid runoff from your yard •Minimize pavement to allow water to soak into the ground •Pick up feces that your animal deposits on you lawn ...
SULIS
... A shallow sunken garden that recycles rain Less than 8” deep Gently sloping sides Rainwater runoff is directed toward it Runoff soaks in ...
... A shallow sunken garden that recycles rain Less than 8” deep Gently sloping sides Rainwater runoff is directed toward it Runoff soaks in ...
THE EFFECT OF AGRICULTURE
... the growing points of grasses due to overgrazing. Without plant cover, the land easily erodes. The trampling of such a large population of animals on soil rapidly compacts it into a hard layer that can hardly absorb any rain. The dry soil is easily blown away. ...
... the growing points of grasses due to overgrazing. Without plant cover, the land easily erodes. The trampling of such a large population of animals on soil rapidly compacts it into a hard layer that can hardly absorb any rain. The dry soil is easily blown away. ...
Rappahannock County Clean Streams Initiative
... In Virginia, NPS pollution occurs mainly through stormwater runoff. When it rains, runoff from farmland, city streets, construction sites & suburban lawns, roofs and driveways enters our waterways. NPS pollution can be unnoticed for years, which makes it more difficult to control. The four major for ...
... In Virginia, NPS pollution occurs mainly through stormwater runoff. When it rains, runoff from farmland, city streets, construction sites & suburban lawns, roofs and driveways enters our waterways. NPS pollution can be unnoticed for years, which makes it more difficult to control. The four major for ...
Effects of Catastrophic Events Notes • Tornadoes
... soil down to the rock; New species of plants can grow in the cleared area; Plants that survive can grow more abundantly than other species, which can hinder plant and animal interaction; Loss of vegetation could lead to soil erosion Hurricanes Effect on Ecosystem Deaths due to flooding; Uproot trees ...
... soil down to the rock; New species of plants can grow in the cleared area; Plants that survive can grow more abundantly than other species, which can hinder plant and animal interaction; Loss of vegetation could lead to soil erosion Hurricanes Effect on Ecosystem Deaths due to flooding; Uproot trees ...
Environmental Requirements for Good Plant Growth
... • Water does not continue to move through the soil at this point • Plant roots must continue to move in search of the soil – Soil surrounding them is dried out by rot absorption – Roots will not grow in air-dry soil where no moisture is present • Field capacity is high in heavy soils (clay particles ...
... • Water does not continue to move through the soil at this point • Plant roots must continue to move in search of the soil – Soil surrounding them is dried out by rot absorption – Roots will not grow in air-dry soil where no moisture is present • Field capacity is high in heavy soils (clay particles ...
Earths Changing Surface
... away from each other. 2. _________ is when 2 oceanic plates move apart. 3. ________ occurs along the boundary of sea floor spreading. 4. Breaks or cracks in earth’s surface are called _____ 5. Earthquakes occur as a result of _______ boundaries. ...
... away from each other. 2. _________ is when 2 oceanic plates move apart. 3. ________ occurs along the boundary of sea floor spreading. 4. Breaks or cracks in earth’s surface are called _____ 5. Earthquakes occur as a result of _______ boundaries. ...
Impact of Land use change on water resources on Mt Elgon
... towers but under stress due to global change (climate change, LUC) • Land use/cover dynamics constitute an important factor esp. in fragile mountain areas e.g. Mt Elgon ...
... towers but under stress due to global change (climate change, LUC) • Land use/cover dynamics constitute an important factor esp. in fragile mountain areas e.g. Mt Elgon ...
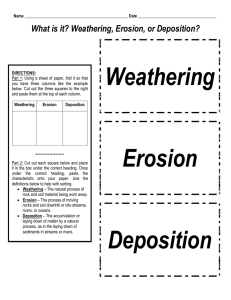
Weathering, Erosion, or Deposition? Weathering Erosion Deposition
... Part 2: Cut out each square below and place it in the box under the correct heading. Once under the correct heading, paste the characteristic onto your paper. Use the definitions below to help with sorting. • Weathering – The natural process of rock and soil material being worn away. • Erosion – The ...
... Part 2: Cut out each square below and place it in the box under the correct heading. Once under the correct heading, paste the characteristic onto your paper. Use the definitions below to help with sorting. • Weathering – The natural process of rock and soil material being worn away. • Erosion – The ...
Section 1 - kjpederson
... 3. gravity: a force that moves rocks and other materials downhill; that force that pulls objects toward each other 4. mass movement: any one of several processes by which gravity moves sediment downhill 5. sediment: small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or organisms; earth materials d ...
... 3. gravity: a force that moves rocks and other materials downhill; that force that pulls objects toward each other 4. mass movement: any one of several processes by which gravity moves sediment downhill 5. sediment: small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or organisms; earth materials d ...
1-20-15 About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
Monitoring soil erosion risk in the agricultural landscapes of South
... production in South Australia. The South Australian Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources (DEWNR) has monitored the erosion protection status of agricultural soils using ground-based observational surveys since 1999. Recent developments in remote sensing provide the potential for mo ...
... production in South Australia. The South Australian Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources (DEWNR) has monitored the erosion protection status of agricultural soils using ground-based observational surveys since 1999. Recent developments in remote sensing provide the potential for mo ...
Water Pollution Notes
... spawning grounds of benthic species, clog harbors & lakes • Heat (Thermal pollution) o Examples include excessive heat o Major sources—water cooling of electric power plants o Lowers DO levels & causes thermal shock in species Forms of water pollution— • Point sources—discharge pollutants at specifi ...
... spawning grounds of benthic species, clog harbors & lakes • Heat (Thermal pollution) o Examples include excessive heat o Major sources—water cooling of electric power plants o Lowers DO levels & causes thermal shock in species Forms of water pollution— • Point sources—discharge pollutants at specifi ...
2974b719ed02e1d05b6180accf6894840a8bcccc
... 22. Arêtes and cirques are features that are associated with which agent of erosion? glaciers 23. What is the most important factor that determines a soil’s characteristic? Soil composition 24. Slump, creep, landslides, and mudflows are all examples of this. Mass movement 25. After a heavy rain, str ...
... 22. Arêtes and cirques are features that are associated with which agent of erosion? glaciers 23. What is the most important factor that determines a soil’s characteristic? Soil composition 24. Slump, creep, landslides, and mudflows are all examples of this. Mass movement 25. After a heavy rain, str ...
Directions: Fill in the 15 blanks ______ in the text using the correct
... rivers, ____________ increasing the salinization of areas downstream and the Aral Sea itself. Other short-sighted agricultural practices in the irrigated land include the extensive use of artificial fertilizers and ____________ pesticides to support production of the two main crops, rice and cotton. ...
... rivers, ____________ increasing the salinization of areas downstream and the Aral Sea itself. Other short-sighted agricultural practices in the irrigated land include the extensive use of artificial fertilizers and ____________ pesticides to support production of the two main crops, rice and cotton. ...
Soil, surface water and ground water phosphorus relationships in a
... surface water (range = 2–2350 mg L 1, median = 85 mg L 1) and soil water (range = 22–802 mg L 1, median = 202 mg L 1) which flowed through organic soils, compared with small concentrations of TDP in ground water which flowed through mineral soils (range = 0–1705 mg L 1, median = 23 mg L 1). Our resu ...
... surface water (range = 2–2350 mg L 1, median = 85 mg L 1) and soil water (range = 22–802 mg L 1, median = 202 mg L 1) which flowed through organic soils, compared with small concentrations of TDP in ground water which flowed through mineral soils (range = 0–1705 mg L 1, median = 23 mg L 1). Our resu ...
4-2 Erosion NOTES
... Material is very poorly sorted at the base of the cliff (big sediments mixed with small sediments) No time for material to be sorted by size Water Erosion Streams erode their channels by abrasion and grinding Sediments become dissolved inside the stream (dissolved load) Sediments being car ...
... Material is very poorly sorted at the base of the cliff (big sediments mixed with small sediments) No time for material to be sorted by size Water Erosion Streams erode their channels by abrasion and grinding Sediments become dissolved inside the stream (dissolved load) Sediments being car ...
External Forces Shaping the Earth
... For erosion to occur, a transporting agent, such as water or wind must be present. When a river enters the ocean, the sediment is deposited in a fan like landform called a delta. ...
... For erosion to occur, a transporting agent, such as water or wind must be present. When a river enters the ocean, the sediment is deposited in a fan like landform called a delta. ...
Fort Wayne City Utilities
... thinking about how lawn and garden care can affect our rivers and streams. What we do in our yards can have huge impacts locally and many miles downstream. While fertilizers, pesticides, and other lawn care chemicals may be good for the lawn or gardens, these chemicals may negatively affect water qu ...
... thinking about how lawn and garden care can affect our rivers and streams. What we do in our yards can have huge impacts locally and many miles downstream. While fertilizers, pesticides, and other lawn care chemicals may be good for the lawn or gardens, these chemicals may negatively affect water qu ...
Surface runoff

Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water that occurs when excess stormwater, meltwater, or other sources flows over the earth's surface. This might occur because soil is saturated to full capacity, because rain arrives more quickly than soil can absorb it, or because impervious areas (roofs and pavement) send their runoff to surrounding soil that cannot absorb all of it. Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent in soil erosion by water.Runoff that occurs on the ground surface before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source. If a nonpoint source contains man-made contaminants, or natural forms of pollution (such as rotting leaves) the runoff is called nonpoint source pollution. A land area which produces runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. When runoff flows along the ground, it can pick up soil contaminants including, but not limited to petroleum, pesticides, or fertilizers that become discharge or nonpoint source pollution.In addition to causing water erosion and pollution, surface runoff in urban areas is a primary cause of urban flooding which can result in property damage, damp and mold in basements, and street flooding.