HORTICULTURE_files/Unit 8
... • Parent material: The original rocky material before weathering has taken place • Lower plant forms such as lichens, moss, and fungi grow on rock matter • Organic matter: The decay of plants and animals which is essential for soil formation ...
... • Parent material: The original rocky material before weathering has taken place • Lower plant forms such as lichens, moss, and fungi grow on rock matter • Organic matter: The decay of plants and animals which is essential for soil formation ...
NAME - KCSE Online
... - Destruction of plates along their margins. (1 x 1 = 1mk) b) Features formed when plates move away from each other at the boundary - Faults - Extension boundary farming - Mid ocean ridges (1 x 1 = 1mk) (b) Effects of climate change - The global warming due to increase of greenhouse gases. - Widespr ...
... - Destruction of plates along their margins. (1 x 1 = 1mk) b) Features formed when plates move away from each other at the boundary - Faults - Extension boundary farming - Mid ocean ridges (1 x 1 = 1mk) (b) Effects of climate change - The global warming due to increase of greenhouse gases. - Widespr ...
Soil Problems
... down by gravity to a tank and allowed to settle. Floatable materials rise. The partly clarified liquid stream flows from a submerged outlet into subsurface trenches filled with gravel, and sand. Microorganisms biologically break down the sewage into less a harmful product. Eventually, it discharges ...
... down by gravity to a tank and allowed to settle. Floatable materials rise. The partly clarified liquid stream flows from a submerged outlet into subsurface trenches filled with gravel, and sand. Microorganisms biologically break down the sewage into less a harmful product. Eventually, it discharges ...
Soil in Persian Poetry and culture
... Geography, Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany (s.alavipanah@ut.ac.ir) ...
... Geography, Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany (s.alavipanah@ut.ac.ir) ...
APES Focus/Ch - cynthiaahmed
... Name some of the rare metals needed to produce electric or hybrid vehicles. Then, describe the process required to remove them. What are the consequences of this process? ...
... Name some of the rare metals needed to produce electric or hybrid vehicles. Then, describe the process required to remove them. What are the consequences of this process? ...
Document
... Earth’s External Processes • Weathering – disintegration of rock at or near the earth’s surface • Mass wasting – transfer of material down slope in response to gravity • Erosion – transportation of material by a mobile agent such as water, wind, or ice ...
... Earth’s External Processes • Weathering – disintegration of rock at or near the earth’s surface • Mass wasting – transfer of material down slope in response to gravity • Erosion – transportation of material by a mobile agent such as water, wind, or ice ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Study Guide
... Examples of erosion: sand being carried away from a beach by wind or water, sediment being washed away by a river, __________ – the dropping off of sediment Examples of deposition: formation of a delta, a river getting narrower and shallower ___________ Movement – whether towards, away from, or ...
... Examples of erosion: sand being carried away from a beach by wind or water, sediment being washed away by a river, __________ – the dropping off of sediment Examples of deposition: formation of a delta, a river getting narrower and shallower ___________ Movement – whether towards, away from, or ...
Weathering and Erosion
... speeds over 140 km per hour. • These terrifying winds can move materials, such as boulders, rocks, sands, and soils. ...
... speeds over 140 km per hour. • These terrifying winds can move materials, such as boulders, rocks, sands, and soils. ...
Part 3: Spreading on Frozen and Snow-covered Ground
... and application of manure to frozen and snowcovered ground is a common practice in Michigan. The challenge for a livestock producer is to apply manure in a way that is labor-efficient, cost-effective and environmentally responsible. Management strategies that capture land-applied manure in the root ...
... and application of manure to frozen and snowcovered ground is a common practice in Michigan. The challenge for a livestock producer is to apply manure in a way that is labor-efficient, cost-effective and environmentally responsible. Management strategies that capture land-applied manure in the root ...
STATION 1: EARTH`S INTERIOR 1. Pressure occurs – remain here 2
... STATION 3: RIVER 1. Water washes away layers – go to MOUNTAINS 2. Sediments form – go to SOIL 3. Ice melts carrying rocks – remain here 4. Floodwater causes silt from river to be deposited on flood plain – go to SOIL 5. Silt washed into ocean – go to OCEAN 6. Sediments under pressure – go to EARTH’ ...
... STATION 3: RIVER 1. Water washes away layers – go to MOUNTAINS 2. Sediments form – go to SOIL 3. Ice melts carrying rocks – remain here 4. Floodwater causes silt from river to be deposited on flood plain – go to SOIL 5. Silt washed into ocean – go to OCEAN 6. Sediments under pressure – go to EARTH’ ...
All About Soil - Mrs. Marshall's 6th Grade Earth Science
... is the topmost layer of the Earth’s Crust. It is a mixture of minerals, rock particles, water, and organic material that can support plant life. ...
... is the topmost layer of the Earth’s Crust. It is a mixture of minerals, rock particles, water, and organic material that can support plant life. ...
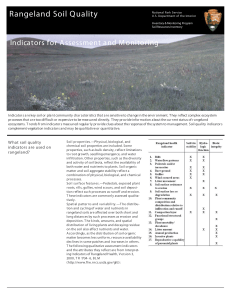
Rangeland Soil Quality
... If the objective is to determine progress or trend, the sites that are representative of the management unit should be selected. If the objective is to provide an opportunity to modify management before degradation occurs, the sites that are most vulnerable should be selected. The detected changes m ...
... If the objective is to determine progress or trend, the sites that are representative of the management unit should be selected. If the objective is to provide an opportunity to modify management before degradation occurs, the sites that are most vulnerable should be selected. The detected changes m ...
Soil Layers - Harperclass
... silt, and clay soils is their grain size. They are also made up of different minerals. • Smallest to largest rock particles. clay, silt, sand ...
... silt, and clay soils is their grain size. They are also made up of different minerals. • Smallest to largest rock particles. clay, silt, sand ...
Martin Hall - Clemson University
... controlling its flow in the Martin Hall area into a rain garden as well as permeable pavement. ...
... controlling its flow in the Martin Hall area into a rain garden as well as permeable pavement. ...
SOIL 205 – SPR 2013 Final Exam Study Topics SOIL
... – know how to calculate Θm and Θv !! – saturation, field capacity, wilting point, air dry, oven dry – how are these defined and what is their practical significance? – relationship between ψ, soi ...
... – know how to calculate Θm and Θv !! – saturation, field capacity, wilting point, air dry, oven dry – how are these defined and what is their practical significance? – relationship between ψ, soi ...
Soil erosion and biodiversity control on small
... conventional and organic farming systems through improved practices for soil husbandry including crop rotations, enhanced climate and environmental performance of agricultural activities through reduced adverse impacts (e.g. of landslides and/or gullies, soil erosion) on agricultural soils, and by a ...
... conventional and organic farming systems through improved practices for soil husbandry including crop rotations, enhanced climate and environmental performance of agricultural activities through reduced adverse impacts (e.g. of landslides and/or gullies, soil erosion) on agricultural soils, and by a ...
Chapter 14 Final Review Weathering and Erosion
... What is Weathering? • Weathering is a process that occurs in nature that disintegrates and decomposes rocks • This happens when the temperature changes or atmospheric and environmental agents change. • Weathering can change the physical or chemical composition of rock materials. ...
... What is Weathering? • Weathering is a process that occurs in nature that disintegrates and decomposes rocks • This happens when the temperature changes or atmospheric and environmental agents change. • Weathering can change the physical or chemical composition of rock materials. ...
File
... Soils that form in limestone bedrock are rich in calcium, Soils that formed from materials at the bottom of lakes are high in clay. ...
... Soils that form in limestone bedrock are rich in calcium, Soils that formed from materials at the bottom of lakes are high in clay. ...
Document
... Horizon C has no organic material. It has only nutrients. C helps determine the pH of B which determines the pH of A. It also determines the rate of absorption and retention of water. There are thousands of types of soils, all carefully classified by geologists but most of the soils can be narrowed ...
... Horizon C has no organic material. It has only nutrients. C helps determine the pH of B which determines the pH of A. It also determines the rate of absorption and retention of water. There are thousands of types of soils, all carefully classified by geologists but most of the soils can be narrowed ...
Soil Types Carsitas - Coachella Valley Water District
... Coachella soils have been worked by water as well as wind. They can usually be found near the old stream bed of the Whitewater River flood course. This is probably the best soil in the Coachella Valley because it is an ideal mix of available water holding capacity, permeability and drainage. Stratif ...
... Coachella soils have been worked by water as well as wind. They can usually be found near the old stream bed of the Whitewater River flood course. This is probably the best soil in the Coachella Valley because it is an ideal mix of available water holding capacity, permeability and drainage. Stratif ...
Soils
... available to the plants 2) Capillary Water is held by cohesive forces greater than gravity and is available to plants 3) Gravitational Water is that water which cannot be held against gravity – as water is pulled down through the soil, nutrients are "leached" out of the soil (nitrogen) ...
... available to the plants 2) Capillary Water is held by cohesive forces greater than gravity and is available to plants 3) Gravitational Water is that water which cannot be held against gravity – as water is pulled down through the soil, nutrients are "leached" out of the soil (nitrogen) ...
Surface runoff

Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water that occurs when excess stormwater, meltwater, or other sources flows over the earth's surface. This might occur because soil is saturated to full capacity, because rain arrives more quickly than soil can absorb it, or because impervious areas (roofs and pavement) send their runoff to surrounding soil that cannot absorb all of it. Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent in soil erosion by water.Runoff that occurs on the ground surface before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source. If a nonpoint source contains man-made contaminants, or natural forms of pollution (such as rotting leaves) the runoff is called nonpoint source pollution. A land area which produces runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. When runoff flows along the ground, it can pick up soil contaminants including, but not limited to petroleum, pesticides, or fertilizers that become discharge or nonpoint source pollution.In addition to causing water erosion and pollution, surface runoff in urban areas is a primary cause of urban flooding which can result in property damage, damp and mold in basements, and street flooding.