Section Nine Earth Science Landforms and Changes to
... The surface of Earth is covered with a variety of different types of landforms. ...
... The surface of Earth is covered with a variety of different types of landforms. ...
Slide 1 - Humble ISD
... • Erosion is the removal of solids (sediment, soil, and other particles) in the natural environment. It usually occurs due to transport by wind, water, or ice; by downslope creep of soil and other material under the force of gravity. ...
... • Erosion is the removal of solids (sediment, soil, and other particles) in the natural environment. It usually occurs due to transport by wind, water, or ice; by downslope creep of soil and other material under the force of gravity. ...
E8C5_CRT_CR_MSTIPS_Final
... 1. Erosion of the Grand Staircase can occur by water, wind, and gravity. 2. Erosion is the movement of rocks whereas weathering is the breakdown of rocks. Each acts on the Grand Staircase by breaking rocks down into sediment and moving them. 3.Sandstone is resistant to weathering and erosion because ...
... 1. Erosion of the Grand Staircase can occur by water, wind, and gravity. 2. Erosion is the movement of rocks whereas weathering is the breakdown of rocks. Each acts on the Grand Staircase by breaking rocks down into sediment and moving them. 3.Sandstone is resistant to weathering and erosion because ...
Studyguide
... ____________________ is the process of wearing away rocks by natural means Blowing wind can cause sand to hit rock and over time the sand will wear away the rock by breaking it into smaller pieces Changes Caused by Moving Water Water can change Earth’s surface by carrying soil and small pieces ...
... ____________________ is the process of wearing away rocks by natural means Blowing wind can cause sand to hit rock and over time the sand will wear away the rock by breaking it into smaller pieces Changes Caused by Moving Water Water can change Earth’s surface by carrying soil and small pieces ...
Impacts of fire on soil
... centimeters of the soil profile to any great extent. More intense, long-lasting fires, such as those under piles of logs, can heat the soil to a greater depth and modify soil properties to approximately 0.5 m, but the temperatures reached depend on factors such as the initial water content and soil ...
... centimeters of the soil profile to any great extent. More intense, long-lasting fires, such as those under piles of logs, can heat the soil to a greater depth and modify soil properties to approximately 0.5 m, but the temperatures reached depend on factors such as the initial water content and soil ...
Topic 5.3 Soil Degradation
... Generally commercial industrialised food production systems reduce soil fertility more than small-scale subsistence farming ...
... Generally commercial industrialised food production systems reduce soil fertility more than small-scale subsistence farming ...
Sample Unit of Study - New York Science Teacher
... A. Identify physical erosion as the breaking down of large pieces to smaller increasing the surface area. B. Identify chemical weathering as the alteration of, or removal of materials in a rock which can change its physical properties making it easier to alter its size and shape. C. Explain how surf ...
... A. Identify physical erosion as the breaking down of large pieces to smaller increasing the surface area. B. Identify chemical weathering as the alteration of, or removal of materials in a rock which can change its physical properties making it easier to alter its size and shape. C. Explain how surf ...
Coastal Map Reading
... features and coastlines. Do you know what concordant and discordant coastlines are? (ii) the fetch and common weather and sea conditions are also important. Remember the fetch is the distance of open water over which wind blows. The longer the fetch, the stronger the winds and the longer they blow, ...
... features and coastlines. Do you know what concordant and discordant coastlines are? (ii) the fetch and common weather and sea conditions are also important. Remember the fetch is the distance of open water over which wind blows. The longer the fetch, the stronger the winds and the longer they blow, ...
NAME - Quia
... 13. The diagram below shows a river. The shaded land areas on either side of the river were most likely formed by A. tectonic activity. B. the deposition of sediments. C. land development by humans. D. compression of preexisting rock. ...
... 13. The diagram below shows a river. The shaded land areas on either side of the river were most likely formed by A. tectonic activity. B. the deposition of sediments. C. land development by humans. D. compression of preexisting rock. ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Physical (or mechanical) weathering includes frost wedging, exfoliation, and thermal expansion. Chemical weathering includes dissolution (soluble rocks and minerals dissolve in acidic waters), hydrolysis (feldspars alter to clay), and oxidation (rusting of iron). Biological weathering - organisms ca ...
... Physical (or mechanical) weathering includes frost wedging, exfoliation, and thermal expansion. Chemical weathering includes dissolution (soluble rocks and minerals dissolve in acidic waters), hydrolysis (feldspars alter to clay), and oxidation (rusting of iron). Biological weathering - organisms ca ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
natcie2 - natscie2-5605
... as the down slope movement of material under the direct influence of gravity. Most types of mass wasting are aided by weathering and usually involve sacrificial (surface) materials. The material moves at rates ranging from almost imperceptible, as in the case of creep, to extremely fast as in a rock ...
... as the down slope movement of material under the direct influence of gravity. Most types of mass wasting are aided by weathering and usually involve sacrificial (surface) materials. The material moves at rates ranging from almost imperceptible, as in the case of creep, to extremely fast as in a rock ...
Conservation Practices - Roberts Conservation District
... fisheries habitat and increasing the vigor and productivity of cropland. By implementing conservation into a farming operation the producer will improve the overall quality of life for all rural and urban residents. Primary conservation practices in South Dakota include: Crop Rotation - Crop rotatio ...
... fisheries habitat and increasing the vigor and productivity of cropland. By implementing conservation into a farming operation the producer will improve the overall quality of life for all rural and urban residents. Primary conservation practices in South Dakota include: Crop Rotation - Crop rotatio ...
Erosion - Cloudfront.net
... Creep is the gradual movement of soil down a slope in response to gravity. This eventually results in a mass downward movement of soil on the slope. ...
... Creep is the gradual movement of soil down a slope in response to gravity. This eventually results in a mass downward movement of soil on the slope. ...
The Sleeping Bear Dunes
... pushing sand off of one side and piling it up on the other side. “The big dune in Sleeping Bear National Lakeshore was measured in 1962 and again in 1980. In those 18 years, the dune shrank 103 feet. The major forces acting on the dunes-wind, water and ice--will continue to change their features ove ...
... pushing sand off of one side and piling it up on the other side. “The big dune in Sleeping Bear National Lakeshore was measured in 1962 and again in 1980. In those 18 years, the dune shrank 103 feet. The major forces acting on the dunes-wind, water and ice--will continue to change their features ove ...
Decision One: Concept Map and Learning Unit
... Make sure most important/critical questions also have extending/refining questions. ...
... Make sure most important/critical questions also have extending/refining questions. ...
Constructive and Destructive Landforms
... Rocks are broken into smaller pieces by physical agents. Ice wedging. Plant and animal actions. Water ...
... Rocks are broken into smaller pieces by physical agents. Ice wedging. Plant and animal actions. Water ...
Chapter Seven: Erosion
... 1. wears away surface materials and moves them from one location to another 2. Agents (causes) of Erosion a) gravity b) glaciers c) wind d) water B. Deposition 1. the more quickly an agent of erosion is moving the more sediments it can carry 2. All agents of erosion drop their load of sediments when ...
... 1. wears away surface materials and moves them from one location to another 2. Agents (causes) of Erosion a) gravity b) glaciers c) wind d) water B. Deposition 1. the more quickly an agent of erosion is moving the more sediments it can carry 2. All agents of erosion drop their load of sediments when ...
Agricultural productivity and land degradation
... Maria Larsson: Agricultural productivity and land degradation - a study of two areas in the highlands of Ethiopia. Abstract - This Minor Field Study was carried out in Ethiopia, March to June 1997. The two areas of concern are one area in Debre Sina wereda, South Wollo and another in Machakel wereda ...
... Maria Larsson: Agricultural productivity and land degradation - a study of two areas in the highlands of Ethiopia. Abstract - This Minor Field Study was carried out in Ethiopia, March to June 1997. The two areas of concern are one area in Debre Sina wereda, South Wollo and another in Machakel wereda ...
Soil Vocabulary
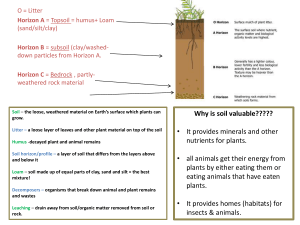
... Soil is the loose material in which plants can grow in the upper layer of Earth. It is made up of rock, humus, air, and water. Soil is made up of 5 important components and has ...
... Soil is the loose material in which plants can grow in the upper layer of Earth. It is made up of rock, humus, air, and water. Soil is made up of 5 important components and has ...
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
... O: We will investigate different types of deposition, weathering, and erosion. A: The strongest agent of weathering, erosion and deposition is water. ...
... O: We will investigate different types of deposition, weathering, and erosion. A: The strongest agent of weathering, erosion and deposition is water. ...
soil study guide 2015
... Conservation of soil - a method to maintain the fertility of the soil by protecting the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Contour plowing - forms ridges, slows the water flow and helps save precious topsoil. Terraced farming - uses "steps" that are built into the side of a mountain or hill. Good ...
... Conservation of soil - a method to maintain the fertility of the soil by protecting the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Contour plowing - forms ridges, slows the water flow and helps save precious topsoil. Terraced farming - uses "steps" that are built into the side of a mountain or hill. Good ...
Erosion

In geomorphology and geology, erosion is the action of exogenicprocesses (such as water flow or wind) which remove soil and rock from one location on the Earth's crust, then transport it to another location where it is deposited. Eroded sediment may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.While erosion is a natural process, human activities have increased by 10-40 times the rate at which erosion is occurring globally. Excessive (or accelerated) erosion causes both ""on-site"" and ""off-site"" problems. On-site impacts include decreases in agricultural productivity and (on natural landscapes) ecological collapse, both because of loss of the nutrient-rich upper soil layers. In some cases, the eventual end result is desertification. Off-site effects include sedimentation of waterways and eutrophication of water bodies, as well as sediment-related damage to roads and houses. Water and wind erosion are the two primary causes of land degradation; combined, they are responsible for about 84% of the global extent of degraded land, making excessive erosion one of the most significant environmental problems world-wide.Intensive agriculture, deforestation, roads, anthropogenic climate change and urban sprawl are amongst the most significant human activities in regard to their effect on stimulating erosion. However, there are many prevention and remediation practices that can curtail or limit erosion of vulnerable soils.