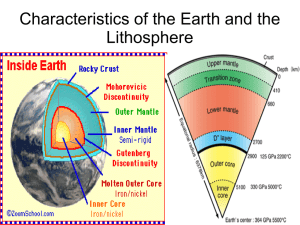
Earth`s Lithosphere Study Guide
... 2) Asthenosphere - the lower layer of the earth's crust; less rigid than the lithosphere 3) Mantle - region below crust extending down to Earth's core; molten rock; flexible 4) Outer Core - made of molten iron/nickel; as it flows, it creates Earth’s magnetic field 5) Inner Core - the solid iron/nick ...
... 2) Asthenosphere - the lower layer of the earth's crust; less rigid than the lithosphere 3) Mantle - region below crust extending down to Earth's core; molten rock; flexible 4) Outer Core - made of molten iron/nickel; as it flows, it creates Earth’s magnetic field 5) Inner Core - the solid iron/nick ...
Earth BootCamp_5.7B_Part 1_AC
... 16. People living on the Texas Gulf Coast have to place stone barriers along the shoreline to prevent wearing away of coastal land by wave action. This process is called: ...
... 16. People living on the Texas Gulf Coast have to place stone barriers along the shoreline to prevent wearing away of coastal land by wave action. This process is called: ...
Wind - Choteau
... Deflation and Ablation Happen to all land surfaces. Occur mostly in deserts, beaches, and ...
... Deflation and Ablation Happen to all land surfaces. Occur mostly in deserts, beaches, and ...
File
... exposes the soil. The three ways in which humans can affect soil are be removing the vegetation by poor land use practices like overgrazing, over cropping and deforestation. This can lead to desertification.Desertifiaction is the spread of desert conditions into new areas. Desertified soils are dry, ...
... exposes the soil. The three ways in which humans can affect soil are be removing the vegetation by poor land use practices like overgrazing, over cropping and deforestation. This can lead to desertification.Desertifiaction is the spread of desert conditions into new areas. Desertified soils are dry, ...
File - Geo-Environmental Science
... H. Rapid Mass Movements a. Rockfall – fall of rock from a steep cliff b. Landslide – sudden movement of masses of loose rock and soil down the slope of a hill, mountain or cliff c. Mudflow – movement of a large mass of mud d. __________________________ – movement of a large piece of soil or rock dow ...
... H. Rapid Mass Movements a. Rockfall – fall of rock from a steep cliff b. Landslide – sudden movement of masses of loose rock and soil down the slope of a hill, mountain or cliff c. Mudflow – movement of a large mass of mud d. __________________________ – movement of a large piece of soil or rock dow ...
application of geosynthetics and modern materials under kerala
... Geo-synthetics have been extensively used in road and airport flexible pavements and in overlays. In unpaved roads(having no blacktop), introducing a very thin non-woven geotextile is found to be of advantage for soft subgrades primarily through separation (thus minimizing pumping) and partly throug ...
... Geo-synthetics have been extensively used in road and airport flexible pavements and in overlays. In unpaved roads(having no blacktop), introducing a very thin non-woven geotextile is found to be of advantage for soft subgrades primarily through separation (thus minimizing pumping) and partly throug ...
Soils NR 200 - Modesto Junior College
... down into the lower horizons of the profile as far as the water penetration will carry them. ii) p - ...
... down into the lower horizons of the profile as far as the water penetration will carry them. ii) p - ...
How Do Soils Form? - Hicksville Public Schools
... soil on earth today ultimately came from rocks created by ancient geologic forces. As this mineral soil is mixed with organic matter, bacteria, fungi and other soil organisms, it develops into a vibrant and very dynamic ecosystem with thousands (some say billions!) of different organisms. ...
... soil on earth today ultimately came from rocks created by ancient geologic forces. As this mineral soil is mixed with organic matter, bacteria, fungi and other soil organisms, it develops into a vibrant and very dynamic ecosystem with thousands (some say billions!) of different organisms. ...
Soil Texture
... normally a slow process 2. ordinarily, new residual soil forms about as fast as the existing soil erodes 3. However, unwise use of the land and unusual climatic conditions can upset this ...
... normally a slow process 2. ordinarily, new residual soil forms about as fast as the existing soil erodes 3. However, unwise use of the land and unusual climatic conditions can upset this ...
Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Depositional Landscapes of Bavaria
... These fluvic and colluvic deposits are characterized by a highly diverse vertical structure and can contain high amounts of soil organic carbon (SOC) over the whole soil profile. Depositional landscapes are therefore not only productive sites for agricultural use but also influence carbon dynamics w ...
... These fluvic and colluvic deposits are characterized by a highly diverse vertical structure and can contain high amounts of soil organic carbon (SOC) over the whole soil profile. Depositional landscapes are therefore not only productive sites for agricultural use but also influence carbon dynamics w ...
limiting soil compaction
... goats or sheep to weed an area rather than a human crew. These animals cause less impact because they are lighter and often have a more delicate removal mechanism than people with hand tools. See the Center for Invasive Plants’ Weed Control Methods page for more information (www.weedcenter.org/manag ...
... goats or sheep to weed an area rather than a human crew. These animals cause less impact because they are lighter and often have a more delicate removal mechanism than people with hand tools. See the Center for Invasive Plants’ Weed Control Methods page for more information (www.weedcenter.org/manag ...
Study Guide Worksheet – Chapter 7 Section 7.1 – Weathering True
... 2. ____________ The removal and transport of weathered materials from one location to another is called erosion. 3. ____________ Weathering must take place before erosion. 4. ____________ The repeated freezing and thawing of water in the cracks of rocks is called frost wedging. 5. ____________ Water ...
... 2. ____________ The removal and transport of weathered materials from one location to another is called erosion. 3. ____________ Weathering must take place before erosion. 4. ____________ The repeated freezing and thawing of water in the cracks of rocks is called frost wedging. 5. ____________ Water ...
Philippines, Sta Rita, Pampanga – Trees to prevent soil erosion
... it from engulfing everything. The mega dikes were built in the midst of agricultural lands where the soil is susceptible to erosion. Over the past years, there have been instances of the mega dikes breaking apart allowing water to flow down, endangering the neighboring areas. With the onset of clima ...
... it from engulfing everything. The mega dikes were built in the midst of agricultural lands where the soil is susceptible to erosion. Over the past years, there have been instances of the mega dikes breaking apart allowing water to flow down, endangering the neighboring areas. With the onset of clima ...
Appendix A: Estimating Soil Loss with the USLE
... sections B and C are reduced to 2.8 and 1.6 tons/acre/year. These losses are acceptable in terms of their amount compared with the established soil loss tolerance for these soils. Replanting these areas may not, however, completely solve erosion problems on this site. Given the long slope lengths, t ...
... sections B and C are reduced to 2.8 and 1.6 tons/acre/year. These losses are acceptable in terms of their amount compared with the established soil loss tolerance for these soils. Replanting these areas may not, however, completely solve erosion problems on this site. Given the long slope lengths, t ...
Verrucated Mountains
... Terrain Class: Mountains - No one process responsible for construction of mountains. They can be uplifted, tectonic, subduction of plates, folding, uplift, up and down warping of the mantle, inflation of molten lower crustal (batholiths), etc. Erosion of mountain systems occurs over time. The rate o ...
... Terrain Class: Mountains - No one process responsible for construction of mountains. They can be uplifted, tectonic, subduction of plates, folding, uplift, up and down warping of the mantle, inflation of molten lower crustal (batholiths), etc. Erosion of mountain systems occurs over time. The rate o ...
Practice Quiz 2
... What is by far the most important agent of chemical weathering and why? A water – it is a good solvent and carrier of acids. B the Sun – it causes uneven heating of earth’s materials C clay materials – they are very unstable in surface soils and rocks. D exfoliation – new cracks gives chemical react ...
... What is by far the most important agent of chemical weathering and why? A water – it is a good solvent and carrier of acids. B the Sun – it causes uneven heating of earth’s materials C clay materials – they are very unstable in surface soils and rocks. D exfoliation – new cracks gives chemical react ...
Practice Quiz 2 NOTE: practice quizzes are always in “rough” form
... What is by far the most important agent of chemical weathering and why? A water – it is a good solvent and carrier of acids. B the Sun – it causes uneven heating of earth’s materials C clay materials – they are very unstable in surface soils and rocks. D exfoliation – new cracks gives chemical react ...
... What is by far the most important agent of chemical weathering and why? A water – it is a good solvent and carrier of acids. B the Sun – it causes uneven heating of earth’s materials C clay materials – they are very unstable in surface soils and rocks. D exfoliation – new cracks gives chemical react ...
Types and forms of erosion by water and by wind
... This takes place during the rain as soon as the infiltration rate is exceeded and a film of water starts to move across the surface. Effects are limited to the transport of fine particles and development of a sandy film in small cultivation furrows (traces) or where the fine particles are trapped by ...
... This takes place during the rain as soon as the infiltration rate is exceeded and a film of water starts to move across the surface. Effects are limited to the transport of fine particles and development of a sandy film in small cultivation furrows (traces) or where the fine particles are trapped by ...
Agricultural Soil and Water Conservation Stewardship
... Create a 10-minute presentation for the young couple and their advisors highlighting potential opportunities for the future of their farm. Incorporate at least three (3) spoken, relevant, and reputable references as you present. During the 10-minute presentation, teams should address the following: ...
... Create a 10-minute presentation for the young couple and their advisors highlighting potential opportunities for the future of their farm. Incorporate at least three (3) spoken, relevant, and reputable references as you present. During the 10-minute presentation, teams should address the following: ...
This dataset consists of 3 GIS maps that indicate the soil biomass
... This dataset consists of 3 GIS maps that indicate the soil biomass productivity of grasslands and pasture, of croplands and of forest areas in the European Union (EU27). The degree to which the soil carries out its biomass production service was evaluated on the basis of soil properties under prevai ...
... This dataset consists of 3 GIS maps that indicate the soil biomass productivity of grasslands and pasture, of croplands and of forest areas in the European Union (EU27). The degree to which the soil carries out its biomass production service was evaluated on the basis of soil properties under prevai ...
Landforms and Erosion - THE GEOGRAPHER ONLINE
... weakness for the processes of weathering and erosion to exploit. Coastal morphology On an indented coastline, headlands and the offshore topography concentrate wave attack on that headland by the process of wave refraction. Many headlands have a wave-cut platform between high and low tide which can ...
... weakness for the processes of weathering and erosion to exploit. Coastal morphology On an indented coastline, headlands and the offshore topography concentrate wave attack on that headland by the process of wave refraction. Many headlands have a wave-cut platform between high and low tide which can ...
Soil Erosion
... Splash erosion is the direct movement of soil by splashing. A soil grain can be thrown as far as 5 feet by a raindrop splash. These splashed particles fill the voids between other aggregates and seal the soil surface. Sheet erosion results when thin layers, or sheets, of soil are worn away. Sheet er ...
... Splash erosion is the direct movement of soil by splashing. A soil grain can be thrown as far as 5 feet by a raindrop splash. These splashed particles fill the voids between other aggregates and seal the soil surface. Sheet erosion results when thin layers, or sheets, of soil are worn away. Sheet er ...
- Catalyst
... elevation of large regions (Himalayas) affects circulation in the atmosphere as predicted by both modeling and observation. ...
... elevation of large regions (Himalayas) affects circulation in the atmosphere as predicted by both modeling and observation. ...
Internal Structure of the Earth and Lithosphere
... Land Use Planning Land use planning is an essential tool for pollution control and prevention. Land use categories refer to the different socioeconomic activities in a certain area, the human behaviors they create and their effect on the environment. These activities take place at a local level but ...
... Land Use Planning Land use planning is an essential tool for pollution control and prevention. Land use categories refer to the different socioeconomic activities in a certain area, the human behaviors they create and their effect on the environment. These activities take place at a local level but ...
Erosion

In geomorphology and geology, erosion is the action of exogenicprocesses (such as water flow or wind) which remove soil and rock from one location on the Earth's crust, then transport it to another location where it is deposited. Eroded sediment may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.While erosion is a natural process, human activities have increased by 10-40 times the rate at which erosion is occurring globally. Excessive (or accelerated) erosion causes both ""on-site"" and ""off-site"" problems. On-site impacts include decreases in agricultural productivity and (on natural landscapes) ecological collapse, both because of loss of the nutrient-rich upper soil layers. In some cases, the eventual end result is desertification. Off-site effects include sedimentation of waterways and eutrophication of water bodies, as well as sediment-related damage to roads and houses. Water and wind erosion are the two primary causes of land degradation; combined, they are responsible for about 84% of the global extent of degraded land, making excessive erosion one of the most significant environmental problems world-wide.Intensive agriculture, deforestation, roads, anthropogenic climate change and urban sprawl are amongst the most significant human activities in regard to their effect on stimulating erosion. However, there are many prevention and remediation practices that can curtail or limit erosion of vulnerable soils.