UPMC St. Margaret Nerve Block Rotation
... Lumbar plexus blocks provide anesthesia or analgesia to the entire distribution of the plexus, including the anterolateral and medial thigh, the knee, and the saphenous nerve below the knee. Continuous infusion is always initiated after an initial bolus of dilute local anesthetic through the cathe ...
... Lumbar plexus blocks provide anesthesia or analgesia to the entire distribution of the plexus, including the anterolateral and medial thigh, the knee, and the saphenous nerve below the knee. Continuous infusion is always initiated after an initial bolus of dilute local anesthetic through the cathe ...
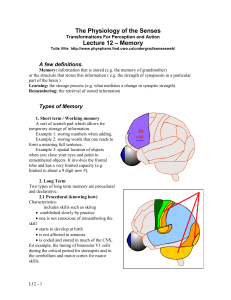
Working Memory
... Ability to temporarily hold visual and spatial information is referred to as Visuospatial sketchpad. – Also involves abstract and cross-modal (more than one sense) spatial information ...
... Ability to temporarily hold visual and spatial information is referred to as Visuospatial sketchpad. – Also involves abstract and cross-modal (more than one sense) spatial information ...
Spinal Cord
... Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
... Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
中樞神經系統
... Sensory pathways to the cerebral cortex are crossed pathways. Impulses are conducted to its sensory areas by way of relays of neurons referred to as sensory pathways. Each side of the brain registers sensations from the opposite side of the body. General sensations of the right side of the b ...
... Sensory pathways to the cerebral cortex are crossed pathways. Impulses are conducted to its sensory areas by way of relays of neurons referred to as sensory pathways. Each side of the brain registers sensations from the opposite side of the body. General sensations of the right side of the b ...
The Nervous System
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
Document
... Pathways through vestibular nuclei • Also, pathways from upper motor neurons to lower motor neurons that control eye movements. ...
... Pathways through vestibular nuclei • Also, pathways from upper motor neurons to lower motor neurons that control eye movements. ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 9
... Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 9: Classical Conditioning ...
... Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 9: Classical Conditioning ...
Study Guide for The Spinal Cord – Chapter 8, Part B Be familiar with
... root ganglion, dura mater, effector, endoneurium, epineurium, ganglion, gray matter, interneuron, lateral gray horn, lumbar enlargement, meninges, monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflex arc, motor neuron (fiber), nerve, nucleus (CNS), perineurium, peripheral nervous system, pia mater, reflex arc, sens ...
... root ganglion, dura mater, effector, endoneurium, epineurium, ganglion, gray matter, interneuron, lateral gray horn, lumbar enlargement, meninges, monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflex arc, motor neuron (fiber), nerve, nucleus (CNS), perineurium, peripheral nervous system, pia mater, reflex arc, sens ...
Types of Memory
... primary visual cortex. Take home message. Procedural memories continue to be consolidated, in the primary sensory and motor regions. Not all plasticity is lost after the critical period (there is hope for elderly profs). ...
... primary visual cortex. Take home message. Procedural memories continue to be consolidated, in the primary sensory and motor regions. Not all plasticity is lost after the critical period (there is hope for elderly profs). ...
Chapter 12- Intro to NS
... they are called ganglia (ganglion) 2. Neuron processes- extensions of the cell body, may be termed dendrites or axons. Dendrites are receptive ends that allow signals to travel towards the cell body. Axons extend out of one side of the cell body called the axon hillock, it may be several feet in len ...
... they are called ganglia (ganglion) 2. Neuron processes- extensions of the cell body, may be termed dendrites or axons. Dendrites are receptive ends that allow signals to travel towards the cell body. Axons extend out of one side of the cell body called the axon hillock, it may be several feet in len ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
Nervous System - Alamo Colleges
... Spinal Reflexes Not all nerve impulses travel to brain Reflex arc: Receptor – site of stimulus Sensory neuron –carries signal to spinal cord Integration center – sensory and motor neurons connected by interneurons Motor neuron – conducts impulses to effector Effector – muscle fiber or ...
... Spinal Reflexes Not all nerve impulses travel to brain Reflex arc: Receptor – site of stimulus Sensory neuron –carries signal to spinal cord Integration center – sensory and motor neurons connected by interneurons Motor neuron – conducts impulses to effector Effector – muscle fiber or ...
Integumentary System Outline
... Protects the body from injury protects the body from the intrusion of harmful microorganisms Protects the body from the ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun helps to maintain proper internal temperature of the body Serves as a site for excretion of waste through perspiration serves as an important senso ...
... Protects the body from injury protects the body from the intrusion of harmful microorganisms Protects the body from the ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun helps to maintain proper internal temperature of the body Serves as a site for excretion of waste through perspiration serves as an important senso ...
Chapter 17.2 Review
... 23. Making Inferences Sensory organs are concentrated in the human head. You cannot see, hear, taste, or smell with any other part of your body. Why are the eyes, ears, tongue, and nose located so close to one another? ______________________________________________________________ __________________ ...
... 23. Making Inferences Sensory organs are concentrated in the human head. You cannot see, hear, taste, or smell with any other part of your body. Why are the eyes, ears, tongue, and nose located so close to one another? ______________________________________________________________ __________________ ...
Slide ()
... Algorithms for differentiating the three major types of diabetes insipidus (DI). In a patient with polydipsia and polyuria, a 24-hour urine osmolarity less than 300 mOsm/L and a negative test for glucosuria, there are two ways to determine the type of DI. One is to measure plasma arginine vasopressi ...
... Algorithms for differentiating the three major types of diabetes insipidus (DI). In a patient with polydipsia and polyuria, a 24-hour urine osmolarity less than 300 mOsm/L and a negative test for glucosuria, there are two ways to determine the type of DI. One is to measure plasma arginine vasopressi ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CH 16: SPECIAL SENSES
... 2.Biconcave, flexible eye structure used to focus light on the retina 3.Taste elicited by bases 4.Olfactory receptor cells are unique because they are the only neurons known to undergo ______ through out adult life. 5.Projections on the tongue which contain taste buds 6.Antibacterial enzyme in tears ...
... 2.Biconcave, flexible eye structure used to focus light on the retina 3.Taste elicited by bases 4.Olfactory receptor cells are unique because they are the only neurons known to undergo ______ through out adult life. 5.Projections on the tongue which contain taste buds 6.Antibacterial enzyme in tears ...
7 - smw15.org
... • Receives input from the spinal cord, sensory systems through the cranial nerve nuclei, and from the cerebral cortex • Cells are arranged in precise, repeating geometrical patterns ▫ Purkinje cells are very flat and exist in sequential planes ▫ parallel fibers are perpendicular to the planes of the ...
... • Receives input from the spinal cord, sensory systems through the cranial nerve nuclei, and from the cerebral cortex • Cells are arranged in precise, repeating geometrical patterns ▫ Purkinje cells are very flat and exist in sequential planes ▫ parallel fibers are perpendicular to the planes of the ...
Functional Framework for Cognition
... Ability to temporarily hold visual and spatial information is referred to as Visuospatial sketchpad. – Also involves abstract and cross-modal (more than one sense) spatial information ...
... Ability to temporarily hold visual and spatial information is referred to as Visuospatial sketchpad. – Also involves abstract and cross-modal (more than one sense) spatial information ...
Zoology Assignment - Wikimedia Commons
... and bivalve molluscs, they are best developed and understood in arthropods. A compound eye may contain thousands of ommatidia, each oriented in a slightly different direction from the others as a result of the eye’s overall convex shape. The visual field of a compound eye is very wide, as anyone who ...
... and bivalve molluscs, they are best developed and understood in arthropods. A compound eye may contain thousands of ommatidia, each oriented in a slightly different direction from the others as a result of the eye’s overall convex shape. The visual field of a compound eye is very wide, as anyone who ...
Biology 231
... involuntary, operates mainly by reflexes REFLEXES – fast, automatic responses to specific stimuli somatic reflexes – involve skeletal muscle protective reflexes, can be consciously overridden autonomic reflexes – involve smooth muscle, cardiac muscle or glands maintain homeostasis in the body Reflex ...
... involuntary, operates mainly by reflexes REFLEXES – fast, automatic responses to specific stimuli somatic reflexes – involve skeletal muscle protective reflexes, can be consciously overridden autonomic reflexes – involve smooth muscle, cardiac muscle or glands maintain homeostasis in the body Reflex ...
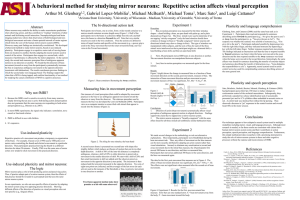
Document
... a behavioral method to study mirror neurons, based on use-induced plasticity. Participants engage in a repetitive motor task of moving beans from one location to another, thereby adapting the neural systems used in control of the action. Participants then engage in a second task, which measures if p ...
... a behavioral method to study mirror neurons, based on use-induced plasticity. Participants engage in a repetitive motor task of moving beans from one location to another, thereby adapting the neural systems used in control of the action. Participants then engage in a second task, which measures if p ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.