Evolution Review Sheet
... 30. What was Lamarck’s theory of how things changed over time? ____________________________________________________________________ 31. What gas was not present before life began? ____________________ 32. What protects us from harmful UV light (other than sunscreen)? _________________ 33. Mutations, ...
... 30. What was Lamarck’s theory of how things changed over time? ____________________________________________________________________ 31. What gas was not present before life began? ____________________ 32. What protects us from harmful UV light (other than sunscreen)? _________________ 33. Mutations, ...
Ch 13 - Evolution
... BIOLOGY Ch 13 – The Theory of Evolution Mrs. Stolipher VOCABULARY Population, natural selection, adaptation, vestigial structure, homologous structure, artificial selection, reproductive isolation, evolution, Darwin, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace ...
... BIOLOGY Ch 13 – The Theory of Evolution Mrs. Stolipher VOCABULARY Population, natural selection, adaptation, vestigial structure, homologous structure, artificial selection, reproductive isolation, evolution, Darwin, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace ...
Evolution - sciencebruemmer
... 3. The added use of an organ will cause it to grow & become more complex, the disuse of an organ will cause it to atrophy or waste away ...
... 3. The added use of an organ will cause it to grow & become more complex, the disuse of an organ will cause it to atrophy or waste away ...
review_answers_ch._7__8
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
chapters_7__8_review_answers_0
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
... chronologically, one could observe the changes in a particular group of organisms. In the same way, organisms could be traced back and their common ancestors identified. 5. Varied answers possible. Your answer should include something along the line of genetic change over time as a result of random ...
File
... 20. ___________________________________________is the random effect that can occur when a small population settles in an area separated from the rest of the population and interbreeds, producing a unique gene pool 21. Describe how mutations can have an effect on the gene pool of a population. ...
... 20. ___________________________________________is the random effect that can occur when a small population settles in an area separated from the rest of the population and interbreeds, producing a unique gene pool 21. Describe how mutations can have an effect on the gene pool of a population. ...
Evolution 2011-2012
... 2. DNA by comparing the DNA sequences of two organisms or the amino acid sequences made from the DNA, scientists can learn which organisms are related; the more DNA two organisms have in common, the more closely related they are ...
... 2. DNA by comparing the DNA sequences of two organisms or the amino acid sequences made from the DNA, scientists can learn which organisms are related; the more DNA two organisms have in common, the more closely related they are ...
Study Guide for Evolution
... Study Guide for Evolution 1. What causes variation in a population? ...
... Study Guide for Evolution 1. What causes variation in a population? ...
Evolution Review
... Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium what does it mean/show? What 5 things have to occur for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg? 5 causes of evolution genetic drift, gene flow, mutations, nonrandom mating, natural selection modes of selection (stabilizing, directional, diversifying, sexual selection) ...
... Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium what does it mean/show? What 5 things have to occur for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg? 5 causes of evolution genetic drift, gene flow, mutations, nonrandom mating, natural selection modes of selection (stabilizing, directional, diversifying, sexual selection) ...
Ch01
... the observational evidence from field research. • Evolution is gradual: small genetic changes regulated by natural selection accumulate over long periods and many genes can “drift” through a population at a given time. Discontinuities amongst species (or other taxa) are explained as originating grad ...
... the observational evidence from field research. • Evolution is gradual: small genetic changes regulated by natural selection accumulate over long periods and many genes can “drift” through a population at a given time. Discontinuities amongst species (or other taxa) are explained as originating grad ...
Name: Evolution: the Process Date: Taxonomy—Naming and
... traits are passed on to offspring o Charles Lyell’s (1797-1875) arguments in favour of a very old Earth that has always been changing—evolution from ancient ancestors can only occur if Earth has been around long enough o Thomas Malthus (1766-1834) ideas on population growth—high birth rates force or ...
... traits are passed on to offspring o Charles Lyell’s (1797-1875) arguments in favour of a very old Earth that has always been changing—evolution from ancient ancestors can only occur if Earth has been around long enough o Thomas Malthus (1766-1834) ideas on population growth—high birth rates force or ...
Chapter 16
... 2. Genetic Shuffling that occurs during sexual reproduction The # of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends on the # of genes controlling the trait. Obviously there are single gene traits and polygenic traits. An example of a single gene trait (each gene can have 2 alleles – dominant or reces ...
... 2. Genetic Shuffling that occurs during sexual reproduction The # of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends on the # of genes controlling the trait. Obviously there are single gene traits and polygenic traits. An example of a single gene trait (each gene can have 2 alleles – dominant or reces ...
SBI 3U1 – EVOLUTION UNIT TEST REVIEW
... 1. State the main contributions of the following scientists to the development of thought on evolution: Buffon, Lamarck, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace, Darwin. 2. How do Lamarck’s explanations of adaptation differ from those of Darwin? 3. Define genetic bottlenecks and the founder effect. Give an example ...
... 1. State the main contributions of the following scientists to the development of thought on evolution: Buffon, Lamarck, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace, Darwin. 2. How do Lamarck’s explanations of adaptation differ from those of Darwin? 3. Define genetic bottlenecks and the founder effect. Give an example ...
Charles Darwin 2
... individuals at either end of the curve stabilizing selection takes place. • Ex: Gall fly ...
... individuals at either end of the curve stabilizing selection takes place. • Ex: Gall fly ...
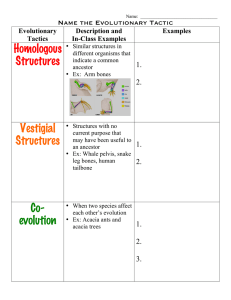
Homologous Structures Vestigial Structures Co
... • Structures with no current purpose that may have been useful to an ancestor • Ex: Whale pelvis, snake leg bones, human tailbone ...
... • Structures with no current purpose that may have been useful to an ancestor • Ex: Whale pelvis, snake leg bones, human tailbone ...
evolution & natural selection powerpoint 2013
... 1. Suggested Earth might be a lot older than a few thousand years by looking at specific fossils & certain living animals were similar but not exactly ...
... 1. Suggested Earth might be a lot older than a few thousand years by looking at specific fossils & certain living animals were similar but not exactly ...
Fossils - pams
... Hutton and Lyell argued that the earth is many millions of years old b/c layers of rock take time to form processes such as volcanoes and earthquakes shaped the earth and still occur today ...
... Hutton and Lyell argued that the earth is many millions of years old b/c layers of rock take time to form processes such as volcanoes and earthquakes shaped the earth and still occur today ...
Bio 1010 Dr. Bonnie A. Bain
... Natural Selection Evolutionary adaptations: The results of natural selection Adaptation: An inherited characteristic that enhances an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment ...
... Natural Selection Evolutionary adaptations: The results of natural selection Adaptation: An inherited characteristic that enhances an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment ...
Theory of Evolution
... likely to survive and reproduce Through inheritance, the adaptations will become more frequent in the population ...
... likely to survive and reproduce Through inheritance, the adaptations will become more frequent in the population ...
Evolution Notes
... 1785: Hutton: proposes Earth is shaped by geological forces; Earth is millions of years old Geologic Time Scale 1798: Malthus: Human population will grow faster than the space and food provided 1809: Lamarck: Inheritance of acquired traits (use/disuse hypothesis); 1st to suggest mechanism in changi ...
... 1785: Hutton: proposes Earth is shaped by geological forces; Earth is millions of years old Geologic Time Scale 1798: Malthus: Human population will grow faster than the space and food provided 1809: Lamarck: Inheritance of acquired traits (use/disuse hypothesis); 1st to suggest mechanism in changi ...
Evolution
... Evolution The term evolution means- a slow and gradual change over time. More specific: Evolution is the change in the inherited traits of a population from one generation to the next. These traits are the expression of genes that are copied and passed on to offspring during reproduction. • A chang ...
... Evolution The term evolution means- a slow and gradual change over time. More specific: Evolution is the change in the inherited traits of a population from one generation to the next. These traits are the expression of genes that are copied and passed on to offspring during reproduction. • A chang ...