Taxonomy (Classification) and Phylogeny (Cladistics)
... • Linnaeus and Whittaker gave us this system • Classifies diverse organisms into “like groups” based on traits. As the traits become more specific, fewer and fewer organisms are together. ...
... • Linnaeus and Whittaker gave us this system • Classifies diverse organisms into “like groups” based on traits. As the traits become more specific, fewer and fewer organisms are together. ...
Chapter 16 Guided Notes
... Section 2 – Evolution as Genetic Change (Part 2) Genetic Drift What is genetic drift? o A random change in allele frequency is called genetic ____________________. o In small populations, individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals do, just by ___ ...
... Section 2 – Evolution as Genetic Change (Part 2) Genetic Drift What is genetic drift? o A random change in allele frequency is called genetic ____________________. o In small populations, individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals do, just by ___ ...
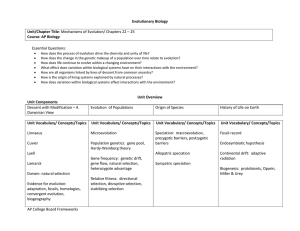
Evolutionary Biology Unit Design
... evaluate evidence provided by data /sets/ to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution. use data from a real or simulated population, based on graphs or models of types of selection and apply mathematical methods to predict what will happen to the popula ...
... evaluate evidence provided by data /sets/ to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution. use data from a real or simulated population, based on graphs or models of types of selection and apply mathematical methods to predict what will happen to the popula ...
Exploring population structure of Mnemiopsis leidyi in north
... understanding of the invasion history and colonization dynamics is vital to mitigate the effects of nonnative species. Furthermore, human mediated invasions provide the opportunity to investigate the evolutionary processes underlying range expansion in real-time. Until now the population structure o ...
... understanding of the invasion history and colonization dynamics is vital to mitigate the effects of nonnative species. Furthermore, human mediated invasions provide the opportunity to investigate the evolutionary processes underlying range expansion in real-time. Until now the population structure o ...
16.4 Evidence of Evolution
... protein which functions in cellular respiration for all types of cells. Testing Natural Selection Use the area below to explain how recent research on the Galapagos finches has supported Darwin’s theory of evolution. This can be done in point form. ...
... protein which functions in cellular respiration for all types of cells. Testing Natural Selection Use the area below to explain how recent research on the Galapagos finches has supported Darwin’s theory of evolution. This can be done in point form. ...
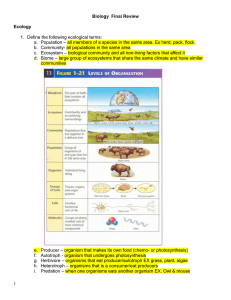
Biology 5 Final Review
... 28. What was Darwin’s theory of evolution? Natural selection is based on excess reproduction, variation, inheritance and the advantages of certain traits in certain environments. The “fittest” survive and reproduce. This can result in the appearance of new species. 29. What did Malthus predict would ...
... 28. What was Darwin’s theory of evolution? Natural selection is based on excess reproduction, variation, inheritance and the advantages of certain traits in certain environments. The “fittest” survive and reproduce. This can result in the appearance of new species. 29. What did Malthus predict would ...
Bacteria (multiple kingdoms)
... Natural selection is an editing mechanism – It results from exposure of heritable variations to environmental factors that favor some individuals over others – Over time this results in evolution of new species adapted to particular environments – Evolution is biology’s core theme and explains uni ...
... Natural selection is an editing mechanism – It results from exposure of heritable variations to environmental factors that favor some individuals over others – Over time this results in evolution of new species adapted to particular environments – Evolution is biology’s core theme and explains uni ...
CHARLES DARWIN AND EVOLUTION I. Geologists have
... a. Evolution-defined by Darwin as “decent with modification.” Essentially what he was saying was that species change with time. According to Darwin, this would account for the great diversity of life on Earth. b. Evolution occurs through a process Darwin referred to as Natural Selection. c. Key Poin ...
... a. Evolution-defined by Darwin as “decent with modification.” Essentially what he was saying was that species change with time. According to Darwin, this would account for the great diversity of life on Earth. b. Evolution occurs through a process Darwin referred to as Natural Selection. c. Key Poin ...
Natural Selection
... Natural Selection Selection = choosing traits (physical and behavioural) that give an organism an advantage in a particular niche Natural = ???????????????????????? ...
... Natural Selection Selection = choosing traits (physical and behavioural) that give an organism an advantage in a particular niche Natural = ???????????????????????? ...
Evolution - Alvinisd.net
... • Stated that populations could not grow indefinitely • This growth would be stopped by: 1. Disease 2. Famine 3. War ...
... • Stated that populations could not grow indefinitely • This growth would be stopped by: 1. Disease 2. Famine 3. War ...
Test Review
... Explain why extinct species are not equally represented in the fossil record. What might improve an organism’s chances of leaving fossil evidence? Explain why the evolutionary cost of failing to mate is extreme. What role does stabilizing selection have on a population when the environment is not ch ...
... Explain why extinct species are not equally represented in the fossil record. What might improve an organism’s chances of leaving fossil evidence? Explain why the evolutionary cost of failing to mate is extreme. What role does stabilizing selection have on a population when the environment is not ch ...
Darwin`s Idea for Natural Selection
... Based on Malthus’s work populations Darwin’s theory states that there must be a struggle for existence. ...
... Based on Malthus’s work populations Darwin’s theory states that there must be a struggle for existence. ...
Ideas that Shaped Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... that sooner or later there wouldn’t be enough living space and food ...
... that sooner or later there wouldn’t be enough living space and food ...
Ch. 15, Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... • Natural Selection= (Dr. Malone’s definition) when individuals who have what it takes survive and reproduce best; survival of the fittest, it’s a dog eat dog, you got to step on someone else to get where you want to go, world • Founder Effect = when a population shrinks down to only a few members, ...
... • Natural Selection= (Dr. Malone’s definition) when individuals who have what it takes survive and reproduce best; survival of the fittest, it’s a dog eat dog, you got to step on someone else to get where you want to go, world • Founder Effect = when a population shrinks down to only a few members, ...
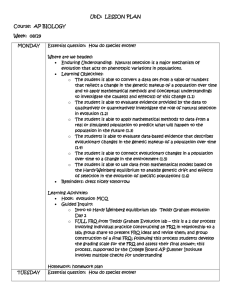
UbD: LESSON PLAN Course: AP BIOLOGY Week: 08/29 MONDAY
... o The student is able to convert a data set from a table of numbers that reflect a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time and to apply mathematical methods and conceptual understandings to investigate the cause(s) and effect(s) of this change (1.1) o The student is able to evaluate e ...
... o The student is able to convert a data set from a table of numbers that reflect a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time and to apply mathematical methods and conceptual understandings to investigate the cause(s) and effect(s) of this change (1.1) o The student is able to evaluate e ...
Multifactorial Traits
... • DNA comparisons confirm the same pattern • Protein sequences confirm the same pattern • 150 years of research by thousands of ...
... • DNA comparisons confirm the same pattern • Protein sequences confirm the same pattern • 150 years of research by thousands of ...
Evolution
... that describes the observed changes in living things over time Scientists use evolution to explain the great diversity of life, but some dispute its ability to describe the origins of life on Earth http://www.bizofshowbiz.com/uploads/Geico%20Cavemen.jpg ...
... that describes the observed changes in living things over time Scientists use evolution to explain the great diversity of life, but some dispute its ability to describe the origins of life on Earth http://www.bizofshowbiz.com/uploads/Geico%20Cavemen.jpg ...
Evolution Review
... and human. • (B) Cytochrome c apparently has an entirely different function in rattlesnakes than in mammals, which explains the difference in the umber of amino acids. • (C) Cytochrome c is not found universally in animals. • (D) Cytochrome c from a rattlesnake could function in a dog, but not in a ...
... and human. • (B) Cytochrome c apparently has an entirely different function in rattlesnakes than in mammals, which explains the difference in the umber of amino acids. • (C) Cytochrome c is not found universally in animals. • (D) Cytochrome c from a rattlesnake could function in a dog, but not in a ...
or biologic succession
... in the population. There will therefore be a shift in the characteristics of the population. “I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection.” —Charles Darwin from The Origin of Species ...
... in the population. There will therefore be a shift in the characteristics of the population. “I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection.” —Charles Darwin from The Origin of Species ...
Examples of Spontaneous Generation
... The random assortment of survivors may have different allele frequencies. This is a type of genetic drift called the bottleneck effect. ...
... The random assortment of survivors may have different allele frequencies. This is a type of genetic drift called the bottleneck effect. ...
CH 17 Taxonomy TErev07v22013
... Theory of Evolution: the change in populations over time Charles Darwin (1809 – 1882) Proposed that species changed over time by natural selection Natural selection – organisms with traits suited to their environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than others less suited Homologous structu ...
... Theory of Evolution: the change in populations over time Charles Darwin (1809 – 1882) Proposed that species changed over time by natural selection Natural selection – organisms with traits suited to their environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than others less suited Homologous structu ...
Lecture #10 Date
... – new layers cover older ones, creating a record over time – fossils within layers show that a succession of organisms have populated Earth throughout a long period of time ...
... – new layers cover older ones, creating a record over time – fossils within layers show that a succession of organisms have populated Earth throughout a long period of time ...
Chapter 28 Review Evolution notes ck this
... and human. • (B) Cytochrome c apparently has an entirely different function in rattlesnakes than in mammals, which explains the difference in the umber of amino acids. • (C) Cytochrome c is not found universally in animals. • (D) Cytochrome c from a rattlesnake could function in a dog, but not in a ...
... and human. • (B) Cytochrome c apparently has an entirely different function in rattlesnakes than in mammals, which explains the difference in the umber of amino acids. • (C) Cytochrome c is not found universally in animals. • (D) Cytochrome c from a rattlesnake could function in a dog, but not in a ...
Ch 14-15 exam review EVOLUTION
... 8. Briefly describe the work of Thomas Malthus and his contribution to Darwin’s theory of Evolution. 9. Describe artificial selection. 10. Vestigial structure (definition and examples) 11. What is an adaptation? Can it be behavioral? Explain. Can it be physical? Explain 12. What does the term fitnes ...
... 8. Briefly describe the work of Thomas Malthus and his contribution to Darwin’s theory of Evolution. 9. Describe artificial selection. 10. Vestigial structure (definition and examples) 11. What is an adaptation? Can it be behavioral? Explain. Can it be physical? Explain 12. What does the term fitnes ...