Vitamins General aspects of vitamins nutrition
... amino acids and fatty acids, which are required in larger amounts Shown to be a dietary essential & its elimination from the diet must result in a deficiency disease and restoration must cure or prevent that deficiency disease because they cannot be synthesized by the body. Compound that has pharmac ...
... amino acids and fatty acids, which are required in larger amounts Shown to be a dietary essential & its elimination from the diet must result in a deficiency disease and restoration must cure or prevent that deficiency disease because they cannot be synthesized by the body. Compound that has pharmac ...
Nutrients and Health
... O What foods holds these vitamins and minerals. O How much fiber is important to body. O How much water is important to the body. O Any other information you feel these students need to ...
... O What foods holds these vitamins and minerals. O How much fiber is important to body. O How much water is important to the body. O Any other information you feel these students need to ...
Supplements Multivitamins and Minerals*
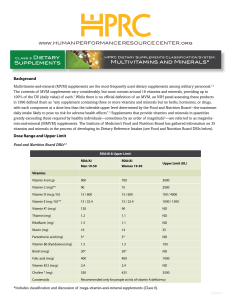
... 100% of the DV (daily value) of each.3 While there is no official definition of an MVM, an NIH panel assessing these products in 1996 defined them as “any supplement containing three or more vitamins and minerals but no herbs, hormones, or drugs, with each component at a dose less than the tolerable ...
... 100% of the DV (daily value) of each.3 While there is no official definition of an MVM, an NIH panel assessing these products in 1996 defined them as “any supplement containing three or more vitamins and minerals but no herbs, hormones, or drugs, with each component at a dose less than the tolerable ...
Vitamin quiz 4 review
... 9. Inflamed mouth membranes are indicative of a dietary deficiency of riboflavin. 10. Milk and milk products provide liberal amounts of which of the following vitamins? 11. What vitamin deficiency disease appeared in people who had subsisted on a diet high in corn and low in Protein (such as those t ...
... 9. Inflamed mouth membranes are indicative of a dietary deficiency of riboflavin. 10. Milk and milk products provide liberal amounts of which of the following vitamins? 11. What vitamin deficiency disease appeared in people who had subsisted on a diet high in corn and low in Protein (such as those t ...
1 Microwaves cause molecules to vibrate. Vibration creates friction
... #24 Vitamin C – Helps to form collagen which holds the cells together, aids in healing. Prevents scurvy. Citrus fruits, strawberries, broccoli, tomatoes are good sources. ...
... #24 Vitamin C – Helps to form collagen which holds the cells together, aids in healing. Prevents scurvy. Citrus fruits, strawberries, broccoli, tomatoes are good sources. ...
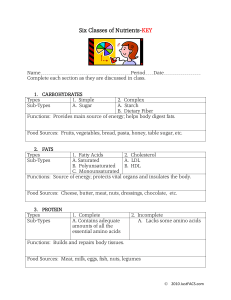
Six Classes of Nutrients-KEY
... Food Sources: Cheese, butter, meat, nuts, dressings, chocolate, etc. 3. PROTEIN Types Sub-Types ...
... Food Sources: Cheese, butter, meat, nuts, dressings, chocolate, etc. 3. PROTEIN Types Sub-Types ...
Chapter 7 objectives
... Enzymes: A complex protein in the body that serves as a catalyst, facilitating reactions between various substances without being changed itself. Folic acid (folate): A water-soluble vitamin that appears to be essential in preventing certain types of anemia. Free radicals: An atom or compound in whi ...
... Enzymes: A complex protein in the body that serves as a catalyst, facilitating reactions between various substances without being changed itself. Folic acid (folate): A water-soluble vitamin that appears to be essential in preventing certain types of anemia. Free radicals: An atom or compound in whi ...
VITAMINS
... in foods like whole grain and enriched cereals and breads, meat and beans. B-Vitamins include: Thiamin (Vitamin B1), Riboflavin (Vitamin B2), Niacin (Vitamin B3), Vitamin B6, Folic Acid (Folate), Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, and Biotin. C is needed for wound healing; for development of blood vesse ...
... in foods like whole grain and enriched cereals and breads, meat and beans. B-Vitamins include: Thiamin (Vitamin B1), Riboflavin (Vitamin B2), Niacin (Vitamin B3), Vitamin B6, Folic Acid (Folate), Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, and Biotin. C is needed for wound healing; for development of blood vesse ...
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies and Toxicities
... requires a diet analysis, clinical evaluation, biochemical analysis, & evaluating the response to corrected intake levels ...
... requires a diet analysis, clinical evaluation, biochemical analysis, & evaluating the response to corrected intake levels ...
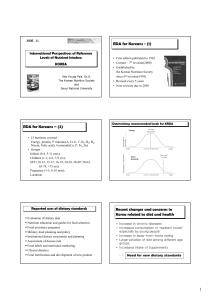
RDA for Koreans - (1) RDA for Koreans – (2) Recent changes and
... • 15 nutrients covered – Energy, protein, 9 vitamins(A, D, E, C, B1, B2, B6, Niacin, Folic acid), 4 minerals(Ca, P, Fe, Zn) • Groups – Infants (0-4, 5-11 mos); Children (1-3, 4-6, 7-9 yrs); M/F (10-12, 13-15, 16-19, 20-29, 30-49, 50-64, 65-74, >75 yrs); Pregnancy (1-5, 6-10 mos); Lactation ...
... • 15 nutrients covered – Energy, protein, 9 vitamins(A, D, E, C, B1, B2, B6, Niacin, Folic acid), 4 minerals(Ca, P, Fe, Zn) • Groups – Infants (0-4, 5-11 mos); Children (1-3, 4-6, 7-9 yrs); M/F (10-12, 13-15, 16-19, 20-29, 30-49, 50-64, 65-74, >75 yrs); Pregnancy (1-5, 6-10 mos); Lactation ...
Eyesight
... well as in green leafy ones such as kale and broccoli. Vitamins C and E and the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin have been found to delay or slow the growth of cataracts. In studies of these supplements, the doses were much higher than the FDA’s recommended daily allowances. It is important to cons ...
... well as in green leafy ones such as kale and broccoli. Vitamins C and E and the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin have been found to delay or slow the growth of cataracts. In studies of these supplements, the doses were much higher than the FDA’s recommended daily allowances. It is important to cons ...
Examine One – Nutrition Course, Biol 1322, Dr. Jennifer Davis The
... Conditions related to food intolerance versus food allergies Why the body needs carbohydrates, and how they are used, what foods contain what types of carbohydrates Fiber rich foods Disaccharides, polysaccharides Which organs secrete insulin, which organs secrete glucagon? The actions of the hormone ...
... Conditions related to food intolerance versus food allergies Why the body needs carbohydrates, and how they are used, what foods contain what types of carbohydrates Fiber rich foods Disaccharides, polysaccharides Which organs secrete insulin, which organs secrete glucagon? The actions of the hormone ...
Water is essential for your body
... Some people don’t get enough minerals through their diet and may need help from mineral supplements. Different medications and health conditions may cause mineral deficiency. Some groups are more in need of mineral supplements than others. For example, if you are pregnant, vegetarian, under a lot of ...
... Some people don’t get enough minerals through their diet and may need help from mineral supplements. Different medications and health conditions may cause mineral deficiency. Some groups are more in need of mineral supplements than others. For example, if you are pregnant, vegetarian, under a lot of ...
The Six Nutrients
... • Plant food and wheat only contain some of those amino acids. • You can combined beans and rice to get a complete protein. ...
... • Plant food and wheat only contain some of those amino acids. • You can combined beans and rice to get a complete protein. ...
Lipids: Fats, Oils, Waxes, etc
... Vitamins are any of several organic substances that are essential for our normal health and growth. Vitamins are distinct from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in function, as well as in the quantities in which we require them. If a vitamin is absent from our diet or is not properly absorbed, a def ...
... Vitamins are any of several organic substances that are essential for our normal health and growth. Vitamins are distinct from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in function, as well as in the quantities in which we require them. If a vitamin is absent from our diet or is not properly absorbed, a def ...
Diet - Healthy Living 1200
... Stored in body fat, principally in the liver Can be toxic at high doses. Because the body cannot get rid of excess amounts, too much vitamins A and D can have cause serious adverse side effects. Too much vitamin A can result in: loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, liver damage, bone pai ...
... Stored in body fat, principally in the liver Can be toxic at high doses. Because the body cannot get rid of excess amounts, too much vitamins A and D can have cause serious adverse side effects. Too much vitamin A can result in: loss of appetite, headaches, irritability, liver damage, bone pai ...
NUTRIONAL SUPPLEMENT
... Food intolerance or allergy (although not common, and often over-diagnosed) may result in the avoidance of certain foods. A child’s nutritional demands also increase as he becomes exposed to childhood illnesses in pre-school or school. Nutritional deficiencies can result in a range of physical and m ...
... Food intolerance or allergy (although not common, and often over-diagnosed) may result in the avoidance of certain foods. A child’s nutritional demands also increase as he becomes exposed to childhood illnesses in pre-school or school. Nutritional deficiencies can result in a range of physical and m ...
Exam style Questions
... • Identify two nutrients found in oily fish. • Give one function of each • PROTEIN- growth and repair, maintenance of body cells • VITAMIN A- help see in dim light/ normal growth in children, maintenance of healthy skin, keep mucous membranes healthy • VITAMIN D- proper formation of bones and teeth ...
... • Identify two nutrients found in oily fish. • Give one function of each • PROTEIN- growth and repair, maintenance of body cells • VITAMIN A- help see in dim light/ normal growth in children, maintenance of healthy skin, keep mucous membranes healthy • VITAMIN D- proper formation of bones and teeth ...
Vitamin and Mineral Supplements - OSU Fact Sheets
... the body’s need for many nutrients increases. Doctors often recommend vitamin and mineral supplements for women who are pregnant or lactating. Some medicines lower the appetite or change the way the body uses nutrients. Drug-nutrient interactions may increase the risk of vitamin or mineral deficienc ...
... the body’s need for many nutrients increases. Doctors often recommend vitamin and mineral supplements for women who are pregnant or lactating. Some medicines lower the appetite or change the way the body uses nutrients. Drug-nutrient interactions may increase the risk of vitamin or mineral deficienc ...
Vitamins are organic substances that cannot be produced by the
... Vitamins are organic substances that cannot be produced by the human body. The only way of getting all of the vitamins the body needs is to ingest them, in small quantities, through the diet. Vitamins are essential for normal cell function, growth and development. There are 13 essential vitamins, wh ...
... Vitamins are organic substances that cannot be produced by the human body. The only way of getting all of the vitamins the body needs is to ingest them, in small quantities, through the diet. Vitamins are essential for normal cell function, growth and development. There are 13 essential vitamins, wh ...
Vitamin C - I.C. “Montalto di Castro”
... Water soluble vitamins The B vitamins There are many different B vitamins and each has a specific function in the body. These include: • vitamin B1 (Thiamin); • vitamin B2 (Riboflavin); • vitamin B3 (Niacin); • vitamin B6; • vitamin B12; • folate/folic acid. ...
... Water soluble vitamins The B vitamins There are many different B vitamins and each has a specific function in the body. These include: • vitamin B1 (Thiamin); • vitamin B2 (Riboflavin); • vitamin B3 (Niacin); • vitamin B6; • vitamin B12; • folate/folic acid. ...
Vitamin

A vitamin (US /ˈvaɪtəmɪn/ and UK /ˈvɪtəmɪn/) is an organic compound and a vital nutrient that an organism requires in limited amounts. An organic chemical compound (or related set of compounds) is called a vitamin when the organism cannot synthesize the compound in sufficient quantities, and it must be obtained through the diet; thus, the term ""vitamin"" is conditional upon the circumstances and the particular organism. For example, ascorbic acid (one form of vitamin C) is a vitamin for humans, but not for most other animal organisms. Supplementation is important for the treatment of certain health problems, but there is little evidence of nutritional benefit when used by otherwise healthy people.By convention, the term vitamin includes neither other essential nutrients, such as dietary minerals, essential fatty acids, or essential amino acids (which are needed in greater amounts than vitamins) nor the great number of other nutrients that promote health, and are required less often to maintain the health of the organism. Thirteen vitamins are universally recognized at present. Vitamins are classified by their biological and chemical activity, not their structure. Thus, each ""vitamin"" refers to a number of vitamer compounds that all show the biological activity associated with a particular vitamin. Such a set of chemicals is grouped under an alphabetized vitamin ""generic descriptor"" title, such as ""vitamin A"", which includes the compounds retinal, retinol, and four known carotenoids. Vitamers by definition are convertible to the active form of the vitamin in the body, and are sometimes inter-convertible to one another, as well.Vitamins have diverse biochemical functions. Some, such as vitamin D, have hormone-like functions as regulators of mineral metabolism, or regulators of cell and tissue growth and differentiation (such as some forms of vitamin A). Others function as antioxidants (e.g., vitamin E and sometimes vitamin C). The largest number of vitamins, the B complex vitamins, function as precursors for enzyme cofactors, that help enzymes in their work as catalysts in metabolism. In this role, vitamins may be tightly bound to enzymes as part of prosthetic groups: For example, biotin is part of enzymes involved in making fatty acids. They may also be less tightly bound to enzyme catalysts as coenzymes, detachable molecules that function to carry chemical groups or electrons between molecules. For example, folic acid may carry methyl, formyl, and methylene groups in the cell. Although these roles in assisting enzyme-substrate reactions are vitamins' best-known function, the other vitamin functions are equally important.Until the mid-1930s, when the first commercial yeast-extract vitamin B complex and semi-synthetic vitamin C supplement tablets were sold, vitamins were obtained solely through food intake, and changes in diet (which, for example, could occur during a particular growing season) usually greatly altered the types and amounts of vitamins ingested. However, vitamins have been produced as commodity chemicals and made widely available as inexpensive semisynthetic and synthetic-source multivitamin dietary and food supplements and additives, since the middle of the 20th century. Study of structural activity, function and their role in maintaining health is called as vitaminology.