The economy - Hanson Canada
... dynamic interaction between buyers and sellers directly impacts the range of products and prices in the free market. Supply refers to the quantity of products that producers are willing to offer for sale at different market prices. Since the business seek to make as much profit as possible , they ar ...
... dynamic interaction between buyers and sellers directly impacts the range of products and prices in the free market. Supply refers to the quantity of products that producers are willing to offer for sale at different market prices. Since the business seek to make as much profit as possible , they ar ...
Major schools of economic theory File
... filthy rich…but rich bankers….what did they ever do for society? 4. Too many useful things make too many useless people…. capitalist are like vampires that sucks the lives of labour. 5. We need to be spending money on highways, education, and research and development. It is not so important that the ...
... filthy rich…but rich bankers….what did they ever do for society? 4. Too many useful things make too many useless people…. capitalist are like vampires that sucks the lives of labour. 5. We need to be spending money on highways, education, and research and development. It is not so important that the ...
WARRIOR RUN SCHOOL DISTRICT
... written assignments, outside readings and research. 2. All students are expected to complete all reading and written assignments on time, and to participate in all class discussions, activities, and simulations. 3. All students will maintain an 80% or better average. 4. All students are expected to ...
... written assignments, outside readings and research. 2. All students are expected to complete all reading and written assignments on time, and to participate in all class discussions, activities, and simulations. 3. All students will maintain an 80% or better average. 4. All students are expected to ...
WWII United States War Boards and Offices
... • Almost 90% of retail food prices were frozen • Quota for each family based on number of people in the household and their needs • Merchants gave coupons to suppliers in order to restock • One of most controversial elements of war – Americans could afford more, but not available ...
... • Almost 90% of retail food prices were frozen • Quota for each family based on number of people in the household and their needs • Merchants gave coupons to suppliers in order to restock • One of most controversial elements of war – Americans could afford more, but not available ...
Lesson 1 - VU LMS - Virtual University
... accomplished based on a standard or criterion. The two primary methods of rationing are markets and governments. Rationing is needed due to the scarcity problem. Because wants and needs are unlimited, but resources are limited, available commodities must be rationed out to competing uses. ECONOMIC S ...
... accomplished based on a standard or criterion. The two primary methods of rationing are markets and governments. Rationing is needed due to the scarcity problem. Because wants and needs are unlimited, but resources are limited, available commodities must be rationed out to competing uses. ECONOMIC S ...
Economic Principles Notes
... a. Producers produce at the lowest cost possible and pay out to workers at the lowest cost possible (Called efficiency or productivity) b. Characterized by division of labor and specialization Production is based on the choices of private businesses and individuals Results: These economies are theor ...
... a. Producers produce at the lowest cost possible and pay out to workers at the lowest cost possible (Called efficiency or productivity) b. Characterized by division of labor and specialization Production is based on the choices of private businesses and individuals Results: These economies are theor ...
CHAPTER 1 THE ECONOMY IS US!
... we have to make it… should market allow us to make our selection or should government have a major say. There are three basic ways to make the necessary choices: ...
... we have to make it… should market allow us to make our selection or should government have a major say. There are three basic ways to make the necessary choices: ...
The Anglo-Saxon vs. the Rhine Model of Kism
... there has never been a will to make it as equal as in some of the Rhine countries. There have also been times when government has taken a lead role in managing key infrastructure industries like finance today or the railroads during WWI, but only temporarily , in cases of national emergency. ...
... there has never been a will to make it as equal as in some of the Rhine countries. There have also been times when government has taken a lead role in managing key infrastructure industries like finance today or the railroads during WWI, but only temporarily , in cases of national emergency. ...
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS!!!!
... Principles of Capitalism Consumer Sovereignty – consumers get to make free choices about what to buy and this helps drive production ...
... Principles of Capitalism Consumer Sovereignty – consumers get to make free choices about what to buy and this helps drive production ...
Lesson Four: Market Systems - North Clackamas School District
... Lack of incentives to work hard leads to unexpected results. Large bureaucracy for economic planning. Not flexible in dealing with minor day to day problems. People with new or unique ideas are stifled. ...
... Lack of incentives to work hard leads to unexpected results. Large bureaucracy for economic planning. Not flexible in dealing with minor day to day problems. People with new or unique ideas are stifled. ...
HOW to Produce? - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • We have to decide what we want most. • We have to sacrifice less-desired activities and goods. ...
... • We have to decide what we want most. • We have to sacrifice less-desired activities and goods. ...
Short-run Causes: Demand-pull and Cost-push
... living begin to increase. Contractual agreements, such as Social Security payments and cost-of-living adjustments, automatically increase wages. Also, in an inflationary economy, people tend to spend today, and this spending also perpetuates demand-pull. ...
... living begin to increase. Contractual agreements, such as Social Security payments and cost-of-living adjustments, automatically increase wages. Also, in an inflationary economy, people tend to spend today, and this spending also perpetuates demand-pull. ...
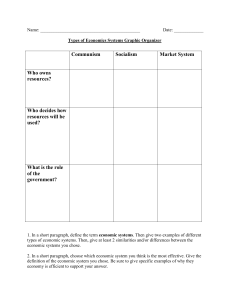
Communism Socialism Market System Who owns resources?
... examples of economic systems are market economies and command economies. Market economies are different than command economies because in a market economy, consumers and producers are in control of the resources in the economy. In command economies resources are owned and ruled by the government. A ...
... examples of economic systems are market economies and command economies. Market economies are different than command economies because in a market economy, consumers and producers are in control of the resources in the economy. In command economies resources are owned and ruled by the government. A ...
The Business Cycle
... leave the markets to sort out. Keynes felt that a slump (or trough) was a short-run problem stemming from a lack of demand. If the private sector was not prepared to spend to boost demand, then the government should do it instead by running a budget deficit. When times were good again and the privat ...
... leave the markets to sort out. Keynes felt that a slump (or trough) was a short-run problem stemming from a lack of demand. If the private sector was not prepared to spend to boost demand, then the government should do it instead by running a budget deficit. When times were good again and the privat ...
Econ 372 - Marietta College
... forms of income and taxation will you include? What population unit will you use? With what country will you compare your country's income distribution? ...
... forms of income and taxation will you include? What population unit will you use? With what country will you compare your country's income distribution? ...
Georgia
... The Strategy states, in particular: “New economic policies under the present Strategy will achieve increased welfare through reducing unemployment, improving labor and living conditions, forming basic social protection system and developing human capital. At the same time, the Government fully int ...
... The Strategy states, in particular: “New economic policies under the present Strategy will achieve increased welfare through reducing unemployment, improving labor and living conditions, forming basic social protection system and developing human capital. At the same time, the Government fully int ...
AHE_03_Provisional_programme_12-6
... economy at the University of Glasgow 1890-1950 Alan Hutton, Glasgow Caledonian University Did Adam Smith invent the concept of public goods and did he entrust their supply to the state? Valentin Petkantchin, University of Aix-Marseille III ...
... economy at the University of Glasgow 1890-1950 Alan Hutton, Glasgow Caledonian University Did Adam Smith invent the concept of public goods and did he entrust their supply to the state? Valentin Petkantchin, University of Aix-Marseille III ...
Economics
... Positive economics (describing "what is") and normative economics (advocating "what ought to be") Economic theory and applied economics Mainstream economics more "orthodox" dealing with the "rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus") and heterodox economics (more "radical" dealing with the ...
... Positive economics (describing "what is") and normative economics (advocating "what ought to be") Economic theory and applied economics Mainstream economics more "orthodox" dealing with the "rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus") and heterodox economics (more "radical" dealing with the ...
Make a list of the 10 material things that you would most want
... Scarcity is the condition that results from society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have Economics is the study of how people try to satisfy what appears to be unlimited and competing wants through the use of relatively scarce resources ...
... Scarcity is the condition that results from society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have Economics is the study of how people try to satisfy what appears to be unlimited and competing wants through the use of relatively scarce resources ...
Subsistence Agriculture
... Supply: how much of a good is available on the market Demand: how much consumers are willing to pay for a good The interaction of supply and demand determines prices in a free market economy. When demand is high, the price goes up. It the supply is high but demand is low, the price goes down. ...
... Supply: how much of a good is available on the market Demand: how much consumers are willing to pay for a good The interaction of supply and demand determines prices in a free market economy. When demand is high, the price goes up. It the supply is high but demand is low, the price goes down. ...
Chapter 1
... No country practices pure capitalism or pure socialism/communism. Economic systems contain various elements of government intervention ...
... No country practices pure capitalism or pure socialism/communism. Economic systems contain various elements of government intervention ...
Economics Fall 2013 Objectives: Student will be able to relate the
... Learning involves a process of discovery and a process of mastery and the most successful way students learn is through an active self-conscious interpretation of the material. According to research, of the information students retain 60% of it comes from student-to-student discussion, 20% comes fro ...
... Learning involves a process of discovery and a process of mastery and the most successful way students learn is through an active self-conscious interpretation of the material. According to research, of the information students retain 60% of it comes from student-to-student discussion, 20% comes fro ...
Leonardo Escobar Mr. Kann APUSH The Affluent Society Chapter 30
... ○ Mechanization reduced for labor necessities + workforce decline for 20 years after WWII. ■ 1960’s: Many U Limited Gains for Unorganized Workers ● Unorganized laborers achieved fewer success than workers who were organized and effecti ...
... ○ Mechanization reduced for labor necessities + workforce decline for 20 years after WWII. ■ 1960’s: Many U Limited Gains for Unorganized Workers ● Unorganized laborers achieved fewer success than workers who were organized and effecti ...