Geology 3015 - Lakehead University
... inorganic, homogenous solid with a chemical composition that is either fixed or varies within certain fixed limits, and a characteristic internal structure manifested in its exterior form and physical properties • Rock: A consolidated or unconsolidated aggregate of mineral grains consisting of one o ...
... inorganic, homogenous solid with a chemical composition that is either fixed or varies within certain fixed limits, and a characteristic internal structure manifested in its exterior form and physical properties • Rock: A consolidated or unconsolidated aggregate of mineral grains consisting of one o ...
Review of the Dissertation of Elena S. Zhitova «Crystal Chemistry of
... belongs to the layered double hydroxides (LDHs), a large class of natural and synthetic compounds. To date, 44 minerals have been described as natural examples of LDH phases; they are commonly known as the ‘hydrotalcites’ or ‘hydrotalcite group’ of minerals. Scientifically, these minerals are intere ...
... belongs to the layered double hydroxides (LDHs), a large class of natural and synthetic compounds. To date, 44 minerals have been described as natural examples of LDH phases; they are commonly known as the ‘hydrotalcites’ or ‘hydrotalcite group’ of minerals. Scientifically, these minerals are intere ...
Sed. Rock Id Lab Intro (B)
... Hard (scratches glass), white to gray to black, breaks in large FLINT when black smooth curved surfaces. Commonly has a soft candle wax luster. or CHERT when white Composed of microcrystalline quartz, Native Americans used this rock for arrow heads, scrapers and knives because it could be flaked int ...
... Hard (scratches glass), white to gray to black, breaks in large FLINT when black smooth curved surfaces. Commonly has a soft candle wax luster. or CHERT when white Composed of microcrystalline quartz, Native Americans used this rock for arrow heads, scrapers and knives because it could be flaked int ...
Ch 2 - 3 Use of Minerals
... 3. It is also used to make frames for eyeglasses, wheelchair parts, bicycles, golf clubs, and tennis rackets. 4. Titanium is a useful element that improves the lives of many humans for hip or knee replacements. ...
... 3. It is also used to make frames for eyeglasses, wheelchair parts, bicycles, golf clubs, and tennis rackets. 4. Titanium is a useful element that improves the lives of many humans for hip or knee replacements. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... An isotope is an atom that exhibits variation in its mass number Some isotopes have unstable nuclei that emit particles and energy in a process known as radioactive decay ...
... An isotope is an atom that exhibits variation in its mass number Some isotopes have unstable nuclei that emit particles and energy in a process known as radioactive decay ...
Minerals
... variation in its mass number Some isotopes have unstable nuclei that emit particles and energy in a process known as radioactive decay ...
... variation in its mass number Some isotopes have unstable nuclei that emit particles and energy in a process known as radioactive decay ...
Name: Date: Subject: Minerals Objectives Objective 1: ASWBAT
... 1. What are rocks made of? Answer: 2. What makes rocks different from each other? Answer: Action! – Look at the minerals out on the desk. How are they different? How are they the same? How are minerals classified? Identifying Minerals Minerals are identified by their properties. Properties are thing ...
... 1. What are rocks made of? Answer: 2. What makes rocks different from each other? Answer: Action! – Look at the minerals out on the desk. How are they different? How are they the same? How are minerals classified? Identifying Minerals Minerals are identified by their properties. Properties are thing ...
Chapter 3: Minerals and Matter
... • Most important mineral group – Comprise most of the rock-forming minerals – Very abundant due to large amounts of silicon and oxygen in Earth’s crust ...
... • Most important mineral group – Comprise most of the rock-forming minerals – Very abundant due to large amounts of silicon and oxygen in Earth’s crust ...
Igneous review - cloudfront.net
... ●Identifying minerals in fine-grained igneous rocks (generally extrusive rocks) can be very difficult. For such rocks, it is sometimes easiest to figure out what kind of rock it is first, hypothesize the minerals that should be present, and then go look for them in the specimens. For example, if you ...
... ●Identifying minerals in fine-grained igneous rocks (generally extrusive rocks) can be very difficult. For such rocks, it is sometimes easiest to figure out what kind of rock it is first, hypothesize the minerals that should be present, and then go look for them in the specimens. For example, if you ...
Atoms and Minerals
... • 40K, 87Rb, 235U, 238U, 232Th are naturally occurring radioactive isotopes ...
... • 40K, 87Rb, 235U, 238U, 232Th are naturally occurring radioactive isotopes ...
Atoms and Minerals Atoms Chemistry
... of minerals as polyhedra where the corners of the polyhedra represent oxygen and center is a cation like Si4+. ...
... of minerals as polyhedra where the corners of the polyhedra represent oxygen and center is a cation like Si4+. ...
Physical Properties of Minerals
... 3- Odor: Some minerals with weak van der Waals bonds have a characteristic smell when rubbed. For example, Realgar (AsS) has the smell of garlic. IV- Specific gravity: This property is defined as the density of a mineral relative to the density of water at 4°C. In practice, it measured by weighing t ...
... 3- Odor: Some minerals with weak van der Waals bonds have a characteristic smell when rubbed. For example, Realgar (AsS) has the smell of garlic. IV- Specific gravity: This property is defined as the density of a mineral relative to the density of water at 4°C. In practice, it measured by weighing t ...
Monthly Statistics of Mineral Production
... minor minerals. To augment the statistics on mining sector, the production data on petroleum & natural gas is obtained from Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, Coal and Lignite from Office of Coal Controller, the data on export/import of various mineral is obtained from Directorate General of Comme ...
... minor minerals. To augment the statistics on mining sector, the production data on petroleum & natural gas is obtained from Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, Coal and Lignite from Office of Coal Controller, the data on export/import of various mineral is obtained from Directorate General of Comme ...
Mineral Formation
... deep within the Earth generally leads to a rock such as granite with visible crystals of feldspar, quartz, mica, amphibole and other minerals. Water in the magma can even facilitate pegmatite formation. Pegmatite is an igneous rock composed of mineral crystals generally with a diameter of several ce ...
... deep within the Earth generally leads to a rock such as granite with visible crystals of feldspar, quartz, mica, amphibole and other minerals. Water in the magma can even facilitate pegmatite formation. Pegmatite is an igneous rock composed of mineral crystals generally with a diameter of several ce ...
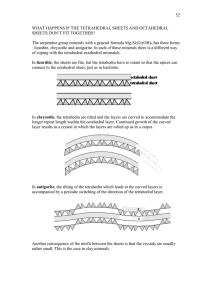
CLAY MINERALS
... interstitial cation sites compared to those in the chain silicate minerals. Thus Na+ and Ca2+ will be considered as 'small' cations compared to K+, while ions such as Mg2+ are too small to play a role in these structures. The aluminosilicate framework minerals are by far the most abundant minerals i ...
... interstitial cation sites compared to those in the chain silicate minerals. Thus Na+ and Ca2+ will be considered as 'small' cations compared to K+, while ions such as Mg2+ are too small to play a role in these structures. The aluminosilicate framework minerals are by far the most abundant minerals i ...
Rock Identification and stories lab
... Story: Shale formed in a low energy environment where water or wind was sufficiently still to allow the very tiny particles to settle out and accumulate. Environments with low energy include lagoons, swamps, marshes, out in the deep part of lakes, and far enough offshore in oceans where the waves do ...
... Story: Shale formed in a low energy environment where water or wind was sufficiently still to allow the very tiny particles to settle out and accumulate. Environments with low energy include lagoons, swamps, marshes, out in the deep part of lakes, and far enough offshore in oceans where the waves do ...
Oxides and Hydroxides
... Refractory (melt at a high temperature) Occurrence: Often found as accessory minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks Because of their hardness, as resistant grains and detrital grains in sediments and sedimentary rocks ...
... Refractory (melt at a high temperature) Occurrence: Often found as accessory minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks Because of their hardness, as resistant grains and detrital grains in sediments and sedimentary rocks ...
Introduction to Environmental Geochemistry
... Refractory (melt at a high temperature) Occurrence: Often found as accessory minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks Because of their hardness, as resistant grains and detrital grains in sediments and sedimentary rocks ...
... Refractory (melt at a high temperature) Occurrence: Often found as accessory minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks Because of their hardness, as resistant grains and detrital grains in sediments and sedimentary rocks ...
049555507X_131305 - ASB
... within this mosaic have their atoms arranged in a specific three-dimensional framework. Fig. 3.8 a-b, p. 67 ...
... within this mosaic have their atoms arranged in a specific three-dimensional framework. Fig. 3.8 a-b, p. 67 ...
BAG 101:
... Colour: often a striking property but not a very reliable means of identification. Streak: can be misleading, but often used. Hardness: refers to the relative resistance of a mineral to scratching. This is governed by crystal structure and by the strength of the bonds between atoms. A scale called M ...
... Colour: often a striking property but not a very reliable means of identification. Streak: can be misleading, but often used. Hardness: refers to the relative resistance of a mineral to scratching. This is governed by crystal structure and by the strength of the bonds between atoms. A scale called M ...
Rocks and Minerals
... Gypsum flowers "grow" in profusion on the wall of the Puketiti Flower Cave in New Zealand. They are rocks, not living plants, despite the flower-like shape. They seem to grow and curve out of the wall, like toothpaste forced out of a tube. Some say they come out of cracks in the wall, ...
... Gypsum flowers "grow" in profusion on the wall of the Puketiti Flower Cave in New Zealand. They are rocks, not living plants, despite the flower-like shape. They seem to grow and curve out of the wall, like toothpaste forced out of a tube. Some say they come out of cracks in the wall, ...
Rock Examination 1
... A rock type generally consists of several minerals, but a single mineral can also form its own rock type. Granite, for example, is composed of feldspar, quartz and mica. Based on the way they were created, rocks are classified as igneous rock (formed from melted and solidified magma), sedimentary ro ...
... A rock type generally consists of several minerals, but a single mineral can also form its own rock type. Granite, for example, is composed of feldspar, quartz and mica. Based on the way they were created, rocks are classified as igneous rock (formed from melted and solidified magma), sedimentary ro ...
Introduction to Environmental Geochemistry
... Refractory (melt at a high temperature) Occurance: Often found as accessory minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks Because of their hardness, as resistant grains and detrital grains in sediments and sedimentary rocks ...
... Refractory (melt at a high temperature) Occurance: Often found as accessory minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks Because of their hardness, as resistant grains and detrital grains in sediments and sedimentary rocks ...
Lesson Plans: September 15-19
... Introduction/Engagement/Invitation (Link to Prior Knowledge) Monday: Students will examine several samples of minerals. Students will record any observations they can make within the 10-15 minute time period, and cite any information that they might know about each mineral. Tuesday: Students will re ...
... Introduction/Engagement/Invitation (Link to Prior Knowledge) Monday: Students will examine several samples of minerals. Students will record any observations they can make within the 10-15 minute time period, and cite any information that they might know about each mineral. Tuesday: Students will re ...
Mineral

A mineral is a naturally occurring substance that is solid and inorganic, representable by a chemical formula, usually abiogenic, and has an ordered atomic structure. It is different from a rock, which can be an aggregate of minerals or non-minerals and does not have a specific chemical composition. The exact definition of a mineral is under debate, especially with respect to the requirement a valid species be abiogenic, and to a lesser extent with regard to it having an ordered atomic structure. The study of minerals is called mineralogy.There are over 4,900 known mineral species; over 4,660 of these have been approved by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA). The silicate minerals compose over 90% of the Earth's crust. The diversity and abundance of mineral species is controlled by the Earth's chemistry. Silicon and oxygen constitute approximately 75% of the Earth's crust, which translates directly into the predominance of silicate minerals. Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish various species, and these properties in turn are influenced by the mineral's geological environment of formation. Changes in the temperature, pressure, or bulk composition of a rock mass cause changes in its minerals. Minerals can be described by various physical properties which relate to their chemical structure and composition. Common distinguishing characteristics include crystal structure and habit, hardness, lustre, diaphaneity, colour, streak, tenacity, cleavage, fracture, parting, and specific gravity. More specific tests for minerals include magnetism, taste or smell, radioactivity and reaction to acid.Minerals are classified by key chemical constituents; the two dominant systems are the Dana classification and the Strunz classification. The silicate class of minerals is subdivided into six subclasses by the degree of polymerization in the chemical structure. All silicate minerals have a base unit of a [SiO4]4− silica tetrahedra—that is, a silicon cation coordinated by four oxygen anions, which gives the shape of a tetrahedron. These tetrahedra can be polymerized to give the subclasses: orthosilicates (no polymerization, thus single tetrahedra), disilicates (two tetrahedra bonded together), cyclosilicates (rings of tetrahedra), inosilicates (chains of tetrahedra), phyllosilicates (sheets of tetrahedra), and tectosilicates (three-dimensional network of tetrahedra). Other important mineral groups include the native elements, sulfides, oxides, halides, carbonates, sulfates, and phosphates.