Analysis of Mode-Dependent Gain in Raman Amplified Few-Mode Fiber
... minimum value for the error function (max(A± m ) − min(Am )), evaluated over all modes m of interest. In order to minimize the MDG along the whole fiber, the configurations for forward- and backward amplification, have to be optimized individually. However the resulting optimum configuration will be ...
... minimum value for the error function (max(A± m ) − min(Am )), evaluated over all modes m of interest. In order to minimize the MDG along the whole fiber, the configurations for forward- and backward amplification, have to be optimized individually. However the resulting optimum configuration will be ...
Si oxidation and dielectrics
... •Easily patterned and etched with plasmas or specific chemicals •Excellent insulators ...
... •Easily patterned and etched with plasmas or specific chemicals •Excellent insulators ...
Microwave Solid State Devices
... Low noise design considerations: * Planar and epitaxial methods of construction use diffusion and surface passivation to protect surfaces from contamination as opposed to diffusion method of mesa structure implementing acid etching. * Shot noise is proportional to the square of current therefore o ...
... Low noise design considerations: * Planar and epitaxial methods of construction use diffusion and surface passivation to protect surfaces from contamination as opposed to diffusion method of mesa structure implementing acid etching. * Shot noise is proportional to the square of current therefore o ...
Technical Basics
... feeder has a lower loss than Coaxial cable This loss is both in Transmit and Receive modes. For some standard cables the loss is: ...
... feeder has a lower loss than Coaxial cable This loss is both in Transmit and Receive modes. For some standard cables the loss is: ...
PDF
... OCIS codes: (130.3120) Integrated optics devices; (230.5750) Resonators; (230.7370) Waveguides. ...
... OCIS codes: (130.3120) Integrated optics devices; (230.5750) Resonators; (230.7370) Waveguides. ...
Optical Forces in Hybrid Plasmonic Waveguides Xiaodong Yang, Yongmin Liu, Rupert F. Oulton,
... 1550 nm.28 The strong coupling between the dielectric waveguide cylinder mode and the SPP mode supported at the interface of air and silver results in an extremely confined hybrid plasmonic mode, while the evanescent coupling between the cylinder mode and the glass substrate acts as a perturbation to ...
... 1550 nm.28 The strong coupling between the dielectric waveguide cylinder mode and the SPP mode supported at the interface of air and silver results in an extremely confined hybrid plasmonic mode, while the evanescent coupling between the cylinder mode and the glass substrate acts as a perturbation to ...
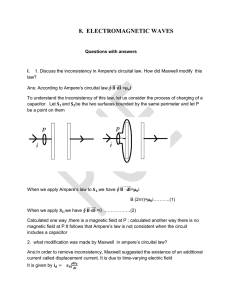
8. electromagnetic waves
... Ans:Waves radiated by accelerated charges and consist of time varying, transverse electric and magnetic fields are called electromagnetic waves 8. Name the scientist who first predicted the existence of e.m waves ...
... Ans:Waves radiated by accelerated charges and consist of time varying, transverse electric and magnetic fields are called electromagnetic waves 8. Name the scientist who first predicted the existence of e.m waves ...
flextherm r - Gabriel Benmayor SA
... AISMALIBAR FLEXTHERM is a high technology thermal insulated metal substrate, also known as a metal core copper clad laminate, for use in the production of conformable metal printed circuit boards. Its low thermal impedance allows the dissipation of temperature from the heating elements of a PCB into ...
... AISMALIBAR FLEXTHERM is a high technology thermal insulated metal substrate, also known as a metal core copper clad laminate, for use in the production of conformable metal printed circuit boards. Its low thermal impedance allows the dissipation of temperature from the heating elements of a PCB into ...
NANOTECHNOLOGY AND ITS ADVENT IN ELECTRONICS AND
... a 3-termirtal device, such an "atom" must be ...
... a 3-termirtal device, such an "atom" must be ...
Filters
... • Recall the use of the 0.707 level to define the bandwidth of a series or parallel resonant circuit (both with the general shape of the pass-band filter). ...
... • Recall the use of the 0.707 level to define the bandwidth of a series or parallel resonant circuit (both with the general shape of the pass-band filter). ...
InPAC2013_245_Vinit_Kumar
... coherent electromagnetic radiation is produced due to the interaction of an electron beam with the co-propagating surface electromagnetic mode supported by the dielectric slab placed over an ideal conductor. Over the last several decades, many theoretical investigations have been made to study the m ...
... coherent electromagnetic radiation is produced due to the interaction of an electron beam with the co-propagating surface electromagnetic mode supported by the dielectric slab placed over an ideal conductor. Over the last several decades, many theoretical investigations have been made to study the m ...
Design of the RF Distribution System for the ESS Spoke Linac
... coaxial circulators (foot-print: 600 mm x 600 mm) with two ferrite loads (foot-print: 641 mm x 1067 mm). WR2300 half height can be used to carry peak power of 400 kW to the spoke cryomodule through the tunnel. The 6-1/8 inch circulator design is available and it can handle 200 kW peak power without ...
... coaxial circulators (foot-print: 600 mm x 600 mm) with two ferrite loads (foot-print: 641 mm x 1067 mm). WR2300 half height can be used to carry peak power of 400 kW to the spoke cryomodule through the tunnel. The 6-1/8 inch circulator design is available and it can handle 200 kW peak power without ...
Waveguide (electromagnetism)

In electromagnetics and communications engineering, the term waveguide may refer to any linear structure that conveys electromagnetic waves between its endpoints. However, the original and most common meaning is a hollow metal pipe used to carry radio waves. This type of waveguide is used as a transmission line mostly at microwave frequencies, for such purposes as connecting microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas, in equipment such as microwave ovens, radar sets, satellite communications, and microwave radio links.A dielectric waveguide employs a solid dielectric rod rather than a hollow pipe. An optical fibre is a dielectric guide designed to work at optical frequencies. Transmission lines such as microstrip, coplanar waveguide, stripline or coaxial cable may also be considered to be waveguides.The electromagnetic waves in a (metal-pipe) waveguide may be imagined as travelling down the guide in a zig-zag path, being repeatedly reflected between opposite walls of the guide. For the particular case of rectangular waveguide, it is possible to base an exact analysis on this view. Propagation in a dielectric waveguide may be viewed in the same way, with the waves confined to the dielectric by total internal reflection at its surface. Some structures, such as non-radiative dielectric waveguides and the Goubau line, use both metal walls and dielectric surfaces to confine the wave.