Bellringer
... understanding: moksha • This takes more than one lifetime! Reincarnation (or rebirth in a new body) occurs after the cycle of life, samsara, is complete • Reaching moksha ends reincarnation ...
... understanding: moksha • This takes more than one lifetime! Reincarnation (or rebirth in a new body) occurs after the cycle of life, samsara, is complete • Reaching moksha ends reincarnation ...
Hinduism
... sacred texts and are all part of the Vedas Ramayana-an epic poem, the hero is Rama. A scripture that offers a hero as a model for the Hindu life. The moral code of conduct, social duty. Gives the model for the ideal Hindu life. Mahabharata- the world’s longest epic poem. Contains many ba ...
... sacred texts and are all part of the Vedas Ramayana-an epic poem, the hero is Rama. A scripture that offers a hero as a model for the Hindu life. The moral code of conduct, social duty. Gives the model for the ideal Hindu life. Mahabharata- the world’s longest epic poem. Contains many ba ...
Hinduism - inglenookreligion
... • The next three nights with a mind better prepared for spiritual guidance, they offer puja to Lakshmi, the goddess of wealth and fortune. • The final three nights are dedicated to Saraswati, the god of knowledge and learning. • On the tenth day, worshipers observe Vijayadasami or the Day of Victory ...
... • The next three nights with a mind better prepared for spiritual guidance, they offer puja to Lakshmi, the goddess of wealth and fortune. • The final three nights are dedicated to Saraswati, the god of knowledge and learning. • On the tenth day, worshipers observe Vijayadasami or the Day of Victory ...
from 1200 BC to 300 CE
... 6th century B.C. : Buddhism, Jainism, Confucianism, Taoism; Shintoism. 6th century B.C: Mahavira Vardhamana (540 - 468B.C), Founder of Jainism 6th century B.C: Gautama Buddha(563-483 B.C.), founder of Buddhism 3th century B.C: King Ashoka (304-232 B.C.E): 2nd founder of Buddhism * 20th centu ...
... 6th century B.C. : Buddhism, Jainism, Confucianism, Taoism; Shintoism. 6th century B.C: Mahavira Vardhamana (540 - 468B.C), Founder of Jainism 6th century B.C: Gautama Buddha(563-483 B.C.), founder of Buddhism 3th century B.C: King Ashoka (304-232 B.C.E): 2nd founder of Buddhism * 20th centu ...
Hinduism and Buddhism
... If you obey your dharma and have good karma you will be reincarnated to achieve moksha. ...
... If you obey your dharma and have good karma you will be reincarnated to achieve moksha. ...
Hinduism and Buddhism - Renton School District
... If you obey your dharma and have good karma you will be reincarnated to achieve moksha. ...
... If you obey your dharma and have good karma you will be reincarnated to achieve moksha. ...
Hinduism and Buddhism
... If you obey your dharma and have good karma you will be reincarnated to achieve moksha. ...
... If you obey your dharma and have good karma you will be reincarnated to achieve moksha. ...
India & China
... India was divided into the Deccan (south) and the Aryan (north) After Asoka died, India divided again & different princes regained rule The Deccan was divided into many kingdoms Each kingdom had their own capital with temples & workshops Many outside people wanted to trade with India ...
... India was divided into the Deccan (south) and the Aryan (north) After Asoka died, India divided again & different princes regained rule The Deccan was divided into many kingdoms Each kingdom had their own capital with temples & workshops Many outside people wanted to trade with India ...
Describe Buddhism
... Buddhism-religion that began in India Buddha-“The Enlightened One” Enlightened-peaceful and happy; the highest state of being Four Noble Truths are four principles a person must accept to free him or herself from desire: suffering is part of life; desires causes suffering; to give up desire ...
... Buddhism-religion that began in India Buddha-“The Enlightened One” Enlightened-peaceful and happy; the highest state of being Four Noble Truths are four principles a person must accept to free him or herself from desire: suffering is part of life; desires causes suffering; to give up desire ...
Hinduism
... Hinduism. Castes are social classes into which a person is born and lives their entire life. If a person has a good karma they may be reincarnated into a higher caste. ...
... Hinduism. Castes are social classes into which a person is born and lives their entire life. If a person has a good karma they may be reincarnated into a higher caste. ...
Hinduism and Buddhism
... hymns or songs by priest speaking Sanskrit (ancient Aryan language.) The Vedas were passed down from generation to generation in oral form and were not written down for hundreds of years. Upanishads- is an explanation of Vedas that is in depth and breaks them down as well. ...
... hymns or songs by priest speaking Sanskrit (ancient Aryan language.) The Vedas were passed down from generation to generation in oral form and were not written down for hundreds of years. Upanishads- is an explanation of Vedas that is in depth and breaks them down as well. ...
Interaction and Integration of Hindu Faith and Primal Faiths with
... perpetual enmity projected by the Vedas, there seem 'racial purity meant nothing to early Aryans·; adoption of the autochthonous· was always possible and practice'.5 It is in the Dharma Sastras, especially in Manu Dharma that we fmd more exacting laws against admixture in order that the twice born A ...
... perpetual enmity projected by the Vedas, there seem 'racial purity meant nothing to early Aryans·; adoption of the autochthonous· was always possible and practice'.5 It is in the Dharma Sastras, especially in Manu Dharma that we fmd more exacting laws against admixture in order that the twice born A ...
Slide 1
... • POLYTHEISTIC = Worship of multiple deities • MONOTHEISTIC = One supreme God: • principle of Brahman - all reality is a unity • PANTHEISTIC – All reality is connected and share a common essence • Water analogy • TRINITARIAN = Brahman is visualized as a trinity – one God with three persons: • Brahma ...
... • POLYTHEISTIC = Worship of multiple deities • MONOTHEISTIC = One supreme God: • principle of Brahman - all reality is a unity • PANTHEISTIC – All reality is connected and share a common essence • Water analogy • TRINITARIAN = Brahman is visualized as a trinity – one God with three persons: • Brahma ...
No original founder Grew out of early Aryan beliefs in
... • Buddha was a god and pay homage to Buddha like deities who came in the form of men and believe they can be saved by the faith in these gods • Allowed for a broader interpretation of the teachings of Buddhism because Buddha had not provided for all the answers ...
... • Buddha was a god and pay homage to Buddha like deities who came in the form of men and believe they can be saved by the faith in these gods • Allowed for a broader interpretation of the teachings of Buddhism because Buddha had not provided for all the answers ...
Indian Religions
... their soul would be reborn into a new body • The body they came back in depended on their actions during their former life…this is called karma-the effects that good or bad actions have on a person’s soul – This is the idea that if you do good, good will happen to you and vice versa ...
... their soul would be reborn into a new body • The body they came back in depended on their actions during their former life…this is called karma-the effects that good or bad actions have on a person’s soul – This is the idea that if you do good, good will happen to you and vice versa ...
Learning About World Religions: Hinduism
... populations. But it is also held together by its core ideals. Many beliefs, forms of worship, and deities are shared but often differ from place to place. The Vedas, to which Hinduism traces its roots are sacred to nearly a billion Hindus worldwide. Along with later sacred texts, the Vedas explain s ...
... populations. But it is also held together by its core ideals. Many beliefs, forms of worship, and deities are shared but often differ from place to place. The Vedas, to which Hinduism traces its roots are sacred to nearly a billion Hindus worldwide. Along with later sacred texts, the Vedas explain s ...
Hinduism-early beginnings
... This shows that there were some Hindus seeking spiritual perfection through ascetic practices like living outdoors, practicing silence, and restricting their diets. ...
... This shows that there were some Hindus seeking spiritual perfection through ascetic practices like living outdoors, practicing silence, and restricting their diets. ...
Hinduism - Baradene
... •The temple is a special place for Hindus. •It is known as the Mandir and is regarded as God’s home on •Earth. •A murti is a diety or image of a Hindu god or godess and are to be found in the Mandir. •The Murti is made according to the instructions of the shilpa shastra. The priest then installs the ...
... •The temple is a special place for Hindus. •It is known as the Mandir and is regarded as God’s home on •Earth. •A murti is a diety or image of a Hindu god or godess and are to be found in the Mandir. •The Murti is made according to the instructions of the shilpa shastra. The priest then installs the ...
Pearl is a Hindu
... the caste system. The caste system was further enforced by the Hindu belief of Karma. Bad deeds can cause a person to be reborn as a lower level, or even as an animal. The unequal distribution of wealth, prestige, suffering are thus seen as natural consequences for one's previous acts, both in this ...
... the caste system. The caste system was further enforced by the Hindu belief of Karma. Bad deeds can cause a person to be reborn as a lower level, or even as an animal. The unequal distribution of wealth, prestige, suffering are thus seen as natural consequences for one's previous acts, both in this ...
Exploring India`s Hinduism and Buddhism
... fully understanding spirit and matter, true knowledge is achieved. As it developed, Sāṃkhya, which was idealistic in nature, became paired with the more practical Yóga system, and it was in the latter that a 26th category of reality was included—God. In the Yóga system, God, like the other 25 catego ...
... fully understanding spirit and matter, true knowledge is achieved. As it developed, Sāṃkhya, which was idealistic in nature, became paired with the more practical Yóga system, and it was in the latter that a 26th category of reality was included—God. In the Yóga system, God, like the other 25 catego ...
Life of Pi definitions
... Imam : Title for a Muslim religious leader or chief. Sikh : A member of a monotheistic religion, founded in the Punjab c1500 by the guru Nanak, that refuses to recognize the Hindu caste system or the Brahmanical priesthood. Brahman : A member of the highest, or priestly, class among the Hindus. Bapu ...
... Imam : Title for a Muslim religious leader or chief. Sikh : A member of a monotheistic religion, founded in the Punjab c1500 by the guru Nanak, that refuses to recognize the Hindu caste system or the Brahmanical priesthood. Brahman : A member of the highest, or priestly, class among the Hindus. Bapu ...
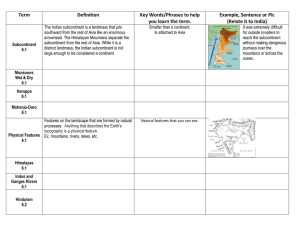
Term Definition Key Words/Phrases to help you learn
... Features on the landscape that are formed by natural processes. Anything that describes the Earth's topography is a physical feature. ...
... Features on the landscape that are formed by natural processes. Anything that describes the Earth's topography is a physical feature. ...
Intro to Hinduism
... may be addressed to any of the numerous gods in the Hindu pantheon. Temples are often dedicated to a particular deity, and typically contain sanctified images of the deity. Puja is addressed to this deity by a priest after ritual purification. The image is also purified by a bath, and is “fed” symbo ...
... may be addressed to any of the numerous gods in the Hindu pantheon. Temples are often dedicated to a particular deity, and typically contain sanctified images of the deity. Puja is addressed to this deity by a priest after ritual purification. The image is also purified by a bath, and is “fed” symbo ...