Popular Hinduism
... The recognition that all people are different, with different temperaments, etc. Common assumptions: authority of Vedas, idea of rebirth, ignorance brings bondage All four exhort or encourage one to adhere to or follow moral preliminaries • Yamas (abstinences): non-violence, truthfulness, non-steali ...
... The recognition that all people are different, with different temperaments, etc. Common assumptions: authority of Vedas, idea of rebirth, ignorance brings bondage All four exhort or encourage one to adhere to or follow moral preliminaries • Yamas (abstinences): non-violence, truthfulness, non-steali ...
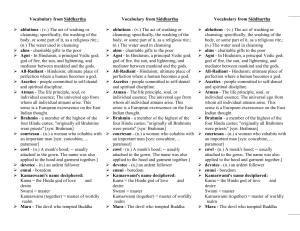
Vocabulary from Siddhartha
... cleansing; specifically, the washing of the body, or some part of it, as a religious rite.; (n.) The water used in cleansing alms - charitable gifts to the poor Agni - In Hinduism, a principal Vedic god; god of fire, the sun, and lightening, and mediator between mankind and the gods. All-Radia ...
... cleansing; specifically, the washing of the body, or some part of it, as a religious rite.; (n.) The water used in cleansing alms - charitable gifts to the poor Agni - In Hinduism, a principal Vedic god; god of fire, the sun, and lightening, and mediator between mankind and the gods. All-Radia ...
document
... • Find release from the samasara cycle • Moksha – release from action and rebirth • Find nirvana by knowledge of the supreme Truth of the brahma-atman the soul is released from the life cycle • Found by very few “As rivers flow and disappear at last In ocean’s waters, name and form renouncing So too ...
... • Find release from the samasara cycle • Moksha – release from action and rebirth • Find nirvana by knowledge of the supreme Truth of the brahma-atman the soul is released from the life cycle • Found by very few “As rivers flow and disappear at last In ocean’s waters, name and form renouncing So too ...
Hinduism - 2
... HOLY PLACES: Benares [a holy city] and the Ganges River are important places to which ...
... HOLY PLACES: Benares [a holy city] and the Ganges River are important places to which ...
Introduction to Hinduism
... natives they subdued (no doubt a connotation Hitler used to indicate Germans as the ‘pure’ Aryan race, but his idea was hogwash). Aryans did see themselves as superior to those they conquered, especially in India, calling themselves ‘noble ones’. ...
... natives they subdued (no doubt a connotation Hitler used to indicate Germans as the ‘pure’ Aryan race, but his idea was hogwash). Aryans did see themselves as superior to those they conquered, especially in India, calling themselves ‘noble ones’. ...
Hinduism How is Hinduism different from other faiths? * Hinduism
... next life is always dependent on how the previous life was lived. (Similar to Buddhist beliefs) Karma is the cause of our particular destiny. *Misfortunes in our present life are the result of acts that we have committed in the past. In the same way, our actions in our present lives will determine o ...
... next life is always dependent on how the previous life was lived. (Similar to Buddhist beliefs) Karma is the cause of our particular destiny. *Misfortunes in our present life are the result of acts that we have committed in the past. In the same way, our actions in our present lives will determine o ...
India - ryanworldhistory
... Chief god was Indra, god of war Brahmins offered sacrifices or food and drink to the gods for their good favor Brahman- a single spiritual power that exists in everything Mystics- people who seek direct communion with divine forces ...
... Chief god was Indra, god of war Brahmins offered sacrifices or food and drink to the gods for their good favor Brahman- a single spiritual power that exists in everything Mystics- people who seek direct communion with divine forces ...
Document
... The nonscriptural literature, the Smriti, contains several major groupings. The first are the Sutras ("threads"), written about 500-200 B.C. These writings present the requirements of Vedic religion. They include social rules (dharma), as well as priestly and domestic duties. The best known Sutra is ...
... The nonscriptural literature, the Smriti, contains several major groupings. The first are the Sutras ("threads"), written about 500-200 B.C. These writings present the requirements of Vedic religion. They include social rules (dharma), as well as priestly and domestic duties. The best known Sutra is ...
Hinduism
... Choosing a particular god or goddess and worshipping them throughout your life in actions, words and deeds. 4 The path of good works - Karma-yoga This involves doing all your duties correctly throughout your life. Why are there so many Hindu Gods? Hindus actually only believe in one God, Brahman, th ...
... Choosing a particular god or goddess and worshipping them throughout your life in actions, words and deeds. 4 The path of good works - Karma-yoga This involves doing all your duties correctly throughout your life. Why are there so many Hindu Gods? Hindus actually only believe in one God, Brahman, th ...
It is a way of life which shapes and unifies much of Indian
... 2. Harijians – Untouchables – outcasts in Hindu society. They are usually poor and less educated then other Hindus. ...
... 2. Harijians – Untouchables – outcasts in Hindu society. They are usually poor and less educated then other Hindus. ...
The Origins of Hinduism
... Unlike other major world religions (Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Buddhism) Hinduism has no founder. The ideas and beliefs of Hinduism developed over thousands of years. Hinduism is the combination of religious practices found from different people throughout India’s history. ...
... Unlike other major world religions (Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Buddhism) Hinduism has no founder. The ideas and beliefs of Hinduism developed over thousands of years. Hinduism is the combination of religious practices found from different people throughout India’s history. ...
hinduism
... People are free to worship any set of doctrines or rules they like. It does not believe in conversion, and does not impose its beliefs on others. However, Hindus are expected to follow specific rules in their personal conduct and daily duties. There is a vast body of rules and rituals for almost eve ...
... People are free to worship any set of doctrines or rules they like. It does not believe in conversion, and does not impose its beliefs on others. However, Hindus are expected to follow specific rules in their personal conduct and daily duties. There is a vast body of rules and rituals for almost eve ...
document
... – When people impose wrong views on appearance, the world becomes illusory and ensnaring. • Therefore the basic ill is ignorance or Avidya ...
... – When people impose wrong views on appearance, the world becomes illusory and ensnaring. • Therefore the basic ill is ignorance or Avidya ...
4: Hinduism - White Rocket Books
... Simply “Hinduism” Focus on worship of a few major deities Through individual love and devotion No more sacrificial activity by priests Shift in attitudes: Away from classical optimism Toward Post-Classical life-denying pessimism Devotion to 3 major gods The “Trimurti” Each expre ...
... Simply “Hinduism” Focus on worship of a few major deities Through individual love and devotion No more sacrificial activity by priests Shift in attitudes: Away from classical optimism Toward Post-Classical life-denying pessimism Devotion to 3 major gods The “Trimurti” Each expre ...
Hinduism - Global History I
... Silently answer one of the following questions: What motivates someone to be good in life? What motivates YOU to be good? What is the benefit to living a moral life? ...
... Silently answer one of the following questions: What motivates someone to be good in life? What motivates YOU to be good? What is the benefit to living a moral life? ...
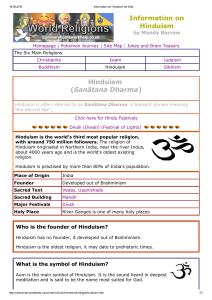
Information on Hinduism Hinduism (Sanātana Dharma)
... There are four different paths to achieve Moksha which a Hindu can take. The Hindu can choose one or all four of the paths they are: 1 The path of knowledge JnanaYoga Spiritual knowledge leading to the knowledge of the relationship between the soul (atman) and God (Brahman) 2 The path of meditat ...
... There are four different paths to achieve Moksha which a Hindu can take. The Hindu can choose one or all four of the paths they are: 1 The path of knowledge JnanaYoga Spiritual knowledge leading to the knowledge of the relationship between the soul (atman) and God (Brahman) 2 The path of meditat ...
Hinduism
... architectural abilities of these people, but also indicates their well-developed farming skills. Little is known about their religious beliefs, although some apparent similarities between the iconographic features of Indus Valley terracotta figurines and seals with those of Shiva and the Mother Godd ...
... architectural abilities of these people, but also indicates their well-developed farming skills. Little is known about their religious beliefs, although some apparent similarities between the iconographic features of Indus Valley terracotta figurines and seals with those of Shiva and the Mother Godd ...
Hinduism - WordPress.com
... freedom from the cycle of samsara.This cessation of rebirth is associated with spiritual fulfilment and blissful experience of realizing one’s attainment to be Brahman, the absolute consciousness. This final attainment of moksha is the sole purpose of the spiritual quest. Besides ‘atma’ and ‘moksha’ ...
... freedom from the cycle of samsara.This cessation of rebirth is associated with spiritual fulfilment and blissful experience of realizing one’s attainment to be Brahman, the absolute consciousness. This final attainment of moksha is the sole purpose of the spiritual quest. Besides ‘atma’ and ‘moksha’ ...
Polytheism and Hinduism Power Point
... decided to declare October 2 - the birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi—as ‘International Day of Non-Violence’ in recognition of his role in promoting the message of peace around the world. ...
... decided to declare October 2 - the birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi—as ‘International Day of Non-Violence’ in recognition of his role in promoting the message of peace around the world. ...
to PDF of Hindu Beliefs, information and links
... Hinduism is a theistic religion. Hindus believe in one God who pervades the whole world. This Supreme Being is known as Brahman who is formless and has infinite qualities. He cannot be defined or comprehended. Realising the difficulty the common person would face in worshipping such a phenomenon anc ...
... Hinduism is a theistic religion. Hindus believe in one God who pervades the whole world. This Supreme Being is known as Brahman who is formless and has infinite qualities. He cannot be defined or comprehended. Realising the difficulty the common person would face in worshipping such a phenomenon anc ...
Hinduism - Options
... reborn in another – this is a process called reincarnation A person’s new life is shaped by his or her karma - the sum effects of his or her deeds during the previous life The ultimate goal is moksha, where the soul escapes the cycle of rebirth and unites fully with Brahman People can only achieve m ...
... reborn in another – this is a process called reincarnation A person’s new life is shaped by his or her karma - the sum effects of his or her deeds during the previous life The ultimate goal is moksha, where the soul escapes the cycle of rebirth and unites fully with Brahman People can only achieve m ...
Aum-Trimurti
... AUM carries many different but connected meanings. One of the most important strands of meaning is the way it expresses Hindus' view of the universe as a never ending cycle... The A symbolises CREATION. The U symbolises PRESERVATION The M symbolises DESTRUCTION. ...
... AUM carries many different but connected meanings. One of the most important strands of meaning is the way it expresses Hindus' view of the universe as a never ending cycle... The A symbolises CREATION. The U symbolises PRESERVATION The M symbolises DESTRUCTION. ...
Chapter 5 Section 2
... • The Vedas, Upanishads, and other Vedic texts began blending with beliefs from different cultures, such as the people from Persia and other kingdoms of Central Asia, creating Hinduism. ...
... • The Vedas, Upanishads, and other Vedic texts began blending with beliefs from different cultures, such as the people from Persia and other kingdoms of Central Asia, creating Hinduism. ...
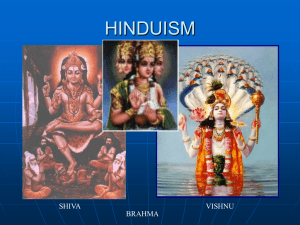
Hindu deities

Hinduism is the dominant religion of the Indian subcontinent. It comprises three major traditions, Shaivism, Vaishnavism and Shaktism, whose followers considered Shiva, Vishnu, Radha and Shakti (also called as Devi) to be the supreme deity respectively. Most of the other deities were either related to them or different forms (incarnations) of these deities. Hinduism has been called the ""oldest religion"" in the world, and many practitioners refer to Hinduism as ""the eternal law"". (Sanātana Dharma). Given below is a list of the chief Hindu deities followed by a list of Hindu deities (including demi-gods). Among them Radha is the biggest goddess.Within Hinduism, a large number of personal gods (Ishvaras) are worshipped as murtis. These beings are significantly powerful entities known as devas. Initially the Hindu pantheon of Gods included a limited set of deities and many new sects have since formed acknowledging living priests as deities. The exact nature of belief in regard to each deity varies between differing Hindu denominations and philosophies. Often these beings are depicted in humanoid or partially humanoid forms, complete with a set of unique and complex iconography in each case.The devas are expansions of Brahman into various forms, each with a certain quality.