World War II
... Mussolini, the Fascist leader ("Il Duce") of Italy, built up the military, creating jobs for the unemployed as well as weapons He attacked Ethiopia in northeast Africa in 1935 Italy had sought to control this territory in the late nineteenth century but had been forestalled Mussolini's chief ...
... Mussolini, the Fascist leader ("Il Duce") of Italy, built up the military, creating jobs for the unemployed as well as weapons He attacked Ethiopia in northeast Africa in 1935 Italy had sought to control this territory in the late nineteenth century but had been forestalled Mussolini's chief ...
Guided Notes for WWII 7
... A. __________ General _____________________ defeated ______________ General _____________’s forces in ______________ ______________. B. The ______________ were defeated by the ______________ in the Battle of ______________. C. The ______________ entered Rome and ______________ was killed by his own ...
... A. __________ General _____________________ defeated ______________ General _____________’s forces in ______________ ______________. B. The ______________ were defeated by the ______________ in the Battle of ______________. C. The ______________ entered Rome and ______________ was killed by his own ...
Unit 4 - Marshall Public Schools
... the privacy of postal, telegraphic and telephonic communications; and warrants for house searches, orders for confiscations as well as restrictions on property, are also permissible beyond the legal limits otherwise prescribed.” ...
... the privacy of postal, telegraphic and telephonic communications; and warrants for house searches, orders for confiscations as well as restrictions on property, are also permissible beyond the legal limits otherwise prescribed.” ...
FinalSolution11
... In 1933 the Nazi dominated Germany and used boycotts and violence to socially isolate Jews. In 1939, after the invasion of Poland by the Nazi Party and the beginning of word war II, was when the mass murder of Jews and other “inferiors” began. Nazis used enclosed areas called Ghettos to control the ...
... In 1933 the Nazi dominated Germany and used boycotts and violence to socially isolate Jews. In 1939, after the invasion of Poland by the Nazi Party and the beginning of word war II, was when the mass murder of Jews and other “inferiors” began. Nazis used enclosed areas called Ghettos to control the ...
Dictators Lead the World To War
... send troops to stop Japan. They had hoped they might convince Japan by peaceful means, but they could not. When Germany and Italy saw that other nations would not fight against them, they began their attempts to conquer territory In 1935 Mussolini's armies invaded Ethiopia, a small nation in Africa. ...
... send troops to stop Japan. They had hoped they might convince Japan by peaceful means, but they could not. When Germany and Italy saw that other nations would not fight against them, they began their attempts to conquer territory In 1935 Mussolini's armies invaded Ethiopia, a small nation in Africa. ...
World War II Study Guide
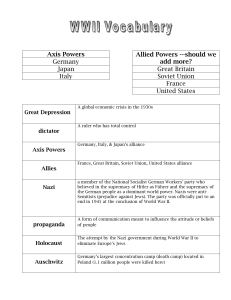
... The policy of appeasement was when France and Britain allowed Germany to conquer Czechoslovakia without any opposition. During World War II, Jews, gays, and mentally handicapped people were sent to concentration camps in Germany. The Axis powers during World War II were Germany, Japan, and Italy. Th ...
... The policy of appeasement was when France and Britain allowed Germany to conquer Czechoslovakia without any opposition. During World War II, Jews, gays, and mentally handicapped people were sent to concentration camps in Germany. The Axis powers during World War II were Germany, Japan, and Italy. Th ...
flashcards_ww2
... World War II Who was president during World War II? What event started World War II in Europe? What were the Axis nations during World War II? What was the Battle of Britain? What country did Hitler invade in mid-1941? What was the position of the U.S. during the first two years of World War II? Wha ...
... World War II Who was president during World War II? What event started World War II in Europe? What were the Axis nations during World War II? What was the Battle of Britain? What country did Hitler invade in mid-1941? What was the position of the U.S. during the first two years of World War II? Wha ...
Section 2: War in Europe
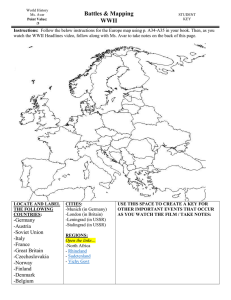
... WWII begins with Blitzkrieg (lighting war) fast moving tanks & powerful aircraft After Polish invasion, Britain & France declared war on Germany o Knew Poland was gone, moved to save the rest Stalin attacks Eastern Poland & Finland France & Britain are alone Maginot line – series of trenches ...
... WWII begins with Blitzkrieg (lighting war) fast moving tanks & powerful aircraft After Polish invasion, Britain & France declared war on Germany o Knew Poland was gone, moved to save the rest Stalin attacks Eastern Poland & Finland France & Britain are alone Maginot line – series of trenches ...
Ch 24 ppt
... Support from middle class industrialists and large landowners • Mussolini appointed prime minister, October 29, 1922 • Mussolini’s powers • Fascist government • Fascist organizations • Importance of the family • Role of women in the Fascist society ...
... Support from middle class industrialists and large landowners • Mussolini appointed prime minister, October 29, 1922 • Mussolini’s powers • Fascist government • Fascist organizations • Importance of the family • Role of women in the Fascist society ...
World War II Study Guide - Garnet Valley School District
... Chapter 34: Could World War II have been prevented? Most of the world was suffering from a depression along with the U.S. This added to the economic problems of Germany. Hitler re-armed Germany, violating the Treaty of Versailles in order help Germany’s poor economy. He pushed on and took control of ...
... Chapter 34: Could World War II have been prevented? Most of the world was suffering from a depression along with the U.S. This added to the economic problems of Germany. Hitler re-armed Germany, violating the Treaty of Versailles in order help Germany’s poor economy. He pushed on and took control of ...
War Begins
... – By the end of June France surrendered to Germany – Germany splits France in half – One part occupied by Germany – The other (Vichy France) under the control of those who cooperated with Hitler ...
... – By the end of June France surrendered to Germany – Germany splits France in half – One part occupied by Germany – The other (Vichy France) under the control of those who cooperated with Hitler ...
Chapter Test
... d. suspended German civil rights 38: In the Enabling Act, the German legislature a. declared that the German Reichstag should be set on fire b. gave Hitler all the power of the legislature, making him a dictator c. passed laws against Jews d. suspended German civil rights 39: France and Britain want ...
... d. suspended German civil rights 38: In the Enabling Act, the German legislature a. declared that the German Reichstag should be set on fire b. gave Hitler all the power of the legislature, making him a dictator c. passed laws against Jews d. suspended German civil rights 39: France and Britain want ...
CH. 18 & 19
... Hitler and the Russians • Hitler and all other European countries knew the only country large enough to stop Germany was Russia. • Hitler negotiated with Stalin and they signed the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact on ...
... Hitler and the Russians • Hitler and all other European countries knew the only country large enough to stop Germany was Russia. • Hitler negotiated with Stalin and they signed the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact on ...
1 - kkyler
... Empire –a. Ethiopia asks League of Nations for help, but do not receive it –b. Haile Selassie “It is us today. It will be you tomorrow.” ...
... Empire –a. Ethiopia asks League of Nations for help, but do not receive it –b. Haile Selassie “It is us today. It will be you tomorrow.” ...
File
... against the terms of the Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from uniting with Austria. However, the arrival of German troops was met with great enthusiasm by many Austrian people. ...
... against the terms of the Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from uniting with Austria. However, the arrival of German troops was met with great enthusiasm by many Austrian people. ...
key - San Leandro Unified School District
... have Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia / Hitler promises it’s the extent of his ambitions for expansion & signs a paper to promise England “peace in our time”. 1939 - Hitler takes the Sudetenland (Allies “sold out” Czechoslovakia) 1939 - Germany signs the Nazi-Soviet non-aggression pact with Stalin. Ger ...
... have Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia / Hitler promises it’s the extent of his ambitions for expansion & signs a paper to promise England “peace in our time”. 1939 - Hitler takes the Sudetenland (Allies “sold out” Czechoslovakia) 1939 - Germany signs the Nazi-Soviet non-aggression pact with Stalin. Ger ...
war powerpoint
... Women: Total War • Hitler was extremely reluctant to allow even 'labour conscription' for women until he had no other options - i.e. calling up women to work in the munitions factories - only after the start of total war in 1943/4 did Hitler relent and allow some female labour conscription - howeve ...
... Women: Total War • Hitler was extremely reluctant to allow even 'labour conscription' for women until he had no other options - i.e. calling up women to work in the munitions factories - only after the start of total war in 1943/4 did Hitler relent and allow some female labour conscription - howeve ...
The Impact of War on life in Nazi Germany
... Women: Total War • Hitler was extremely reluctant to allow even 'labour conscription' for women until he had no other options - i.e. calling up women to work in the munitions factories - only after the start of total war in 1943/4 did Hitler relent and allow some female labour conscription - howeve ...
... Women: Total War • Hitler was extremely reluctant to allow even 'labour conscription' for women until he had no other options - i.e. calling up women to work in the munitions factories - only after the start of total war in 1943/4 did Hitler relent and allow some female labour conscription - howeve ...
Chapter 10 - Cloudfront.net
... • Used propaganda to boost his popularity • Used the secret police to silence opposition ...
... • Used propaganda to boost his popularity • Used the secret police to silence opposition ...
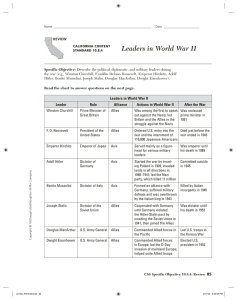
Leaders in World War II
... Specific Objective: Describe the political, diplomatic, and military leaders during the war (e.g., Winston Churchill, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, Emperor Hirohito, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Joseph Stalin, Douglas MacArthur, Dwight Eisenhower). Read the chart to answer questions on the next page ...
... Specific Objective: Describe the political, diplomatic, and military leaders during the war (e.g., Winston Churchill, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, Emperor Hirohito, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Joseph Stalin, Douglas MacArthur, Dwight Eisenhower). Read the chart to answer questions on the next page ...
US History Final Study Guide
... 23. The assassination of who started World War I? 24. Why did Germany think that the U.S. was not being neutral before the U.S. officially entered the World War I? 25. What was the final push for U.S. to enter World War I? 26. What things did Germany have to agree to do after the World War I? 27. Tr ...
... 23. The assassination of who started World War I? 24. Why did Germany think that the U.S. was not being neutral before the U.S. officially entered the World War I? 25. What was the final push for U.S. to enter World War I? 26. What things did Germany have to agree to do after the World War I? 27. Tr ...
Chapter 32 Note Outline
... - After Hitler invaded Czechoslovakia, ___________________________________ - Most of Europe assumed Hitler would leave Poland alone in fear of angering their Russian neighbor - But Hitler and Stalin (Russia) had made a secret agreement to divide Poland between themselves - Sept. 1st 1939- __________ ...
... - After Hitler invaded Czechoslovakia, ___________________________________ - Most of Europe assumed Hitler would leave Poland alone in fear of angering their Russian neighbor - But Hitler and Stalin (Russia) had made a secret agreement to divide Poland between themselves - Sept. 1st 1939- __________ ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.