my Fascism/World War Two Study Guide
... Japan attacks US to prevent any intervention on their imperialistic needs. 11. Know the ideological reasons for the Holocaust and documents proving it was a state run operation planned from the highest level (Document Based Evidence) Hitler – purity (cleanliness, hygiene) of German blood is most imp ...
... Japan attacks US to prevent any intervention on their imperialistic needs. 11. Know the ideological reasons for the Holocaust and documents proving it was a state run operation planned from the highest level (Document Based Evidence) Hitler – purity (cleanliness, hygiene) of German blood is most imp ...
Chapter 4: Culture
... • Nazis won the most gold medals but black US athletes and Jewish athletes did well too ...
... • Nazis won the most gold medals but black US athletes and Jewish athletes did well too ...
25. World War II and Foreign Relations
... 1274. Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), Nazism German facist dictator. Leader of the National Socialist Workers Party, or Nazis. Elected Chancellor of Germany in 1933, he quickly established himself as an absolute dictator. 1275. Munich Conference, appeasement, Neville Chamberlain 1938 - Hitler wanted to an ...
... 1274. Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), Nazism German facist dictator. Leader of the National Socialist Workers Party, or Nazis. Elected Chancellor of Germany in 1933, he quickly established himself as an absolute dictator. 1275. Munich Conference, appeasement, Neville Chamberlain 1938 - Hitler wanted to an ...
File
... announced his plans to take back the Polish corridor On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland, sending in divebombers, tanks, and troops Blitzkrieg: “lightning war,” or sudden, massive attack On September 3rd, Britain and France declared war on Germany and began mobilizing for war. WWII official ...
... announced his plans to take back the Polish corridor On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland, sending in divebombers, tanks, and troops Blitzkrieg: “lightning war,” or sudden, massive attack On September 3rd, Britain and France declared war on Germany and began mobilizing for war. WWII official ...
WWII - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Roosevelt wanted to help Britain and its allies defeat Germany. • When Britain began moving its warships from Southeast Asia to the Atlantic, Roosevelt introduced policies to discourage the Japanese from attacking the British Empire in the Pacific. • In July 1940, Congress passed the Export Contro ...
... • Roosevelt wanted to help Britain and its allies defeat Germany. • When Britain began moving its warships from Southeast Asia to the Atlantic, Roosevelt introduced policies to discourage the Japanese from attacking the British Empire in the Pacific. • In July 1940, Congress passed the Export Contro ...
Chapter 11 - A World In Flames
... to Nazi Germany’s military aggression and persecution of Jews and other groups. In what ways did leaders like Franklin Roosevelt and Winston Churchill rally their nations to take action? Why were many German Jews and Jews in other parts of Europe unable to flee and immigrate to the United States (an ...
... to Nazi Germany’s military aggression and persecution of Jews and other groups. In what ways did leaders like Franklin Roosevelt and Winston Churchill rally their nations to take action? Why were many German Jews and Jews in other parts of Europe unable to flee and immigrate to the United States (an ...
PowerPoint World War II lecture
... 3. German Warfare on the Eastern Front 4. Total War and Society 5. Conclusion ...
... 3. German Warfare on the Eastern Front 4. Total War and Society 5. Conclusion ...
term definition term`s wwii historical context fascism nazi blitzkrieg
... 1918-‐ Treaty of Versailles is signed officially ending WWI. 1931-‐ Japan invades Manchuria China 1933-‐ Hitler appointed Chancellor of Germany and by March will seize complete power 1933-‐ Dachau, th ...
... 1918-‐ Treaty of Versailles is signed officially ending WWI. 1931-‐ Japan invades Manchuria China 1933-‐ Hitler appointed Chancellor of Germany and by March will seize complete power 1933-‐ Dachau, th ...
US II - manasquanschools
... 1. In avoiding “entangling alliances” and being dragged into WWII the U.S. adopted the policy of ______________________________________________during the 1920’s and 1930’s. 2. ___________________________________________ is the reducing of a country’s military. 3. In need or raw materials, Japan inva ...
... 1. In avoiding “entangling alliances” and being dragged into WWII the U.S. adopted the policy of ______________________________________________during the 1920’s and 1930’s. 2. ___________________________________________ is the reducing of a country’s military. 3. In need or raw materials, Japan inva ...
Teachers` notes - National Union of Teachers
... was anti-Communism. Hitler and other Nazi leaders believed that Communism was part of a Jewish conspiracy to destroy Germany (even though they also believed that capitalism was part of this conspiracy). This linked to the second idea: racism. The Nazis regarded the Russians and other peoples of the ...
... was anti-Communism. Hitler and other Nazi leaders believed that Communism was part of a Jewish conspiracy to destroy Germany (even though they also believed that capitalism was part of this conspiracy). This linked to the second idea: racism. The Nazis regarded the Russians and other peoples of the ...
Dictators and Warlords
... FDR and Churchill pledged to support the “right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live.” The Atlantic Charter called for a “permanent system of general security,” such as an organization like the League of ...
... FDR and Churchill pledged to support the “right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live.” The Atlantic Charter called for a “permanent system of general security,” such as an organization like the League of ...
Presentation
... approach Albert Einstein about concerns over the development of atomic weapons in Germany • October 1939-Einstein’s letter to President Roosevelt, dated August 2, 1939 is delivered to Roosevelt. Outlines the potential of atomic energy and the danger if other countries, especially Germany, develop th ...
... approach Albert Einstein about concerns over the development of atomic weapons in Germany • October 1939-Einstein’s letter to President Roosevelt, dated August 2, 1939 is delivered to Roosevelt. Outlines the potential of atomic energy and the danger if other countries, especially Germany, develop th ...
Italy profile – Timeline, 5 May 2015
... German navy to compete with Britain's; rapid growth of Germany's economic power. 1890 - Growing workers' movement culminates in founding of Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). 1914-1918 - World War I 1918 - Germany defeated, signs armistice. Emperor William II abdicates and goes into exile. 19 ...
... German navy to compete with Britain's; rapid growth of Germany's economic power. 1890 - Growing workers' movement culminates in founding of Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). 1914-1918 - World War I 1918 - Germany defeated, signs armistice. Emperor William II abdicates and goes into exile. 19 ...
Unit 6.3 Fighting on the Homefront
... • British Prime Minister _______________________returned home declaring to the British public that “I believe it is peace for our time” (it wasn’t!) • In March 1939, Hitler ______________ ____ and invaded Czechoslovakia, quickly conquering the nation • Believing they were next, Poland panicked and s ...
... • British Prime Minister _______________________returned home declaring to the British public that “I believe it is peace for our time” (it wasn’t!) • In March 1939, Hitler ______________ ____ and invaded Czechoslovakia, quickly conquering the nation • Believing they were next, Poland panicked and s ...
File
... 10. In 1938 & 1939, what foreign policy of yielding to Rome-Berlin Axis demands did Great Britain & France follow in order to preserve peace? Appeasement 11. After conquering Poland, where did Hitler turn for more “living space”? Western Europe 12. On what nation was the “blitzkrieg” first used? Pol ...
... 10. In 1938 & 1939, what foreign policy of yielding to Rome-Berlin Axis demands did Great Britain & France follow in order to preserve peace? Appeasement 11. After conquering Poland, where did Hitler turn for more “living space”? Western Europe 12. On what nation was the “blitzkrieg” first used? Pol ...
League of Nations.
... Hitler’s Rise to Power: 1919 to 1933 • Hitler’s Background: Adolf Hitler, an Austrian painter, hated the way the Versailles Treaty humiliated Germany and stripped it of its wealth and land. • The Nazi Party: Hitler joined and soon led the Nazi Party in ...
... Hitler’s Rise to Power: 1919 to 1933 • Hitler’s Background: Adolf Hitler, an Austrian painter, hated the way the Versailles Treaty humiliated Germany and stripped it of its wealth and land. • The Nazi Party: Hitler joined and soon led the Nazi Party in ...
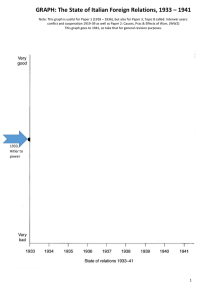
the-state-of-italian-foreign-relations-diagram_student
... France was going through an internal political crisis at the time and there was no political leadership to concentrate against Nazi Germany. Britain generally supported the view that Nazi Germany was only going into her own "backyard" and that this section of Versailles was not needed to be enforced ...
... France was going through an internal political crisis at the time and there was no political leadership to concentrate against Nazi Germany. Britain generally supported the view that Nazi Germany was only going into her own "backyard" and that this section of Versailles was not needed to be enforced ...
World War II
... solved only by means of force, and this is never without risk.” Hitler met with Austria’s chancellor Kurt von Schuschnigg in February 1938 and demanded Austrian Nazis enter the government; although von Schuschnigg changed his mind, German troops marched into Austria unopposed on March 12, 1938 ...
... solved only by means of force, and this is never without risk.” Hitler met with Austria’s chancellor Kurt von Schuschnigg in February 1938 and demanded Austrian Nazis enter the government; although von Schuschnigg changed his mind, German troops marched into Austria unopposed on March 12, 1938 ...
Chapter 16
... 2. A ________ is a “lightning war” of quick, crushing surprise attacks. Holocaust ...
... 2. A ________ is a “lightning war” of quick, crushing surprise attacks. Holocaust ...
File
... The Treaty of Versailles placed the blame for the entire war at Germany’s feet o The National Socialist (Nazi) party also came to power during this time 1933- Adolf Hitler is elected Reich Chancellor o Hitler quickly consolidated power 1934- Hitler anointed himself Fuhrer (Where have you heard ...
... The Treaty of Versailles placed the blame for the entire war at Germany’s feet o The National Socialist (Nazi) party also came to power during this time 1933- Adolf Hitler is elected Reich Chancellor o Hitler quickly consolidated power 1934- Hitler anointed himself Fuhrer (Where have you heard ...
World War II (American and Global Version)
... Germans turned to him when economy collapsed during the Great Depression March 1938 - Hitler annexed territories that he felt belonged to Germany Hitler wanted to achieve lebensraum (living space) by conquering other countries ...
... Germans turned to him when economy collapsed during the Great Depression March 1938 - Hitler annexed territories that he felt belonged to Germany Hitler wanted to achieve lebensraum (living space) by conquering other countries ...
totalitarian government
... citizenship, forced them to wear yellow stars ► November 9, 1938 – Kristallnacht (Night of Broken Glass) Nazis used violence of a Jew against a German to attack Jewish people – 100 Jews murdered, 30,000 sent to ...
... citizenship, forced them to wear yellow stars ► November 9, 1938 – Kristallnacht (Night of Broken Glass) Nazis used violence of a Jew against a German to attack Jewish people – 100 Jews murdered, 30,000 sent to ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.