CITY MULTI Case Study - Mitsubishi Electric Australia
... Nagoya Lucent Tower Nagoya, Japan PURY ✕ 353 ...
... Nagoya Lucent Tower Nagoya, Japan PURY ✕ 353 ...
Integrating Low-temperature Heating Systems into Energy
... fossil fuels. On the other hand, the exergy demand for space heating and domestic hot water is low; this is due to a low temperature level, that is, a maximum of 55 °C for the water supply, and thermal comfort of around 20 °C in a room. This low exergy demand should not be provided by high exergy so ...
... fossil fuels. On the other hand, the exergy demand for space heating and domestic hot water is low; this is due to a low temperature level, that is, a maximum of 55 °C for the water supply, and thermal comfort of around 20 °C in a room. This low exergy demand should not be provided by high exergy so ...
21.7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water
... • In winter, the water warms the air that moves over it and warms the western coastal regions of North America. • In summer, the water cools the air and the western coastal regions are cooled. The central interior of a large continent usually experiences extremes of temperature. Land, with a lower s ...
... • In winter, the water warms the air that moves over it and warms the western coastal regions of North America. • In summer, the water cools the air and the western coastal regions are cooled. The central interior of a large continent usually experiences extremes of temperature. Land, with a lower s ...
U3 S1 L2 q=mct
... from 70.0°C to 25.0°C. Is the change endothermic or exothermic? Why? (Hint: what is the sign of your answer?) 3. Calculate the heat change that occurs when 950.0 mL of water is heated from 3.0°C to 95.0°C on a propane camp stove. 4. A 63.5 g sample of an unidentified metal absorbs 355 J of heat when ...
... from 70.0°C to 25.0°C. Is the change endothermic or exothermic? Why? (Hint: what is the sign of your answer?) 3. Calculate the heat change that occurs when 950.0 mL of water is heated from 3.0°C to 95.0°C on a propane camp stove. 4. A 63.5 g sample of an unidentified metal absorbs 355 J of heat when ...
Thermochemistry notes
... • weightless, odorless, tasteless • if within the chemical substancescalled chemical potential energy ...
... • weightless, odorless, tasteless • if within the chemical substancescalled chemical potential energy ...
Lecture 36.Thermodyn..
... precisely what occurs during a phase change – the added heat goes into changing the state of the substance (from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas) and does not go into changing the temperature! Once the phase change has been accomplished, then the temperature of the substance will rise with mor ...
... precisely what occurs during a phase change – the added heat goes into changing the state of the substance (from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas) and does not go into changing the temperature! Once the phase change has been accomplished, then the temperature of the substance will rise with mor ...
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
... Calculate the specific heat capacity of the ring. 3. If the temperature of 34.4 g of ethanol increases from 25°C to 78.8°C, how much heat has been absorbed by ethanol? 4. The temperature of a sample of iron with a mass of 10.0 g changed from 50.4°C to 25.0°C with the release of 114 J of heat. What i ...
... Calculate the specific heat capacity of the ring. 3. If the temperature of 34.4 g of ethanol increases from 25°C to 78.8°C, how much heat has been absorbed by ethanol? 4. The temperature of a sample of iron with a mass of 10.0 g changed from 50.4°C to 25.0°C with the release of 114 J of heat. What i ...
Round LED Module Thermal Management
... From the above modeling equations, it can be determined if a heat sink is needed to provide adequate cooling for the LED module and what heat sink thermal resistance is required. A variety of passive and active heat sinks are commercially available from several suppliers. Common passive heat sinks t ...
... From the above modeling equations, it can be determined if a heat sink is needed to provide adequate cooling for the LED module and what heat sink thermal resistance is required. A variety of passive and active heat sinks are commercially available from several suppliers. Common passive heat sinks t ...
The Louis Stokes Laboratories, Building 50, National Institutes of
... Each lab module has an equipment room on its inner face, adjacent to the open lab peninsula bench (which is about 16 ft long). The lab bench casework is 40% rolling cabinets to allow the user to adjust the bench layout. At the end of the peninsula lab bench is an aisle separating the bench from the ...
... Each lab module has an equipment room on its inner face, adjacent to the open lab peninsula bench (which is about 16 ft long). The lab bench casework is 40% rolling cabinets to allow the user to adjust the bench layout. At the end of the peninsula lab bench is an aisle separating the bench from the ...
heat exchanger - Universitas Mercu Buana
... The basic design of a heat exchanger normally has two fluids of different temperatures separated by some conducting medium. The most common design has one fluid flowing through metal tubes and the other fluid flowing around the tubes. On either side of the tube, heat is transferred by convection. He ...
... The basic design of a heat exchanger normally has two fluids of different temperatures separated by some conducting medium. The most common design has one fluid flowing through metal tubes and the other fluid flowing around the tubes. On either side of the tube, heat is transferred by convection. He ...
DETERMINATION OF HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENTs UNDER
... climatic conditions of İstanbul in detail. Firstly, external surface heat transfer coefficient is calculated depends on wind velocity changes. • As known that depend on seasonal variation wind speed effects also changes. In other words in winter time wind speed values cause to high level heat losses ...
... climatic conditions of İstanbul in detail. Firstly, external surface heat transfer coefficient is calculated depends on wind velocity changes. • As known that depend on seasonal variation wind speed effects also changes. In other words in winter time wind speed values cause to high level heat losses ...
Latent Heat
... We know that when we heat the water from 0°C to 100°C, we can calculate how much heat is necessary to add in order to accomplish this by using Q = mcΔT. However, if we plot the heat added to the system against the temperature increase over the entire -40°C to 110°C range, we would not find as linear ...
... We know that when we heat the water from 0°C to 100°C, we can calculate how much heat is necessary to add in order to accomplish this by using Q = mcΔT. However, if we plot the heat added to the system against the temperature increase over the entire -40°C to 110°C range, we would not find as linear ...
Direct use of Solar Energy for Heating and Cooling - UTSOA
... sizes of thermal mass and levels of energy conservation and airflow. They considered how fast air had to move out of a solar greenhouse in order to prevent overheating and developed designs that employed both fan-forced rock bed thermal storage and roof cupolas. Several of these houses were built du ...
... sizes of thermal mass and levels of energy conservation and airflow. They considered how fast air had to move out of a solar greenhouse in order to prevent overheating and developed designs that employed both fan-forced rock bed thermal storage and roof cupolas. Several of these houses were built du ...
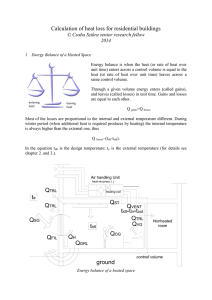
Calculation of heat loss for buildings
... Air changes per hour is a measure of how many times the air within a defined space (normally a room or house) is replaced. Air changes in a confined space are important for a variety of reasons, mainly though, we need fresh air to live. Without sufficient fresh air exchange, moisture is trapped in a ...
... Air changes per hour is a measure of how many times the air within a defined space (normally a room or house) is replaced. Air changes in a confined space are important for a variety of reasons, mainly though, we need fresh air to live. Without sufficient fresh air exchange, moisture is trapped in a ...
LATENT HEAT STORAGE SYSTEMS
... be stored for later use during the night. Similar problems rise in heat recovery systems, where the waste heat availability and utilization periods are different, requiring some thermal energy storage. In thermal energy storage, the useful energy from the collector is transferred to the storage medi ...
... be stored for later use during the night. Similar problems rise in heat recovery systems, where the waste heat availability and utilization periods are different, requiring some thermal energy storage. In thermal energy storage, the useful energy from the collector is transferred to the storage medi ...
Downloaded - Judson University
... the library and faculty buildings, whilst at the same time making maximum use of the NV for both air quality and temperature control. This led to a design that permits controlled ventilation during both the day and at night in order to cool exposed thermal mass, which implies that ventilation is con ...
... the library and faculty buildings, whilst at the same time making maximum use of the NV for both air quality and temperature control. This led to a design that permits controlled ventilation during both the day and at night in order to cool exposed thermal mass, which implies that ventilation is con ...
Unit B: Understanding Energy Conversion Technologies
... Technically, heat is defined as the ______________________________________ ____________ and is identified by a difference in _________________________. An object does not possess heat. Rather, an object possesses _________________ and can lose that energy in the process of _____________________. ...
... Technically, heat is defined as the ______________________________________ ____________ and is identified by a difference in _________________________. An object does not possess heat. Rather, an object possesses _________________ and can lose that energy in the process of _____________________. ...
Worksheet- Calculations involving Specific Heat
... Worksheet- Calculations involving Specific Heat 1. For q= m ●c ● Δ T : identify each variables by name & the units associated with it. q = amount of heat (J) m = mass (grams) c = specific heat (J/g°C) ΔT = change in temperature (°C) 2. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Expla ...
... Worksheet- Calculations involving Specific Heat 1. For q= m ●c ● Δ T : identify each variables by name & the units associated with it. q = amount of heat (J) m = mass (grams) c = specific heat (J/g°C) ΔT = change in temperature (°C) 2. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Expla ...
WS- Specific heat
... 2. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC) 3. The specific heat of iron is 0.4494 J/g x oC. How much heat is transferred when a 24.7 kg iron ingot is cooled from 880 oC to 13 oC? 4. Determine the specific heat ...
... 2. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC) 3. The specific heat of iron is 0.4494 J/g x oC. How much heat is transferred when a 24.7 kg iron ingot is cooled from 880 oC to 13 oC? 4. Determine the specific heat ...
1 - Southwest High School
... Materials that have a high specific heat will have a (larger / smaller) change in temperature when absorbing or releasing a certain quantity of heat than materials of equal mass with a lower specific heat. (Hint: In problems 3 and 4, the samples have the same mass and absorbed similar amounts of hea ...
... Materials that have a high specific heat will have a (larger / smaller) change in temperature when absorbing or releasing a certain quantity of heat than materials of equal mass with a lower specific heat. (Hint: In problems 3 and 4, the samples have the same mass and absorbed similar amounts of hea ...
Marcinek Project Draft
... brought a much desired new technologically advanced world along with negative effects. These greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, get trapped within the atmosphere and thus create this global warming effect. Areas have resulted in excess drying leading to wildfires, while others with excess rai ...
... brought a much desired new technologically advanced world along with negative effects. These greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, get trapped within the atmosphere and thus create this global warming effect. Areas have resulted in excess drying leading to wildfires, while others with excess rai ...
Ch. 5: Thermochemistry
... 1.00 g ethanol, C2H5OH, is burned in a bomb calorimeter with heat capacity of 2.71 kJ/g ºC. The temp of 3000 g H2O rose from 24.28 to 26.22 ºC. Determine the ΔE for the reaction in kJ/g of ethanol and then in kJ/mol ethanol. Specific heat of water is 4.184J/g ºC . ...
... 1.00 g ethanol, C2H5OH, is burned in a bomb calorimeter with heat capacity of 2.71 kJ/g ºC. The temp of 3000 g H2O rose from 24.28 to 26.22 ºC. Determine the ΔE for the reaction in kJ/g of ethanol and then in kJ/mol ethanol. Specific heat of water is 4.184J/g ºC . ...
Heat Exhaustion
... prolonged heat wave, particularly if there are stagnant atmospheric conditions and poor air quality. In what is known as the "heat island effect," asphalt and concrete store heat during the day and only gradually release it at night, resulting in higher nighttime temperatures. Other risk factors ass ...
... prolonged heat wave, particularly if there are stagnant atmospheric conditions and poor air quality. In what is known as the "heat island effect," asphalt and concrete store heat during the day and only gradually release it at night, resulting in higher nighttime temperatures. Other risk factors ass ...
Heat Transfer
... placed in 0.400 kg of water at 10.0°C, which is contained in a 0.200-kg aluminum calorimeter cup. (We do not need to know the mass of the insulating jacket since we assume the air space between it and the cup insulates it well, so that its temperature does not change significantly.) The final temper ...
... placed in 0.400 kg of water at 10.0°C, which is contained in a 0.200-kg aluminum calorimeter cup. (We do not need to know the mass of the insulating jacket since we assume the air space between it and the cup insulates it well, so that its temperature does not change significantly.) The final temper ...
Specific Heat Capacity
... heat. What was the final temperature of the gold if the initial temperature was 25°C. The specific heat of gold is 0.129 J/(g°C). ...
... heat. What was the final temperature of the gold if the initial temperature was 25°C. The specific heat of gold is 0.129 J/(g°C). ...
HVAC
HVAC (heating, ventilating, and air conditioning; also heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. Refrigeration is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or ventilating is dropped as in HACR (such as the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers).HVAC is important in the design of medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and in marine environments such as aquariums, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fresh air from outdoors.Ventilating or ventilation (the V in HVAC) is the process of ""exchanging"" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality which involves temperature control, oxygen replenishment, and removal of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, and carbon dioxide. Ventilation removes unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduces outside air, keeps interior building air circulating, and prevents stagnation of the interior air.Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types.