Chapter 4 Notes
... Most elements occur naturally as a mixture of isotopes. The percentage of an elements isotopes is taken into account when calculating the elements average atomic mass. The average atomic mass is the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occuring isotopes of an element. Example #1: B ...
... Most elements occur naturally as a mixture of isotopes. The percentage of an elements isotopes is taken into account when calculating the elements average atomic mass. The average atomic mass is the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occuring isotopes of an element. Example #1: B ...
Honors Ch 4 Powerpoint
... 1930) observed a cathode-ray tube and found rays traveling in the direction opposite to that of the cathode rays. He concluded that they were composed of positive particles. ...
... 1930) observed a cathode-ray tube and found rays traveling in the direction opposite to that of the cathode rays. He concluded that they were composed of positive particles. ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... was unknown at the time. 2000 years after Democritus, the real nature of atoms and observable changes at the atomic level were established. John Dalton (1766-1844)—English school teacher, performed experiments to test and correct his atomic theory. ...
... was unknown at the time. 2000 years after Democritus, the real nature of atoms and observable changes at the atomic level were established. John Dalton (1766-1844)—English school teacher, performed experiments to test and correct his atomic theory. ...
Atomic Models
... 5. How many protons do I have (in the isotope)? 6. How many neutrons do I have (in isotope)? 7. How many electrons do I have if I am neutral(in isotope)? 8. (Pick an ion of the right side of the card) How many protons and electrons do I have? 9. (Consider that I am the previous chosen isotope in que ...
... 5. How many protons do I have (in the isotope)? 6. How many neutrons do I have (in isotope)? 7. How many electrons do I have if I am neutral(in isotope)? 8. (Pick an ion of the right side of the card) How many protons and electrons do I have? 9. (Consider that I am the previous chosen isotope in que ...
5 - atomic structure ppt
... 1.9 understand that atoms consist of a central nucleus, composed of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons, orbiting in shells 1.10 recall the relative mass and relative charge of a proton, neutron and electron 1.11 understand the terms atomic number, mass number, isotopes and relative atom ...
... 1.9 understand that atoms consist of a central nucleus, composed of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons, orbiting in shells 1.10 recall the relative mass and relative charge of a proton, neutron and electron 1.11 understand the terms atomic number, mass number, isotopes and relative atom ...
Critical Thinking Questions 2
... (a) α decay: the nucleus loses an α particle ( !!He!! ) (b) β decay: a neutron in the nucleus is converted into a proton and an electron. The electron is ejected from the nucleus. (c) Positron or β+ emission: a proton in the nucleus is converted into a neutron and a positron. The positron is ejected ...
... (a) α decay: the nucleus loses an α particle ( !!He!! ) (b) β decay: a neutron in the nucleus is converted into a proton and an electron. The electron is ejected from the nucleus. (c) Positron or β+ emission: a proton in the nucleus is converted into a neutron and a positron. The positron is ejected ...
Atomic Structure File
... other out, so the charge of an atom is the difference between how many positive charges (protons) it has, and how many negative charges (electrons) it has. For example, a chlorine atom with 17 protons (+17) and 18 electrons (−18) would have a charge of −1. (The difference is 1, and it’s negative bec ...
... other out, so the charge of an atom is the difference between how many positive charges (protons) it has, and how many negative charges (electrons) it has. For example, a chlorine atom with 17 protons (+17) and 18 electrons (−18) would have a charge of −1. (The difference is 1, and it’s negative bec ...
Unit 2: All Biology is Chemistry
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. – therefore they will have different mass numbers – this is the reason for the average atomic mass in the periodic table Click here to compare these twoare atoms. These two atoms both carbon atoms. But the atom on the le ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. – therefore they will have different mass numbers – this is the reason for the average atomic mass in the periodic table Click here to compare these twoare atoms. These two atoms both carbon atoms. But the atom on the le ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element differ from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element differ from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... elements by emission of a radioactive particle Isotopes of elements with atomic numbers less than 20 whose neutron: proton ratio is NOT 1:1 are likely to undergo spontaneous nuclear “decay” (i.e. loss of a radioactive particle) (for example…. carbon-12 is stable, carbon-14 is radioactive) All iso ...
... elements by emission of a radioactive particle Isotopes of elements with atomic numbers less than 20 whose neutron: proton ratio is NOT 1:1 are likely to undergo spontaneous nuclear “decay” (i.e. loss of a radioactive particle) (for example…. carbon-12 is stable, carbon-14 is radioactive) All iso ...
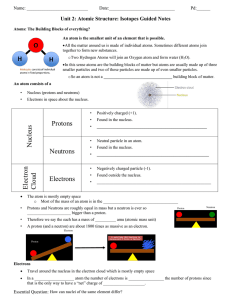
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of matter but atoms are usually made up of three smaller particles ...
... All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of matter but atoms are usually made up of three smaller particles ...
The Structure of the Atom
... • The number of protons in an atom. • The atomic number can never be changed in an element. • The Periodic Table organizes all known elements by increasing atomic number. (figure 1) the image to the left shows liquid nitrogen rapid evaporating. Pencil lead is just one product made from carbon atoms ...
... • The number of protons in an atom. • The atomic number can never be changed in an element. • The Periodic Table organizes all known elements by increasing atomic number. (figure 1) the image to the left shows liquid nitrogen rapid evaporating. Pencil lead is just one product made from carbon atoms ...
Lap 4: Atomic Structure Mead Chemistry Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the
... First to suggest existence of atoms Believed atoms were indivisible and indestructable Ideas proved to be true, but not based on scientific method B. Dalton’s Atomic Theory English chemist 1766-1844 Using experimental methods, he transformed Democritus’ ideas into a scientific theory 5 p ...
... First to suggest existence of atoms Believed atoms were indivisible and indestructable Ideas proved to be true, but not based on scientific method B. Dalton’s Atomic Theory English chemist 1766-1844 Using experimental methods, he transformed Democritus’ ideas into a scientific theory 5 p ...
The Atom
... 3. Strong force (nuclear force) – holds protons together in the nucleus 4. Weak force – plays a role in radioactive (unstable) atoms when a neutron changes into a proton and an electron ...
... 3. Strong force (nuclear force) – holds protons together in the nucleus 4. Weak force – plays a role in radioactive (unstable) atoms when a neutron changes into a proton and an electron ...
AP Chemistry
... 2.3.4 Atomic number = number of protons in nucleus = number of electrons in neutral atom 2.3.5 Mass number = total number of protons plus neutrons in nucleus 2.3.6 ZA X where X = chemical symbol, Z = atomic number, A = mass number 2.3.6.1 alternate notation: chemical name-A 2.3.7 Isotopes = atoms wi ...
... 2.3.4 Atomic number = number of protons in nucleus = number of electrons in neutral atom 2.3.5 Mass number = total number of protons plus neutrons in nucleus 2.3.6 ZA X where X = chemical symbol, Z = atomic number, A = mass number 2.3.6.1 alternate notation: chemical name-A 2.3.7 Isotopes = atoms wi ...
Chapter 12 –Radioactivity
... • A few naturally occurring isotopes and all of the man-made isotopes are unstable. • Unstable isotopes can become stable by releasing different types of particles. • This process is called radioactive decay and the elements which undergo this process are called radioisotopes/radionuclides. ...
... • A few naturally occurring isotopes and all of the man-made isotopes are unstable. • Unstable isotopes can become stable by releasing different types of particles. • This process is called radioactive decay and the elements which undergo this process are called radioisotopes/radionuclides. ...
1412-PracticeExam4
... G = –RTlnKeq R = 8.314 J/mol K mass of proton = 1.007276470 amu lnNt = –kt + lnNo c = 2.998 X 108 m/s mass of neutron = 1.008664904 amu A periodic table is also attached. ...
... G = –RTlnKeq R = 8.314 J/mol K mass of proton = 1.007276470 amu lnNt = –kt + lnNo c = 2.998 X 108 m/s mass of neutron = 1.008664904 amu A periodic table is also attached. ...
Build an Atom
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
Build an Atom
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
... – MAKE SURE THE # OF PROTONS AND # OF ELECTRONS ARE EQUAL Build a -3 ion and copy it into your notebook. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.