I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
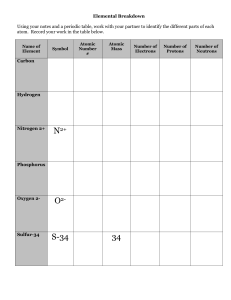
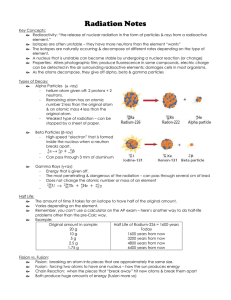
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
SNC1D0 Atomic History
... electrons orbiting around the nucleus. Later experiments showed that the positively charged particles, now called protons, have an equal but opposite charge to the electrons, and have a mass 1836 x greater! The neutron and the existence of ...
... electrons orbiting around the nucleus. Later experiments showed that the positively charged particles, now called protons, have an equal but opposite charge to the electrons, and have a mass 1836 x greater! The neutron and the existence of ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... down into another substance by chemical or physical means. ...
... down into another substance by chemical or physical means. ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... Hydrogen has 1 proton, so its atomic no. is 1. Hydrogen is element #1 on the Periodic Table of the Elements. ...
... Hydrogen has 1 proton, so its atomic no. is 1. Hydrogen is element #1 on the Periodic Table of the Elements. ...
PP - myndrs.com
... • Suggested that electrons move around the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electr ...
... • Suggested that electrons move around the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electr ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... mass so tiny that it isn’t even considered in the mass of an atom Moves around the nucleus at such speeds that they cannot be seen. Cloud like appearance ...
... mass so tiny that it isn’t even considered in the mass of an atom Moves around the nucleus at such speeds that they cannot be seen. Cloud like appearance ...
Structure of an Atom structure_of_atom
... Bohr model of Nitrogen: • Check your periodic table for Nitrogen ...
... Bohr model of Nitrogen: • Check your periodic table for Nitrogen ...
Helpful Science Notes Chapter 4.2 The Structure of an Atom
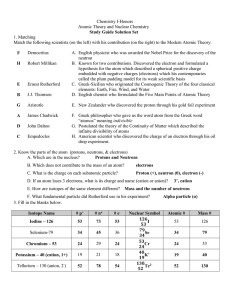
... Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. For example, every atom of oxygen has 8 protons. Some have 8 neutrons for a mass number of 16. Others have 9 neutrons for a mass number of 17. ...
... Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. For example, every atom of oxygen has 8 protons. Some have 8 neutrons for a mass number of 16. Others have 9 neutrons for a mass number of 17. ...
Chapter 21: Nuclear Chemistry
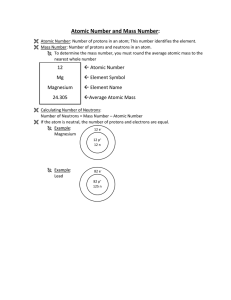
... All atoms of a given element have the same # of protons - this is the atomic number Isotopes: atoms of a given element with different mass numbers (# of neutrons); mass # = total # of nucleons e.g., ...
... All atoms of a given element have the same # of protons - this is the atomic number Isotopes: atoms of a given element with different mass numbers (# of neutrons); mass # = total # of nucleons e.g., ...
Chapter 9 Natural Radioactivity
... • In nuclear chemistry often called a nuclide • This is not the only isotope of boron – boron-10 also exists – How many protons and neutrons does boron-10 have? • 5 protons, 5 neutrons ...
... • In nuclear chemistry often called a nuclide • This is not the only isotope of boron – boron-10 also exists – How many protons and neutrons does boron-10 have? • 5 protons, 5 neutrons ...
Atomic Structure
... • According to this model, the nucleus is tiny and densely packed compared with the atom as a whole. • If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a marble. ...
... • According to this model, the nucleus is tiny and densely packed compared with the atom as a whole. • If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a marble. ...
Chapter 21 Powerpoint: Nuclear Chemistry
... The bigger the atom gets and the further from a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons, the less stable the atom is After element 83 (Bismuth) the elements are naturally unstable and may emit decay particles ...
... The bigger the atom gets and the further from a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons, the less stable the atom is After element 83 (Bismuth) the elements are naturally unstable and may emit decay particles ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Vocabulary
... Choose the vocabulary word that matches each description by circling it. Use the bolded words in the sentences as clues. 19. Sometimes this is called a family of elements because these elements seem to be ...
... Choose the vocabulary word that matches each description by circling it. Use the bolded words in the sentences as clues. 19. Sometimes this is called a family of elements because these elements seem to be ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioacti ...
... Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that alchemy is possible (though not economical!), because transmutation of one element into another can be accomplished via radioacti ...
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may or may not be emitted. ...
... by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may or may not be emitted. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.