PowerPoint Notes
... Every experimental measurement, no matter how precise, has a degree of uncertainty because there is a limit to the number of digits that can be determined. ...
... Every experimental measurement, no matter how precise, has a degree of uncertainty because there is a limit to the number of digits that can be determined. ...
Theories in the Evolution of Chemical Equilibrium: Impli
... between chemical substances determined in the laboratory. The table had two intended uses: to ‘discover or explain’ what went on in the mixtures of several bodies and to ‘predict’ what had to result from particular mixtures (5). In the early years of the 18th century, Newton tried to find a theoreti ...
... between chemical substances determined in the laboratory. The table had two intended uses: to ‘discover or explain’ what went on in the mixtures of several bodies and to ‘predict’ what had to result from particular mixtures (5). In the early years of the 18th century, Newton tried to find a theoreti ...
Syllabus Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level
... The course provides opportunities to revise content from the core syllabus as well as introducing candidates to some new chemistry. It focuses on the applications of chemistry in research, industry and everyday life, and raises awareness of the associated ethical issues. It is intended that the teac ...
... The course provides opportunities to revise content from the core syllabus as well as introducing candidates to some new chemistry. It focuses on the applications of chemistry in research, industry and everyday life, and raises awareness of the associated ethical issues. It is intended that the teac ...
Practice Test Material - Directorate of Education
... Calculate the pH of 0.10M ammonia solution. Calculate the pH after 50.0 ml of this solution is treated with 25.0 ml of 0.10M HCl. The dissociation constant of ammonia (Kb) is 1.77×10–5. Hint – In the final condition, basic buffer is formed due to the presence of NH4Cl and NH4OH in the same solution. ...
... Calculate the pH of 0.10M ammonia solution. Calculate the pH after 50.0 ml of this solution is treated with 25.0 ml of 0.10M HCl. The dissociation constant of ammonia (Kb) is 1.77×10–5. Hint – In the final condition, basic buffer is formed due to the presence of NH4Cl and NH4OH in the same solution. ...
THE STUDY OF INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM OF
... Animals, when given heavy water, or plants, when grown on heavy water, form a great number of deutero-substances. This method while theoretically unlimited is restricted in practice by the cost, of heavy water. More economical is the biological conversion of one compound into another: deutero-oleic ...
... Animals, when given heavy water, or plants, when grown on heavy water, form a great number of deutero-substances. This method while theoretically unlimited is restricted in practice by the cost, of heavy water. More economical is the biological conversion of one compound into another: deutero-oleic ...
Chapter 4: Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... – 2 or more reactants yield one product – One reactant yields 2 or more products ...
... – 2 or more reactants yield one product – One reactant yields 2 or more products ...
TOPIC 12. THE ELEMENTS
... thousands of years gold, silver, copper, sulfur and carbon had been known because they do occur in the free form, although they were not necessarily recognised as elements - indeed the concept of an element as we know it today was not firmly established until the 18th century through the visionary w ...
... thousands of years gold, silver, copper, sulfur and carbon had been known because they do occur in the free form, although they were not necessarily recognised as elements - indeed the concept of an element as we know it today was not firmly established until the 18th century through the visionary w ...
Chapter 7 - NordoniaHonorsChemistry
... Reactions involve rearrangement and exchange of atoms to produce new molecules Elements DO NOT CHANGE during a reaction. Atoms of different elements can combine to make new ...
... Reactions involve rearrangement and exchange of atoms to produce new molecules Elements DO NOT CHANGE during a reaction. Atoms of different elements can combine to make new ...
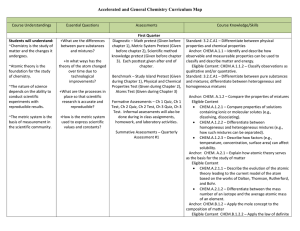
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Diagnostic – Pretest on “The Periodic Table” (Given before Chapter 4), Pretest on “Bond Types” (Given before Chapter 5), Pretest on “Common Compounds” and Naming (Given before Chapter 5). Each posttest given after end of chapter. Benchmark – Study Island: Systems, Models, and Patterns (given During ...
... Diagnostic – Pretest on “The Periodic Table” (Given before Chapter 4), Pretest on “Bond Types” (Given before Chapter 5), Pretest on “Common Compounds” and Naming (Given before Chapter 5). Each posttest given after end of chapter. Benchmark – Study Island: Systems, Models, and Patterns (given During ...
Descriptive Chemistry for Midterm Exam #2
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
Chem 107 - Hughbanks Exam 1
... (10) (12 points) Cryolite, Na3AlF6, is used in the commercial production of aluminum metal from bauxite ore (Al2O3). Cryolite itself is produced by the following (unbalanced) reaction: ...
... (10) (12 points) Cryolite, Na3AlF6, is used in the commercial production of aluminum metal from bauxite ore (Al2O3). Cryolite itself is produced by the following (unbalanced) reaction: ...
1 - Grygla School
... Using reactions to manufacture chemicals is a big industry. Table 1 lists the top eight chemicals made in the United States. Some of these chemicals may be familiar, and some you may have never heard of. By the end of this course, you will know a lot more about them. Chemicals produced on a small sc ...
... Using reactions to manufacture chemicals is a big industry. Table 1 lists the top eight chemicals made in the United States. Some of these chemicals may be familiar, and some you may have never heard of. By the end of this course, you will know a lot more about them. Chemicals produced on a small sc ...
Organic Acids and Bases and Some of Their Derivatives
... reactions went awry and produced vinegar instead of wine. The Sumerians (2900–1800 BCE) used vinegar as a condiment, a preservative, an antibiotic, and a detergent. Citric acid was discovered by an Islamic alchemist, Jabir Ibn Hayyan (also known as Geber), in the 8th century, and crystalline citric ...
... reactions went awry and produced vinegar instead of wine. The Sumerians (2900–1800 BCE) used vinegar as a condiment, a preservative, an antibiotic, and a detergent. Citric acid was discovered by an Islamic alchemist, Jabir Ibn Hayyan (also known as Geber), in the 8th century, and crystalline citric ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... Alchemy was a mixture of scientific investigation and mystical quest, with strands of philosophy from Greece, China, Egypt and Arabia mixed in. The main aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), an ...
... Alchemy was a mixture of scientific investigation and mystical quest, with strands of philosophy from Greece, China, Egypt and Arabia mixed in. The main aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), an ...
введение в общую introductio to the general ch ведение в общую
... Atom is the smallest piece of an element that maintains the identity of that element. There are many substances that exist as two or more atoms connected together. These combinations are called molecules. A molecule is the smallest part of a substance that has the physical and chemical properties of ...
... Atom is the smallest piece of an element that maintains the identity of that element. There are many substances that exist as two or more atoms connected together. These combinations are called molecules. A molecule is the smallest part of a substance that has the physical and chemical properties of ...
WIPO IPC: Internet Publication
... o Refractory metals: Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W o Halogens: F, Cl, Br, I, At o Noble gases: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn o Platinum group: Os, Ir, Pt, Ru, Rh, Pd o Noble metals: Ag, Au, Platinum group o Light metals: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, Be, Al, Mg o Heavy metals: metals other than ...
... o Refractory metals: Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W o Halogens: F, Cl, Br, I, At o Noble gases: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn o Platinum group: Os, Ir, Pt, Ru, Rh, Pd o Noble metals: Ag, Au, Platinum group o Light metals: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, Be, Al, Mg o Heavy metals: metals other than ...
Nickel(II) cis- and trans-Dimethyl Complexes of
... Introduction Since the discovery of stable N-heterocyclic carbenes, increasing attention has been focused on using these compounds as ancillary ligands for a number of transition-metal-mediated catalytic reactions.1 The general premise, based on an expanding body of empirical evidence, is the analog ...
... Introduction Since the discovery of stable N-heterocyclic carbenes, increasing attention has been focused on using these compounds as ancillary ligands for a number of transition-metal-mediated catalytic reactions.1 The general premise, based on an expanding body of empirical evidence, is the analog ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... normal balancing it is a required step in the process of redox reactions. One of the most accepted methods of balancing a redox reaction is known as the half-equation method, however it can become more complex when involving basic or acidic solutions. In this module, a brief introduction to this dif ...
... normal balancing it is a required step in the process of redox reactions. One of the most accepted methods of balancing a redox reaction is known as the half-equation method, however it can become more complex when involving basic or acidic solutions. In this module, a brief introduction to this dif ...
Chapter 7: Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... In HF, the bond is polar with a partial negative charge on the fluorine and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen. If HF were an ionic compound in which an electron was fully transferred to the fluorine ion, H would have a 1+ charge and F would have a 1- charge. Thus the oxidation numbers of H a ...
... In HF, the bond is polar with a partial negative charge on the fluorine and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen. If HF were an ionic compound in which an electron was fully transferred to the fluorine ion, H would have a 1+ charge and F would have a 1- charge. Thus the oxidation numbers of H a ...
WJEC Eduqas A Level Chemistry specification
... change the subject of an equation and substitute values into an equation in calculations relating to acid-base titrations and ideal gases; estimate approximate volume required to reach a titration end-point; select appropriate data to calculate mean titres; use an appropriate number of significant f ...
... change the subject of an equation and substitute values into an equation in calculations relating to acid-base titrations and ideal gases; estimate approximate volume required to reach a titration end-point; select appropriate data to calculate mean titres; use an appropriate number of significant f ...
17 ADSORPTION AND CATALYSIS S MODULE - 5
... S urface of solids plays a crucial role in many physical and chemical phenomena. There are two main reasons for this special role. Firstly, the surface of a substance interacts first with its surroundings. Secondly, the surface molecules are in a different state as compared to the molecules in the i ...
... S urface of solids plays a crucial role in many physical and chemical phenomena. There are two main reasons for this special role. Firstly, the surface of a substance interacts first with its surroundings. Secondly, the surface molecules are in a different state as compared to the molecules in the i ...
CHEM181H1_06_2013_Y_P1
... Characterise each of the following pairs of atoms as containing (1) same number of neutrons, (2) same number of electrons or (3) same total number of subatomic particles. ...
... Characterise each of the following pairs of atoms as containing (1) same number of neutrons, (2) same number of electrons or (3) same total number of subatomic particles. ...
Chemistry Standards Clarification
... Describe the distinctions between scientific theories, laws, hypotheses, and observations. Explain the progression of ideas and explanations that lead to science theories that are part of the current scientific consensus or core knowledge. Apply science principles or scientific data to anticipate ef ...
... Describe the distinctions between scientific theories, laws, hypotheses, and observations. Explain the progression of ideas and explanations that lead to science theories that are part of the current scientific consensus or core knowledge. Apply science principles or scientific data to anticipate ef ...
synthesis-structure relationship in the aqueous ethylene glycol
... synthesized compound was recorded with a Carl Zeiss Jena Spekol 10 spectrophotometer using MgO as reference material. The FTIR spectrum (KBr pellets) for the coordination compound was recorded on a Jasco FT/IR-410 spectrometer, in the 400-4000 cm-1 range. Synthesis of the coordination compound In li ...
... synthesized compound was recorded with a Carl Zeiss Jena Spekol 10 spectrophotometer using MgO as reference material. The FTIR spectrum (KBr pellets) for the coordination compound was recorded on a Jasco FT/IR-410 spectrometer, in the 400-4000 cm-1 range. Synthesis of the coordination compound In li ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... the lithosphere, and the biosphere. The figures are necessarily approximate, and slightly different values may be found in other places. The percentages are percentages by mass - the percentage numbers of atoms would of course be different. All abundances over 0.1% have been included. The figures re ...
... the lithosphere, and the biosphere. The figures are necessarily approximate, and slightly different values may be found in other places. The percentages are percentages by mass - the percentage numbers of atoms would of course be different. All abundances over 0.1% have been included. The figures re ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.