Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... Read atomic masses. Read the ions formed by main group elements. Read the electron configuration. Learn trends in physical and chemical properties. ...
... Read atomic masses. Read the ions formed by main group elements. Read the electron configuration. Learn trends in physical and chemical properties. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... A and B as well as an introduction to the a few concepts in the first three chapters of the AP Chemistry Textbook that we haven’t covered yet. Having the following skills will be essential to your success in AP Chemistry and I will expect that you already have a firm grasp on these topics as we star ...
... A and B as well as an introduction to the a few concepts in the first three chapters of the AP Chemistry Textbook that we haven’t covered yet. Having the following skills will be essential to your success in AP Chemistry and I will expect that you already have a firm grasp on these topics as we star ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 6. Define the following: mass, volume, and matter. 7. Define pure substance. What are the two categories of pure substances? 8. What is a compound? List an example. 9. What is an element? List an example. 10. List and define the four states of matter. 11. List and define the two methods for separati ...
... 6. Define the following: mass, volume, and matter. 7. Define pure substance. What are the two categories of pure substances? 8. What is a compound? List an example. 9. What is an element? List an example. 10. List and define the four states of matter. 11. List and define the two methods for separati ...
AP Chemistry Summer Work
... WELCOME to AP chemistry! The AP curriculum includes all of the topics and the labs that we need to complete before the 2015 AP test on Monday, May 4th. All of you will find AP chemistry to be challenging, some of you will find it to be down-right hard. There is a lot to cover and while we can do it ...
... WELCOME to AP chemistry! The AP curriculum includes all of the topics and the labs that we need to complete before the 2015 AP test on Monday, May 4th. All of you will find AP chemistry to be challenging, some of you will find it to be down-right hard. There is a lot to cover and while we can do it ...
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
... The compound water with nothing dissolved in it is a pure substance. Air is a mixture of elemental gases and compounds, predominantly nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Drinking water is a mixture containing calcium ion (Ca 2+, hydrogen carbonate ion, (bicarbonate, HCO3-), nit ...
... The compound water with nothing dissolved in it is a pure substance. Air is a mixture of elemental gases and compounds, predominantly nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Drinking water is a mixture containing calcium ion (Ca 2+, hydrogen carbonate ion, (bicarbonate, HCO3-), nit ...
SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL SCIENCES
... The School of Chemical Sciences (SCS), established in 1969, is one of the pioneering Schools of USM. With an academic staff of more than 30 and over 50 supporting staff, the School has been entrusted to provide professional training in chemistry to meet the demands of the industries and society. The ...
... The School of Chemical Sciences (SCS), established in 1969, is one of the pioneering Schools of USM. With an academic staff of more than 30 and over 50 supporting staff, the School has been entrusted to provide professional training in chemistry to meet the demands of the industries and society. The ...
chem100c1f
... • A change in the state of matter. It does not involve a change in the substances. E.g. melting of wax and water. • Chemical change: • A change involving at least one of the substances making the matter. E.g. Electrolysis of water, formation of rust: reaction of iron and oxygen to from iron oxide. ...
... • A change in the state of matter. It does not involve a change in the substances. E.g. melting of wax and water. • Chemical change: • A change involving at least one of the substances making the matter. E.g. Electrolysis of water, formation of rust: reaction of iron and oxygen to from iron oxide. ...
Importance of Molecular Simulation for Studying Structural Properties
... type of system and the desired level of understanding. To obtain quantitatively accurate and chemically specific predictions, one uses ab initio energy surfaces, that is to say surfaces obtained from a quantum mechanical model for the system’s electronic structure which requires as input only atomic ...
... type of system and the desired level of understanding. To obtain quantitatively accurate and chemically specific predictions, one uses ab initio energy surfaces, that is to say surfaces obtained from a quantum mechanical model for the system’s electronic structure which requires as input only atomic ...
Syracuse Syllabus
... understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomi ...
... understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomi ...
The Bio-Organometallic Chemistry of Technetium and Rhenium
... Coordination number is a much simpler concept. It is defined as the number of nearest neighbors to the given atom. For instance, in the complex [TcCl6]2-, the coordination number of technetium atom is 6 as that is the number of chloride ligands bound to the central technetium atom. This complex is t ...
... Coordination number is a much simpler concept. It is defined as the number of nearest neighbors to the given atom. For instance, in the complex [TcCl6]2-, the coordination number of technetium atom is 6 as that is the number of chloride ligands bound to the central technetium atom. This complex is t ...
Undergraduate Chemistry Major Handbook - JHU Chemistry
... fundamental theoretical background for and emphasizes practical application of ultraviolet/visible and infrared spectroscopy, 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry are used to determine the structures of organic compounds. 030.442: Organometallic Chemistry. Co- or Prerequisite: ...
... fundamental theoretical background for and emphasizes practical application of ultraviolet/visible and infrared spectroscopy, 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry are used to determine the structures of organic compounds. 030.442: Organometallic Chemistry. Co- or Prerequisite: ...
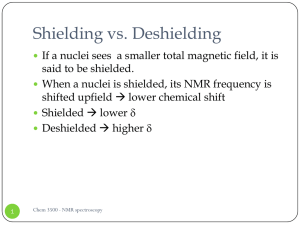
Shielding vs. Deshielding
... Shielding vs. Deshielding If a nuclei sees a smaller total magnetic field, it is ...
... Shielding vs. Deshielding If a nuclei sees a smaller total magnetic field, it is ...
Chapter 1 Student Notes
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
... All matter is composed of about 118 different kinds of atoms. These atoms can be physically mixed or chemically joined together to make up all kinds of matter. Atom the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Since matter exists in so many different forms, having ...
Matter and Measurement Ppt.
... (Homo: Same) Solution • A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout. Many homogeneous mixtures are commonly referred to as solutions. • All components are all in the same phase. • Particles are uniform in size (atoms or molecules) • Can not be separated by physic ...
... (Homo: Same) Solution • A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout. Many homogeneous mixtures are commonly referred to as solutions. • All components are all in the same phase. • Particles are uniform in size (atoms or molecules) • Can not be separated by physic ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... e. Chromatography from crystallization 31. An extensive property is one that depends on the amount of the sample. Which of the following properties are extensive? a. volume b. density c. temperature d. energy ...
... e. Chromatography from crystallization 31. An extensive property is one that depends on the amount of the sample. Which of the following properties are extensive? a. volume b. density c. temperature d. energy ...
Chapters 1-4 Numbers and Measurements in Chemistry Units SI
... called dimensional analysis: 1. To carry out dimensional analysis, we must know the relationship between units (equivalents): e.g. 1 nm = 10-9 m; 2. Use equivalents to determine unit factors: e.g. 1 = 1 nm/10-9 m; 3. Multiply result by appropriate unit factor(s) to convert units. ...
... called dimensional analysis: 1. To carry out dimensional analysis, we must know the relationship between units (equivalents): e.g. 1 nm = 10-9 m; 2. Use equivalents to determine unit factors: e.g. 1 = 1 nm/10-9 m; 3. Multiply result by appropriate unit factor(s) to convert units. ...
Proposed syllabus and Scheme of Examination B.Sc. (Program) with Chemistry Submitted To
... 2. Estimation of oxalic acid by titrating it with KMnO4. 3. Estimation of water of crystallization in Mohr’s salt by titrating with KMnO4. 4. Estimation of Fe (II) ions by titrating it with K2Cr2O7 using internal indicator. 5. Estimation of Cu (II) ions iodometrically using Na2S2O3. Section B: Organ ...
... 2. Estimation of oxalic acid by titrating it with KMnO4. 3. Estimation of water of crystallization in Mohr’s salt by titrating with KMnO4. 4. Estimation of Fe (II) ions by titrating it with K2Cr2O7 using internal indicator. 5. Estimation of Cu (II) ions iodometrically using Na2S2O3. Section B: Organ ...
ap chemistry 2005/2006
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation Present and future energy sources Lab: Observing Heat Changes (30 minutes) – mixing/observation of three thermochemical reactions, identification of endothermic or exothermic, identification as physical or chemical change. Lab: Determining the Specific Heat of an Unk ...
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation Present and future energy sources Lab: Observing Heat Changes (30 minutes) – mixing/observation of three thermochemical reactions, identification of endothermic or exothermic, identification as physical or chemical change. Lab: Determining the Specific Heat of an Unk ...
ap chemistry 2005/2006
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation Present and future energy sources Lab: Observing Heat Changes (30 minutes) – mixing/observation of three thermochemical reactions, identification of endothermic or exothermic, identification as physical or chemical change. Lab: Determining the Specific Heat of an Unk ...
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation Present and future energy sources Lab: Observing Heat Changes (30 minutes) – mixing/observation of three thermochemical reactions, identification of endothermic or exothermic, identification as physical or chemical change. Lab: Determining the Specific Heat of an Unk ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements comb ...
... All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements comb ...
2010 Exam
... Which term represents a process that uses heat, in the absence of air, to break large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller molecules? (A) ...
... Which term represents a process that uses heat, in the absence of air, to break large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller molecules? (A) ...
Chapter 4 - U of L Class Index
... of a lead(II) nitrate solution to produce lead(II) iodide as a yellow solid with a mass of 27.14 g. What was the molarity of the initial lead(II) nitrate solution? (Assume lead(II) nitrate was the limiting reactant.) ...
... of a lead(II) nitrate solution to produce lead(II) iodide as a yellow solid with a mass of 27.14 g. What was the molarity of the initial lead(II) nitrate solution? (Assume lead(II) nitrate was the limiting reactant.) ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomi ...
... understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomi ...
Chemistry - CBSE Academic
... based, content -oriented courses are introduced. Students reach this stage after 10 years of general education and opt for Chemistry with a purpose of pursuing their career in basic sciences or professional courses like medicine, engineering, technology and study courses in applied areas of science ...
... based, content -oriented courses are introduced. Students reach this stage after 10 years of general education and opt for Chemistry with a purpose of pursuing their career in basic sciences or professional courses like medicine, engineering, technology and study courses in applied areas of science ...
Analytical chemistry

Analytical chemistry is the study of the separation, identification, and quantification of the chemical components of natural and artificial materials. Qualitative analysis gives an indication of the identity of the chemical species in the sample, and quantitative analysis determines the amount of certain components in the substance. The separation of components is often performed prior to analysis.Analytical methods can be separated into classical and instrumental. Classical methods (also known as wet chemistry methods) use separations such as precipitation, extraction, and distillation and qualitative analysis by color, odor, or melting point. Classical quantitative analysis is achieved by measurement of weight or volume. Instrumental methods use an apparatus to measure physical quantities of the analyte such as light absorption, fluorescence, or conductivity. The separation of materials is accomplished using chromatography, electrophoresis or field flow fractionation methods.Analytical chemistry is also focused on improvements in experimental design, chemometrics, and the creation of new measurement tools to provide better chemical information. Analytical chemistry has applications in forensics, bioanalysis, clinical analysis, environmental analysis, and materials analysis.