Response of ocean phytoplankton community structure to climate
... Here we study the differential impact of climate driven changes in upper ocean nutrients, temperature and light on phytoplankton biomass and community structure. The Biogeosciences, 7, 3941–3959, 2010 ...
... Here we study the differential impact of climate driven changes in upper ocean nutrients, temperature and light on phytoplankton biomass and community structure. The Biogeosciences, 7, 3941–3959, 2010 ...
Projected expansion of the subtropical biome and contraction of the
... box at the beginning and the end of the century reveal the temperate seasonality, with a spring peak at the beginning of the century that is replaced by a subtropical, less seasonally variable, pattern at the end of the century (Figure 4). The mean annual primary production in each of the three biom ...
... box at the beginning and the end of the century reveal the temperate seasonality, with a spring peak at the beginning of the century that is replaced by a subtropical, less seasonally variable, pattern at the end of the century (Figure 4). The mean annual primary production in each of the three biom ...
Climate - MSc Epidemiology
... The Syndrom of Weather Sensitivity (1) - Who is Susceptible? Reacting to weather („Wetterreagierende“): Everybody – normal physiological response to atmospheric stimuli in the sense of an adaptive procedure. This should happen automatically without producing any stress except for maybe slight mood ...
... The Syndrom of Weather Sensitivity (1) - Who is Susceptible? Reacting to weather („Wetterreagierende“): Everybody – normal physiological response to atmospheric stimuli in the sense of an adaptive procedure. This should happen automatically without producing any stress except for maybe slight mood ...
Integrating Climate Change into Northeast and Midwest State
... the amount of total precipitation (rain and snow) are less certain. Severe weather events (e.g., thunderstorms, tornadoes) are challenging to detect. Soil moisture and evapotranspiration trends are neither robustly observed nor consistent amongst modeling studies. ...
... the amount of total precipitation (rain and snow) are less certain. Severe weather events (e.g., thunderstorms, tornadoes) are challenging to detect. Soil moisture and evapotranspiration trends are neither robustly observed nor consistent amongst modeling studies. ...
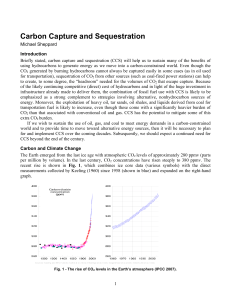
Carbon Capture and Sequestration
... surveying, and other techniques already available within the oil and gas industry. Leakage Through Old Wells. Where CO2 storage is sought in spent oil and gas wells, the infrastructure of the existing wells present a particular problem because these wells by design penetrate the seals that serve to ...
... surveying, and other techniques already available within the oil and gas industry. Leakage Through Old Wells. Where CO2 storage is sought in spent oil and gas wells, the infrastructure of the existing wells present a particular problem because these wells by design penetrate the seals that serve to ...
IPCC WGII AR5 Chapter 4 SECOND
... evolutionary response species are going to undertake, and by simply falling into the trap of writing more about species dispersal (as there are more papers on it) misses something. The authors may wish to consider including a section about what is missing around understanding these other adaptive st ...
... evolutionary response species are going to undertake, and by simply falling into the trap of writing more about species dispersal (as there are more papers on it) misses something. The authors may wish to consider including a section about what is missing around understanding these other adaptive st ...
Technical Summary
... Climate change: A change in the state of the climate that can be identified (e.g., by using statistical tests) by changes in the mean and/or the variability of its properties, and that persists for an extended period, typically decades or longer. Climate change may be due to natural internal process ...
... Climate change: A change in the state of the climate that can be identified (e.g., by using statistical tests) by changes in the mean and/or the variability of its properties, and that persists for an extended period, typically decades or longer. Climate change may be due to natural internal process ...
Variations in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types over the Ocean from
... in the northeast Pacific, concluding that total cloud cover is reduced when SST warmed. These studies have produced a consistent finding that reduced LTS can be caused by increasing SST, which causes a decrease in cloud fraction by initiating a trade-off from stratiform to cumuliform cloud cover. Cl ...
... in the northeast Pacific, concluding that total cloud cover is reduced when SST warmed. These studies have produced a consistent finding that reduced LTS can be caused by increasing SST, which causes a decrease in cloud fraction by initiating a trade-off from stratiform to cumuliform cloud cover. Cl ...
the effects of climate change in the netherlands: 2012
... system responds slowly to stimuli and the knock-on environmental impacts are equally slow to manifest, the changes will persist for some time to come – even if global greenhouse gas emissions decline. These changes also present opportunities, including benefits to agriculture and tourism. The unfavo ...
... system responds slowly to stimuli and the knock-on environmental impacts are equally slow to manifest, the changes will persist for some time to come – even if global greenhouse gas emissions decline. These changes also present opportunities, including benefits to agriculture and tourism. The unfavo ...
Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Management in
... Fisheries and aquaculture in the CARICOM region are extremely vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and variability, and to several hazards that typically result in disasters. The concern is with hydro-meteorological and geological hazards while acknowledging interaction with technological haz ...
... Fisheries and aquaculture in the CARICOM region are extremely vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and variability, and to several hazards that typically result in disasters. The concern is with hydro-meteorological and geological hazards while acknowledging interaction with technological haz ...
Carbon to Climate Change
... organic C stored in permafrost (perennially frozen) ground, and on the vulnerability to change under an increasingly warmer climate. Global climate models project the strongest future warming in the high latitudes, with some models predicting a 7 to 8 degree Celsius (oC) warming over land in these r ...
... organic C stored in permafrost (perennially frozen) ground, and on the vulnerability to change under an increasingly warmer climate. Global climate models project the strongest future warming in the high latitudes, with some models predicting a 7 to 8 degree Celsius (oC) warming over land in these r ...
Click here to download.
... Koyukon Elders of Alaska’s Interior observe that “cold weather is growing old” and recent warming is contributing to a world out of balance. Alaska is among the most rapidly warming places globally, with the Interior experiencing the most pronounced warming statewide, and with significant regional-s ...
... Koyukon Elders of Alaska’s Interior observe that “cold weather is growing old” and recent warming is contributing to a world out of balance. Alaska is among the most rapidly warming places globally, with the Interior experiencing the most pronounced warming statewide, and with significant regional-s ...
How Corporations Have Influenced the U.S. Dialogue on Climate
... Francesca Grifo is the senior scientist and director of the UCS Scientific Integrity Program. She holds a Ph.D. in botany from Cornell University. Gretchen Goldman is an analyst with the UCS Scientific Integrity Program. She holds a Ph.D. in environmental engineering from the Georgia Institute of Te ...
... Francesca Grifo is the senior scientist and director of the UCS Scientific Integrity Program. She holds a Ph.D. in botany from Cornell University. Gretchen Goldman is an analyst with the UCS Scientific Integrity Program. She holds a Ph.D. in environmental engineering from the Georgia Institute of Te ...
Gauteng Climate Change Risk and vulnerability assessment
... probability of occurrence of hazardous events or trends multiplied by the impacts if these events or trends occur. Risk results from the interaction of vulnerability, exposure, and hazard. In this report, the term risk is used primarily to refer to the risks of climate-change impacts. ...
... probability of occurrence of hazardous events or trends multiplied by the impacts if these events or trends occur. Risk results from the interaction of vulnerability, exposure, and hazard. In this report, the term risk is used primarily to refer to the risks of climate-change impacts. ...
Long-run relative importance of temperature as the main driver to
... South Africa has a warm climate, and much of the country experiences average annual temperatures of above 17°C (DST, 2010). M Malaria transmission is distinctly seasonal and limited to warm and rainy summer months. Case notifications generally increase from November, peak in late March to May, and t ...
... South Africa has a warm climate, and much of the country experiences average annual temperatures of above 17°C (DST, 2010). M Malaria transmission is distinctly seasonal and limited to warm and rainy summer months. Case notifications generally increase from November, peak in late March to May, and t ...
A Practitioner`s Guide to Climate Change Adaptation
... A Changing Climate in Ontario The average annual global temperature warmed by about 0.76oC over the last century (IPCC, 2007a), but average warming across Canada was more than double the world average (Environment Canada, 2011). In the last 63 years, the average temperature in Canada has increased a ...
... A Changing Climate in Ontario The average annual global temperature warmed by about 0.76oC over the last century (IPCC, 2007a), but average warming across Canada was more than double the world average (Environment Canada, 2011). In the last 63 years, the average temperature in Canada has increased a ...
Abbreviations and acronyms - Caribbean Regional Fisheries
... Fisheries and aquaculture in the CARICOM region are extremely vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and variability, and to several hazards that typically result in disasters. The concern is with hydro-meteorological and geological hazards while acknowledging interaction with technological haz ...
... Fisheries and aquaculture in the CARICOM region are extremely vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and variability, and to several hazards that typically result in disasters. The concern is with hydro-meteorological and geological hazards while acknowledging interaction with technological haz ...
Science Plan - IGOS Cryosphere
... of glacier geometry and mass balance, should continue to be monitored for change. Records of past climatic variability at the multi-decadal and longer time-scales are available from historic and geomorphologic records of glacier fluctuations, borehole temperatures and ice cores. These data complemen ...
... of glacier geometry and mass balance, should continue to be monitored for change. Records of past climatic variability at the multi-decadal and longer time-scales are available from historic and geomorphologic records of glacier fluctuations, borehole temperatures and ice cores. These data complemen ...
A Practitioner`s Guide to Climate Change Adaptation
... A Changing Climate in Ontario The average annual global temperature warmed by about 0.76oC over the last century (IPCC, 2007a), but average warming across Canada was more than double the world average (Environment Canada, 2011). In the last 63 years, the average temperature in Canada has increased a ...
... A Changing Climate in Ontario The average annual global temperature warmed by about 0.76oC over the last century (IPCC, 2007a), but average warming across Canada was more than double the world average (Environment Canada, 2011). In the last 63 years, the average temperature in Canada has increased a ...
Global warming hiatus
A global warming hiatus, also sometimes referred to as a global warming pause or a global warming slowdown, is a period of relatively little change in globally averaged surface temperatures. In the current episode of global warming many such periods are evident in the surface temperature record, along with robust evidence of the long term warming trend.The exceptionally warm El Niño year of 1998 was an outlier from the continuing temperature trend, and so gave the appearance of a hiatus: by January 2006 assertions had been made that this showed that global warming had stopped. A 2009 study showed that decades without warming were not exceptional, and in 2011 a study showed that if allowances were made for known variability, the rising temperature trend continued unabated. There was increased public interest in 2013 in the run-up to publication of the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, and despite concerns that a 15-year period was too short to determine a meaningful trend, the IPCC included a section on a hiatus, which it defined as a much smaller increasing linear trend over the 15 years from 1998 to 2012, than over the 60 years from 1951 to 2012. Various studies examined possible causes of the short term slowdown. Even though the overall climate system had continued to accumulate energy due to Earth's positive energy budget, the available temperature readings at the earth's surface indicated slower rates of increase in surface warming than in the prior decade. Since measurements at the top of the atmosphere show that Earth is receiving more energy than it is radiating back into space, the retained energy should be producing warming in at least one of the five parts of Earth's climate system.A July 2015 paper on the updated NOAA dataset cast doubt on the existence of this supposed hiatus, and found no indication of a slowdown. This analysis incorporated the latest corrections for known biases in ocean temperature measurements, and new land temperature data. Scientists working on other datasets welcomed this study, though the view was expressed that the short term warming trend had been slower than in previous periods of the same length.