Gymnosperm and Angiosperm Notes
... Characteristics Gymnosperms do not produce flowers or fruits but do produce seeds and pollen. of Gymnosperms ____________ – carries sperm cell; is not dependent on water; carried by wind ____________ – embryo of a plant; after pollination fertilized egg develops into a seed Examples: ______________ ...
... Characteristics Gymnosperms do not produce flowers or fruits but do produce seeds and pollen. of Gymnosperms ____________ – carries sperm cell; is not dependent on water; carried by wind ____________ – embryo of a plant; after pollination fertilized egg develops into a seed Examples: ______________ ...
Flowering Plants
... wind, insects, bats, birds and mammals to transfer pollen from the male (stamen) part of the flower to the female (stigma) part of the flower A flower is pollinated when a pollen grain lands on its ...
... wind, insects, bats, birds and mammals to transfer pollen from the male (stamen) part of the flower to the female (stigma) part of the flower A flower is pollinated when a pollen grain lands on its ...
22.3_Seed_Plants
... of pollen from the male reproductive structure to the female reproductive structure. ...
... of pollen from the male reproductive structure to the female reproductive structure. ...
MSdoc - Stevens County
... property; minimize exposed soil and overgrazing; don’t play sword-fights with the stalks which is a great way to spread the seeds! Biological – None present and no current research Cultural – Good vegetative cover and management are the best means to avoid proliferation of mullein Mechanical – Will ...
... property; minimize exposed soil and overgrazing; don’t play sword-fights with the stalks which is a great way to spread the seeds! Biological – None present and no current research Cultural – Good vegetative cover and management are the best means to avoid proliferation of mullein Mechanical – Will ...
Halo Example-Grades5
... As the seeds mature and ripen, the outside of the pistil swells to become the seed pod. The leaves and flowers slowly wilt and fall off. Inside each seed is a tiny embryo, waiting for water and warmth so it can germinate into a new plant. ...
... As the seeds mature and ripen, the outside of the pistil swells to become the seed pod. The leaves and flowers slowly wilt and fall off. Inside each seed is a tiny embryo, waiting for water and warmth so it can germinate into a new plant. ...
Unit 14 Plants Angiosperms Notes
... Advantage = added protection the fruit provides Anthophytes = division 2 classes 1. Monocotyledons = one seed leaf 60,000 species Familiar: grasses, orchids, lilies, and palms 2. Dicotyledons = two seed leaves Majority 170,000 species Familiar = shrubs, trees (except conifers), wildflowers, and herb ...
... Advantage = added protection the fruit provides Anthophytes = division 2 classes 1. Monocotyledons = one seed leaf 60,000 species Familiar: grasses, orchids, lilies, and palms 2. Dicotyledons = two seed leaves Majority 170,000 species Familiar = shrubs, trees (except conifers), wildflowers, and herb ...
Seed Characteristics
... “above the cotyledons”. It becomes the above-ground shoot. Hypocotyl: means “below the cotyledons”. It becomes the below-ground root system. ...
... “above the cotyledons”. It becomes the above-ground shoot. Hypocotyl: means “below the cotyledons”. It becomes the below-ground root system. ...
Starting Plants from Seeds
... This is the process of getting the little plants used to the conditions they are going to live in outdoors. Start the hardening process about two weeks before transplanting. Gradually lower their temperatures and relative humidity. Reduce water, which causes an accumulation of carbohydrates and ...
... This is the process of getting the little plants used to the conditions they are going to live in outdoors. Start the hardening process about two weeks before transplanting. Gradually lower their temperatures and relative humidity. Reduce water, which causes an accumulation of carbohydrates and ...
Organisms can be classified into two major groups
... grass, roses, fruit trees) • Some flowers become fruit. • Non-flowering plants are plants that make seeds within cones or produce spores instead of seeds. (ex: ferns, mosses, cedar trees, pine trees) ...
... grass, roses, fruit trees) • Some flowers become fruit. • Non-flowering plants are plants that make seeds within cones or produce spores instead of seeds. (ex: ferns, mosses, cedar trees, pine trees) ...
Life Cycle of a Plant
... Seeds are dispersed from parent plant (wind, water, animals): a. they can lay dormant or b. they can grow immediately if conditions are ideal. Early stage of seed growth known as germination. Roots grow downward and stem and leaves grow upward. ...
... Seeds are dispersed from parent plant (wind, water, animals): a. they can lay dormant or b. they can grow immediately if conditions are ideal. Early stage of seed growth known as germination. Roots grow downward and stem and leaves grow upward. ...
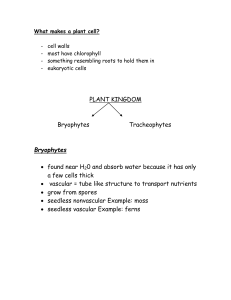
plant class notes
... a few cells thick vascular = tube like structure to transport nutrients grow from spores seedless nonvascular Example: moss seedless vascular Example: ferns ...
... a few cells thick vascular = tube like structure to transport nutrients grow from spores seedless nonvascular Example: moss seedless vascular Example: ferns ...
Plant Life Cycle PowerPoint
... grasses, or many years for plants such as Oak trees. Flowers contain male and female parts. In most plants, these are both together in the same flowers. However, in some, they are in separate flowers on the same plant (Hazel). Some species may have separate male and female plants (Holly). ...
... grasses, or many years for plants such as Oak trees. Flowers contain male and female parts. In most plants, these are both together in the same flowers. However, in some, they are in separate flowers on the same plant (Hazel). Some species may have separate male and female plants (Holly). ...
Seed Propagation
... well as regulate and initiate the process of germination. It is made up of two layers of tissue. The outer layer, called the testa, is hard, dry, and generally darker in color than the inner layer. Plants produce stored food supply as either tissue surrounding the embryo, called the endosperm, or ti ...
... well as regulate and initiate the process of germination. It is made up of two layers of tissue. The outer layer, called the testa, is hard, dry, and generally darker in color than the inner layer. Plants produce stored food supply as either tissue surrounding the embryo, called the endosperm, or ti ...
Seeds Powerpoint
... Some seeds use hooks to grab a ride on passing animals. The animals carry them away from the parent plant. After a while the seed falls off and can begin to grow. ...
... Some seeds use hooks to grab a ride on passing animals. The animals carry them away from the parent plant. After a while the seed falls off and can begin to grow. ...
The Tiny Seed
... • burst: to split apart suddenly because of excess internal pressure • roots: the part of a plant that has no leaves and usually spreads underground • stems: the main stalk of a plant • weed: a wild plant growing where it is not wanted • Summer: the warmest season of the year (June – August) • petal ...
... • burst: to split apart suddenly because of excess internal pressure • roots: the part of a plant that has no leaves and usually spreads underground • stems: the main stalk of a plant • weed: a wild plant growing where it is not wanted • Summer: the warmest season of the year (June – August) • petal ...
Benha University
... 19- In the following, there are some stem functions, what is the modified one? a- bearing the different vegetative organs. b- conduction of the soil solution and the prepared food. c- photosynthesis and storage. d- none of the above. 20- The embryonic shoot bud which grows into the shoot system is c ...
... 19- In the following, there are some stem functions, what is the modified one? a- bearing the different vegetative organs. b- conduction of the soil solution and the prepared food. c- photosynthesis and storage. d- none of the above. 20- The embryonic shoot bud which grows into the shoot system is c ...
Ch 24 Plant Reproduction and Response
... tissue and support the development of the growing embryo within the seed Fruit Mature angiosperm ovary, usually containing seeds Fruit isn’t limited to “fruits” like apples but also includes rice, corn, etc… ...
... tissue and support the development of the growing embryo within the seed Fruit Mature angiosperm ovary, usually containing seeds Fruit isn’t limited to “fruits” like apples but also includes rice, corn, etc… ...
24.2_Fruits_and_Seeds
... tissue and support the development of the growing embryo within the seed Fruit Mature angiosperm ovary, usually containing seeds Fruit isn’t limited to “fruits” like apples but also includes rice, corn, etc… ...
... tissue and support the development of the growing embryo within the seed Fruit Mature angiosperm ovary, usually containing seeds Fruit isn’t limited to “fruits” like apples but also includes rice, corn, etc… ...
AP Biology 11 LO Cards: Plants
... 1. Define the following terms: cuticle, secondary compounds, stomata, vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), lignin, rhizoids, roots, leaves, megaspore, microspore 2. Compare and contrast the life cycle of the fern with that of the moss. Chapter 30: Plant Diversity II 1. List and explain the four most ...
... 1. Define the following terms: cuticle, secondary compounds, stomata, vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), lignin, rhizoids, roots, leaves, megaspore, microspore 2. Compare and contrast the life cycle of the fern with that of the moss. Chapter 30: Plant Diversity II 1. List and explain the four most ...
HOUNDSTONGUE - Delta County
... Control Methods: Mechanical removal is very effective for small infestations, particularly after plants have bolted, when herbicides may not be as effective. Rosettes should be killed manually or with herbicides in the spring or fall. Plants that are bolting should be removed manually or sprayed as ...
... Control Methods: Mechanical removal is very effective for small infestations, particularly after plants have bolted, when herbicides may not be as effective. Rosettes should be killed manually or with herbicides in the spring or fall. Plants that are bolting should be removed manually or sprayed as ...
Germination
... Dormant- inactive, latent, but capable of being activated, suspension of metabolic process. ...
... Dormant- inactive, latent, but capable of being activated, suspension of metabolic process. ...
Document
... A. Following fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit with seeds inside, while the rest of the flower dies B. Fruits help protect the seeds until they mature and help scatter seeds into new habitats -Fruits are the part of the plant that contains seeds: cucumbers, maple “helicopters”, green ...
... A. Following fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit with seeds inside, while the rest of the flower dies B. Fruits help protect the seeds until they mature and help scatter seeds into new habitats -Fruits are the part of the plant that contains seeds: cucumbers, maple “helicopters”, green ...
Plant Diversity II – The Evolution of Seed Plants
... Pollen and the Production of Sperm A Pollen grain is a male gametophyte. It contains two sperm nuclei. Has a waterproof coating, allowing for transfer by the wind. Water no longer required for sperm transfer. ...
... Pollen and the Production of Sperm A Pollen grain is a male gametophyte. It contains two sperm nuclei. Has a waterproof coating, allowing for transfer by the wind. Water no longer required for sperm transfer. ...
Plant Science Unit 7 Review – Sexual Propagation 7.1 Define Terms
... 19. Identify which Stage of germination is described in each of the following: __________A. Metabolic activity surges. Proteins are synthesized. Gibberellins stimulate the production of enzymes. Starches are converted to sugars. Stored proteins are broken down in to amino acids. The sugars and amino ...
... 19. Identify which Stage of germination is described in each of the following: __________A. Metabolic activity surges. Proteins are synthesized. Gibberellins stimulate the production of enzymes. Starches are converted to sugars. Stored proteins are broken down in to amino acids. The sugars and amino ...
Seed

A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering known as the seed coat.It is a characteristic of spermatophytes (gymnosperm and angiosperm plants) and the product of the ripened ovule which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant. The formation of the seed completes the process of reproduction in seed plants (started with the development of flowers and pollination), with the embryo developed from the zygote and the seed coat from the integuments of the ovule.Seeds have been an important development in the reproduction and spread of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants, relative to more primitive plants such as ferns, mosses and liverworts, which do not have seeds and use other means to propagate themselves. This can be seen by the success of seed plants (both gymnosperms and angiosperms) in dominating biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates.The term ""seed"" also has a general meaning that antedates the above—anything that can be sown, e.g. ""seed"" potatoes, ""seeds"" of corn or sunflower ""seeds"". In the case of sunflower and corn ""seeds"", what is sown is the seed enclosed in a shell or husk, whereas the potato is a tuber.Many structures commonly referred to as ""seeds"" are actually dry fruits. Plants producing berries are called baccate. Sunflower seeds are sometimes sold commercially while still enclosed within the hard wall of the fruit, which must be split open to reach the seed. Different groups of plants have other modifications, the so-called stone fruits (such as the peach) have a hardened fruit layer (the endocarp) fused to and surrounding the actual seed. Nuts are the one-seeded, hard-shelled fruit of some plants with an indehiscent seed, such as an acorn or hazelnut.