important terminologies
... Group of flower on main axis is called infloresence. It is of two types. i. Racemose ii. Cymose Racemose: In this case the main axis (stem) continues to grow and develop lateral flower. It may be. 1. Terminal raceme: When recemose inflorescene is present at tip of the stem. 2. Panicle: A branched ra ...
... Group of flower on main axis is called infloresence. It is of two types. i. Racemose ii. Cymose Racemose: In this case the main axis (stem) continues to grow and develop lateral flower. It may be. 1. Terminal raceme: When recemose inflorescene is present at tip of the stem. 2. Panicle: A branched ra ...
Plant Propagation - Havelock Agricultural Education
... rootstock be in a condition of active growth such that the "bark is slipping". This means that the vascular cambium is actively growing, and the bark can be peeled easily from the stock piece with little damage. ...
... rootstock be in a condition of active growth such that the "bark is slipping". This means that the vascular cambium is actively growing, and the bark can be peeled easily from the stock piece with little damage. ...
Basic Botany - Clemson University
... Internally, there are three major parts of a root (Figure 3.3). The meristem at the tip manufactures new cells; it is the region of cell division. Behind it is the region of cell elongation. Here, the cells lengthen to push the root through the soil. Following the region of cell elongation is the re ...
... Internally, there are three major parts of a root (Figure 3.3). The meristem at the tip manufactures new cells; it is the region of cell division. Behind it is the region of cell elongation. Here, the cells lengthen to push the root through the soil. Following the region of cell elongation is the re ...
Regulation of Plant Growth
... studies of Arabidopsis thaliana. It is used as a model organism— it is small, matures quickly, it s genome is small and has been fully sequenced. Mutants provide insights into mechanisms of hormones and receptors. ...
... studies of Arabidopsis thaliana. It is used as a model organism— it is small, matures quickly, it s genome is small and has been fully sequenced. Mutants provide insights into mechanisms of hormones and receptors. ...
Document
... Some plant species have evolved modified leaves that serve various functions. (a) Tendrils. The tendrils by which this pea plant clings to a support are modified leaves. After it has “lassoed” a support, a tendril forms a coil that brings the plant closer to the support. Tendrils are typically modif ...
... Some plant species have evolved modified leaves that serve various functions. (a) Tendrils. The tendrils by which this pea plant clings to a support are modified leaves. After it has “lassoed” a support, a tendril forms a coil that brings the plant closer to the support. Tendrils are typically modif ...
pdf - University of Bacau - Universitatea "Vasile Alecsandri"
... indicators of growth and development processes speed. In order to have more accurate results, the studies were accomplished in the root meristematic tips on three different plants, originated from Vegetable Research and Development Station Bacău, Romania. The repartition of cells on phases of divisi ...
... indicators of growth and development processes speed. In order to have more accurate results, the studies were accomplished in the root meristematic tips on three different plants, originated from Vegetable Research and Development Station Bacău, Romania. The repartition of cells on phases of divisi ...
THE SOIL ASSOCIATION APPRENTICESHIP SCHEME
... Binomial nomenclature can give descriptive clues about the plant e.g. colour, form, who discovered it and where it originated. Plants are also grouped together within a species. These subgroups are called varieties and cultivars (cultivated varieties). A variety is a group of plants (showing a varia ...
... Binomial nomenclature can give descriptive clues about the plant e.g. colour, form, who discovered it and where it originated. Plants are also grouped together within a species. These subgroups are called varieties and cultivars (cultivated varieties). A variety is a group of plants (showing a varia ...
Growth Response of Plants
... What has happened to the shoots of plants A, B and C ? Ans: The shoots in pot A respond by growing towards the light source. The shoot in pot B do not show any curvature but grow vertically upwards... ...
... What has happened to the shoots of plants A, B and C ? Ans: The shoots in pot A respond by growing towards the light source. The shoot in pot B do not show any curvature but grow vertically upwards... ...
plants and flower notes
... fluids but it does provide support. When you look at a tree stump you can see the each ring, one ring is created each year of the trees life. Count the rings and you can see how old the tree is. Each contains both kinds of vascular tissue as well as other ...
... fluids but it does provide support. When you look at a tree stump you can see the each ring, one ring is created each year of the trees life. Count the rings and you can see how old the tree is. Each contains both kinds of vascular tissue as well as other ...
Advances in Environmental Biology Masoumeh Mirzaei and Saeid Soltani
... be of high use. In Iran traditional medicine as a comprehensive school having exclusive basics rooted in the history of people. It is declared that introducing medicines using in traditional medicine especially herbal ones open a window towards compiling research projects in acquiring new medicines ...
... be of high use. In Iran traditional medicine as a comprehensive school having exclusive basics rooted in the history of people. It is declared that introducing medicines using in traditional medicine especially herbal ones open a window towards compiling research projects in acquiring new medicines ...
Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and
... 23. Dioecious plant - A plant having only either the staminate or carpellate flower 24. Pollination - The placement of the pollen grain from the anther to the stigma of a carpel 25. Pollen grain - The immature male gametophyte that develops within the anthers of stamens; derived from the microsporoc ...
... 23. Dioecious plant - A plant having only either the staminate or carpellate flower 24. Pollination - The placement of the pollen grain from the anther to the stigma of a carpel 25. Pollen grain - The immature male gametophyte that develops within the anthers of stamens; derived from the microsporoc ...
The Plant Kingdom
... The pistil consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky part that traps and holds the pollen. The style is the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma. The ovary and the ovule are at the bottom of the style. ...
... The pistil consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky part that traps and holds the pollen. The style is the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma. The ovary and the ovule are at the bottom of the style. ...
Barnaby Bear Investigates: My Plant Information
... How do I recognise cow parsley ? The white flower makes them stand out.. Look for the umbrella flowers. You will see a number of them on each stalk . Check - If it’s taller than you it won’t be cow parsley! ...
... How do I recognise cow parsley ? The white flower makes them stand out.. Look for the umbrella flowers. You will see a number of them on each stalk . Check - If it’s taller than you it won’t be cow parsley! ...
AIM - ncert
... AIM To prepare a temporary mount of human cheek epithelial cells, and to study its characteristics. ...
... AIM To prepare a temporary mount of human cheek epithelial cells, and to study its characteristics. ...
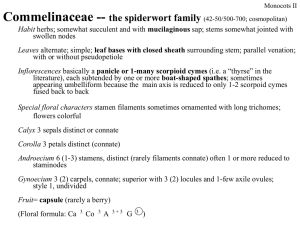
Commelinaceae -- the spiderwort family (42-50/500-700
... food, but also for timber, pulp, and utensils. Some bamboos grow vegetatively for years (up to 150 yrs), flower, and then die. This has caused problems in the past (particularly for pandas) because clones can spread over large areas of land, and when it is time for that plant to flower all the clone ...
... food, but also for timber, pulp, and utensils. Some bamboos grow vegetatively for years (up to 150 yrs), flower, and then die. This has caused problems in the past (particularly for pandas) because clones can spread over large areas of land, and when it is time for that plant to flower all the clone ...
Across 1. One bushel of corn weighs _____ pounds 4. Most
... 10. Once corn seed starts to swell, it makes this type of root first 11. By the time the ___ leaf collars appear on a corn plant, the growing point will be above the soil surface and the plant will start to develop rapidly 13. Occurs in a corn plant when the pollen grains from the tassel fall on the ...
... 10. Once corn seed starts to swell, it makes this type of root first 11. By the time the ___ leaf collars appear on a corn plant, the growing point will be above the soil surface and the plant will start to develop rapidly 13. Occurs in a corn plant when the pollen grains from the tassel fall on the ...
plants vascular systems
... the microscope (it is the picture on the bottom of the slide. Draw the cross section as observed under low power in one of the circles provided. A vascular bundle is the xylem and phloem put together. You can see a picture of a single bundle on the right. The vascular bundles are arranged in a ring ...
... the microscope (it is the picture on the bottom of the slide. Draw the cross section as observed under low power in one of the circles provided. A vascular bundle is the xylem and phloem put together. You can see a picture of a single bundle on the right. The vascular bundles are arranged in a ring ...
Anatomy of Plants – Teacher Notes
... Evolves from the maturing ovary after pollination and fertilization ...
... Evolves from the maturing ovary after pollination and fertilization ...
ASSESSMENT OF PHARMACOGNOSTICAL CHARACTERS OF THE FRUIT OF STEREOSPERMUM COLAIS BUCH
... The standardization of a crude drug is an integral part for establishing its correct identity. Before any crude drug can be included in an herbal pharmacopoeia, pharmacognostic parameters and standards must be established. Microscopic method is one of the simplest and cheapest methods to start with ...
... The standardization of a crude drug is an integral part for establishing its correct identity. Before any crude drug can be included in an herbal pharmacopoeia, pharmacognostic parameters and standards must be established. Microscopic method is one of the simplest and cheapest methods to start with ...
****Types of leaves:
... veins. The major vein of leaf, with respect to the size is termed the primary vein, from the primary (vein)s, smaller, later veins may branch off these known as secondary veins. ***Venation patterns:- Very general venation classes are as follow: 1- Uninervous: In which, there is a central midrib wit ...
... veins. The major vein of leaf, with respect to the size is termed the primary vein, from the primary (vein)s, smaller, later veins may branch off these known as secondary veins. ***Venation patterns:- Very general venation classes are as follow: 1- Uninervous: In which, there is a central midrib wit ...
Common foods and plant parts
... discuss what is meant by ‘fruit’ and ‘vegetable’. To a botanist, a fruit is part of a flower that develops to protect seeds – that includes pumpkins, chillies and cucumbers, but you won’t find those in the fruit section of the supermarket. Botanists classify plant parts by their functions more than ...
... discuss what is meant by ‘fruit’ and ‘vegetable’. To a botanist, a fruit is part of a flower that develops to protect seeds – that includes pumpkins, chillies and cucumbers, but you won’t find those in the fruit section of the supermarket. Botanists classify plant parts by their functions more than ...
Product profile No 1:_Bong bark ,“Peuak Bong, Yang Bong”
... more, which takes 3-5 years to grow (Champasak, 1 village). Because of its easy regeneration and colonising behaviour in disturbed forests the species becomes not easily endangered. Conservation status: Female plants are rare. Processing: Before use drying in sun is required and storage in ventilate ...
... more, which takes 3-5 years to grow (Champasak, 1 village). Because of its easy regeneration and colonising behaviour in disturbed forests the species becomes not easily endangered. Conservation status: Female plants are rare. Processing: Before use drying in sun is required and storage in ventilate ...
Concepts of Micropropagation
... Organogensis refers to that period of time during development when the organs are being formed. After an egg has been fertilized, and has been implanted in the uterus, the developing form is known as the embryo. Organogenesis takes place during this embryonic phase. In fact, most organogenesis has b ...
... Organogensis refers to that period of time during development when the organs are being formed. After an egg has been fertilized, and has been implanted in the uterus, the developing form is known as the embryo. Organogenesis takes place during this embryonic phase. In fact, most organogenesis has b ...
Meristem

A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells), found in zones of the plant where growth can take place.Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. The shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function.The term meristem was first used in 1858 by Karl Wilhelm von Nägeli (1817–1891) in his book Beiträge zur Wissenschaftlichen Botanik. It is derived from the Greek word merizein (μερίζειν), meaning to divide, in recognition of its inherent function.In general, differentiated plant cells cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Therefore, cell division in the meristem is required to provide new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body.Meristematic cells are incompletely or not at all differentiated, and are capable of continued cellular division (youthful). Furthermore, the cells are small and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The vacuoles are extremely small. The cytoplasm does not contain differentiated plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), although they are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together without intercellular cavities. The cell wall is a very thin primary cell wall.Maintenance of the cells requires a balance between two antagonistic processes: organ initiation and stem cell population renewal.Apical meristems are the completely undifferentiated (indeterminate) meristems in a plant. These differentiate into three kinds of primary meristems. The primary meristems in turn produce the two secondary meristem types. These secondary meristems are also known as lateral meristems because they are involved in lateral growth.At the meristem summit, there is a small group of slowly dividing cells, which is commonly called the central zone. Cells of this zone have a stem cell function and are essential for meristem maintenance. The proliferation and growth rates at the meristem summit usually differ considerably from those at the periphery.Meristems also are induced in the roots of legumes such as soybean, Lotus japonicus, pea, and Medicago truncatula after infection with soil bacteria commonly called Rhizobium. Cells of the inner or outer cortex in the so-called ""window of nodulation"" just behind the developing root tip are induced to divide. The critical signal substance is the lipo-oligosaccharide Nod-factor, decorated with side groups to allow specificity of interaction. The Nod factor receptor proteins NFR1 and NFR5 were cloned from several legumes including Lotus japonicus, Medicago truncatula and soybean (Glycine max). Regulation of nodule meristems utilizes long distance regulation commonly called ""Autoregulation of Nodulation"" (AON). This process involves a leaf-vascular tissue located LRR receptor kinases (LjHAR1, GmNARK and MtSUNN), CLE peptide signalling, and KAPP interaction, similar to that seen in the CLV1,2,3 system. LjKLAVIER also exhibits a nodule regulation phenotype though it is not yet known how this relates to the other AON receptor kinases.