Notes on Meiosis
... Definition: a process of reduction division that produces gametes ( sex cells) in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half (haploid) through the separation of homologous chromosomes. ...
... Definition: a process of reduction division that produces gametes ( sex cells) in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half (haploid) through the separation of homologous chromosomes. ...
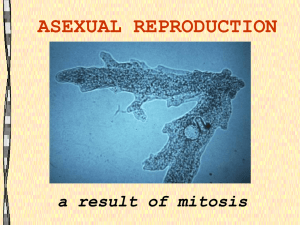
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION a result of mitosis
... organism produces offspring without meiosis and fertilization. Because the offspring inherit all their DNA from one parent, they are genetically identical to each other and to their parent. ...
... organism produces offspring without meiosis and fertilization. Because the offspring inherit all their DNA from one parent, they are genetically identical to each other and to their parent. ...
Unit 6
... 1.- The flower is a major evolutionary advancement for the fallowing reasons: a) The flowering is a special adaptation to attract pollinators, such as insects and birds. b) The ovules are protected inside an ovary. c) The ovary develops into a fruit which fosters the dispersal of seeds by wind, inse ...
... 1.- The flower is a major evolutionary advancement for the fallowing reasons: a) The flowering is a special adaptation to attract pollinators, such as insects and birds. b) The ovules are protected inside an ovary. c) The ovary develops into a fruit which fosters the dispersal of seeds by wind, inse ...
L to J PowerPoint
... reproduction in which a male reproductive cell and a female reproductive cell combine to form a new cell that can develop into a new organism ...
... reproduction in which a male reproductive cell and a female reproductive cell combine to form a new cell that can develop into a new organism ...
Sexual reproduction
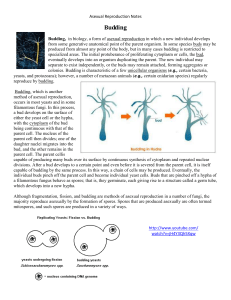
... – Parent cell undergoes mitosis to form daughter cells – Mitosis in vegetative cells may be concurrent with budding to produce a daughter cell – May proceed through a spore form ...
... – Parent cell undergoes mitosis to form daughter cells – Mitosis in vegetative cells may be concurrent with budding to produce a daughter cell – May proceed through a spore form ...
Reproductive Strategies
... K-strategists are usually close to the carrying-capacity. In stable ecosystems natural selection favours species that can maximize use of natural resources and have a high probability of survival so K-strategists outcompete r-strategists. In contrast, invertebrates and fish use lots of energy in the ...
... K-strategists are usually close to the carrying-capacity. In stable ecosystems natural selection favours species that can maximize use of natural resources and have a high probability of survival so K-strategists outcompete r-strategists. In contrast, invertebrates and fish use lots of energy in the ...
3) ALL LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO A STIMULUS
... bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
... bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult form (mature). ...
Document
... a. budding b. Binary fission c. Fragmentation d. Alternation of generations 26. A form of asexual reproduction in which part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism. a. Budding b. Binary fission c. Fragmentation d. Alternation of generations 27. Part of a multicelluar organism br ...
... a. budding b. Binary fission c. Fragmentation d. Alternation of generations 26. A form of asexual reproduction in which part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism. a. Budding b. Binary fission c. Fragmentation d. Alternation of generations 27. Part of a multicelluar organism br ...
Directed Reading 11.2 - Blair Community Schools
... pair all along their length and then crossing-over occurs. _____________________ 9. After one division of the nucleus, a new spindle forms around each group of chromosomes. _____________________ 10. Individual chromosomes line up along the equator, attached at their centromeres to spindle fibers. __ ...
... pair all along their length and then crossing-over occurs. _____________________ 9. After one division of the nucleus, a new spindle forms around each group of chromosomes. _____________________ 10. Individual chromosomes line up along the equator, attached at their centromeres to spindle fibers. __ ...
Document
... Sex- Linked Gene- located on X chromosome (Y only carries SRY gene for male determination) Nondisjuntion- chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis. Get 1 or 3 copies of a chromosome instead of 2. Sex chromosome- X,Y, (number 23) Ch. 15: Evolution Evolution- Change over time, modern organ ...
... Sex- Linked Gene- located on X chromosome (Y only carries SRY gene for male determination) Nondisjuntion- chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis. Get 1 or 3 copies of a chromosome instead of 2. Sex chromosome- X,Y, (number 23) Ch. 15: Evolution Evolution- Change over time, modern organ ...
Human Biology 4.3
... – Each contains hundreds of egg cells. – Pituitary gland releases a hormone that stimulates some of the eggs to develop and grow every 28 days. ...
... – Each contains hundreds of egg cells. – Pituitary gland releases a hormone that stimulates some of the eggs to develop and grow every 28 days. ...
Sex: a pluralist approach includes species selection. (One step
... generations if asexual reproduction implied a cost larger than 2 per generation (a point raised by Stearns, 1987). In aphid Rhopalosiphum padi, sex is maintained by the need for producing eggs (parthenogenesis is viviparous and winter frost kills all animals but not eggs) as shown by Rispe et al. (1 ...
... generations if asexual reproduction implied a cost larger than 2 per generation (a point raised by Stearns, 1987). In aphid Rhopalosiphum padi, sex is maintained by the need for producing eggs (parthenogenesis is viviparous and winter frost kills all animals but not eggs) as shown by Rispe et al. (1 ...
Introduction to Animals Crosswords
... 4. Fertilization restores this chromosome number 7. Outer germ layer 8. Hollow ball cell stage of a developing zygote 9. More than 95% of all animals are this 11. Circulatory system in which blood empties into the body cavity to bathe tissues 14. development in which the young animal looks like that ...
... 4. Fertilization restores this chromosome number 7. Outer germ layer 8. Hollow ball cell stage of a developing zygote 9. More than 95% of all animals are this 11. Circulatory system in which blood empties into the body cavity to bathe tissues 14. development in which the young animal looks like that ...
Name: Date: Subject: Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Objectives
... Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. We call them clones. This doesn’t mean that they are exactly the same, it just means that they have the same DNA or genes. Asexual reproduction requires only 1 parent so asexually reproducing organisms do ...
... Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. We call them clones. This doesn’t mean that they are exactly the same, it just means that they have the same DNA or genes. Asexual reproduction requires only 1 parent so asexually reproducing organisms do ...
117 Chicks come from eggs. What other things come
... The best answer is: Everything on the list comes from an egg except for four things—soil, bacteria, rock, and single-celled organism. The rest are multicellular plants and animals that reproduce sexually. During sexual reproduction, an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell. This fertilized egg then ...
... The best answer is: Everything on the list comes from an egg except for four things—soil, bacteria, rock, and single-celled organism. The rest are multicellular plants and animals that reproduce sexually. During sexual reproduction, an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell. This fertilized egg then ...
A Closer Look at Conception presentation
... Each of us inherits many personal characteristics from our parents. EX: physical build, skin color, hair color & texture, eye color & shape. ...
... Each of us inherits many personal characteristics from our parents. EX: physical build, skin color, hair color & texture, eye color & shape. ...
Unit 4 Notes #3Terrestrial Plants and Their Adaptations To Land
... - Male sperm cell packaged up in - Ovules formed and protected in ___________________________. ________________of female part. ...
... - Male sperm cell packaged up in - Ovules formed and protected in ___________________________. ________________of female part. ...
Human Reproduction Notes
... aware, also the lips and parts of the nose in both sexes. The most densely innervated and sensitive parts in both males and females are their respective glans and prepuces. ...
... aware, also the lips and parts of the nose in both sexes. The most densely innervated and sensitive parts in both males and females are their respective glans and prepuces. ...
Chapter 19
... Usually committed by men against women but can be vice versa 1 in 10 rape survivors are male One of the most underreported crimes Aside from physical trauma of raper, risk of sexually transmitted disease, HIV, pregnancy and psychological sequelae occur ...
... Usually committed by men against women but can be vice versa 1 in 10 rape survivors are male One of the most underreported crimes Aside from physical trauma of raper, risk of sexually transmitted disease, HIV, pregnancy and psychological sequelae occur ...
6.2 workbook - Fetal Development
... fertilization is common with animals that live in water and with plants that live in moist places. When sperm and egg cells join inside the body of the female parent, the joining is called internal fertilization. This type of fertilization is common with birds, mammals, and flowering and cone-formin ...
... fertilization is common with animals that live in water and with plants that live in moist places. When sperm and egg cells join inside the body of the female parent, the joining is called internal fertilization. This type of fertilization is common with birds, mammals, and flowering and cone-formin ...
Chapter 3
... from an acorn. A maple tree will not grow from an acorn. • All organisms _______________ traits. • ____________________ also affects characteristics of an individual. Example: tree height • Organisms also have traits that they did not _______ such as talents - these traits are _____________ traits ...
... from an acorn. A maple tree will not grow from an acorn. • All organisms _______________ traits. • ____________________ also affects characteristics of an individual. Example: tree height • Organisms also have traits that they did not _______ such as talents - these traits are _____________ traits ...
Amphibians
... What are fish? • Habitat: nearly every aquatic environment • Respiration: use gills to breathe • Circulation: 2 chambered heart • Reproduction: sexual (mostly external) • Nervous System: lateral line system that can detect ...
... What are fish? • Habitat: nearly every aquatic environment • Respiration: use gills to breathe • Circulation: 2 chambered heart • Reproduction: sexual (mostly external) • Nervous System: lateral line system that can detect ...
Asexual Reproduction Jigsaw
... Parthenogenesis Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction found in females, where growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization by a male. In plants, parthenogenesis means development of an embryo from an unfertilized egg cell, and is a component process of apomixis. The wor ...
... Parthenogenesis Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction found in females, where growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization by a male. In plants, parthenogenesis means development of an embryo from an unfertilized egg cell, and is a component process of apomixis. The wor ...
Phylum Annelida
... – Initiates “anchor” and longitudinal muscles contract to quickly pull worm away from stimulus ...
... – Initiates “anchor” and longitudinal muscles contract to quickly pull worm away from stimulus ...
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphologically distinct types of specialized reproductive cells called gametes fuse together, involving a female's large ovum (or egg) and a male's smaller sperm. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of normal cells. They are created by a specialized type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, known as meiosis. The two gametes fuse during fertilization to produce DNA replication and the creation of a single-celled zygote which includes genetic material from both gametes. In a process called genetic recombination, genetic material (DNA) joins up so that homologous chromosome sequences are aligned with each other, and this is followed by exchange of genetic information. Two rounds of cell division then produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes from each original parent cell, and the same number of chromosomes as both parents, though self-fertilization can occur. For instance, in human reproduction each human cell contains 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, except gamete cells, which only contain 23 chromosomes, so the child will have 23 chromosomes from each parent genetically recombined into 23 pairs. Cell division initiates the development of a new individual organism in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants, for the vast majority of whom this is the primary method of reproduction. A species is defined as a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms where two hybrids are capable of reproducing fertile offspring, typically using sexual reproduction, although the species problem encompasses a series of difficult related questions that often come up when biologists define the word species. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle because asexual reproduction should be able to outcompete it as every young organism created can bear its own young. This implies that an asexual population has an intrinsic capacity to grow more rapidly with each generation. This 50% cost is a fitness disadvantage of sexual reproduction. The two-fold cost of sex includes this cost and the fact that any organism can only pass on 50% of its own genes to its offspring. One definite advantage of sexual reproduction is that it prevents the accumulation of genetic mutations.Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which some individuals out-reproduce others of a population because they are better at securing mates for sexual reproduction. It has been described as ""a powerful evolutionary force that does not exist in asexual populations""Prokaryotes reproduce through asexual reproduction but may display processes similar to sexual reproduction (mechanisms for lateral gene transfer such as bacterial conjugation, transformation and transduction), but they do not lead to reproduction. In prokaryotes, the initial cell has additional or transformed genetic material.