Chapter 16: Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
... Hutton/Lyell argued Earth was old – but how old? Modern geologists use radioactive dating to determine age of rocks/fossils Earth is about 4.5 billion years old Darwin’s study of fossils convinced him, but paleontologists had not yet found enough fossils of intermediate species Since then, m ...
... Hutton/Lyell argued Earth was old – but how old? Modern geologists use radioactive dating to determine age of rocks/fossils Earth is about 4.5 billion years old Darwin’s study of fossils convinced him, but paleontologists had not yet found enough fossils of intermediate species Since then, m ...
Vocabulary Review
... species that, compared to other anatomical structures in another species, originated from a single anatomical structure in a common ancestor of the two species ...
... species that, compared to other anatomical structures in another species, originated from a single anatomical structure in a common ancestor of the two species ...
Biology – Unit 3, Chapter 8, Sections 1 through 7
... 1. What is a central theme in all fields of biology? 2. What did Carolus Linnaeus develop that is still in use by scientists today? 3. What idea did Gorges Louis Leclerc de Buffon propose? 4. What idea did Erasmus Darwin propose? 5. What did Lamarck say caused an organism’s behavior to change and wh ...
... 1. What is a central theme in all fields of biology? 2. What did Carolus Linnaeus develop that is still in use by scientists today? 3. What idea did Gorges Louis Leclerc de Buffon propose? 4. What idea did Erasmus Darwin propose? 5. What did Lamarck say caused an organism’s behavior to change and wh ...
Notes part 1
... iii. Therefore – those individuals “more fit” survive to produce offspring with their “more fit” characteristics iv. Example – peppered moths (see slide) E. Adaptations – variations in populations that have an advantage over others in the same population (refer back to peppered moths) ...
... iii. Therefore – those individuals “more fit” survive to produce offspring with their “more fit” characteristics iv. Example – peppered moths (see slide) E. Adaptations – variations in populations that have an advantage over others in the same population (refer back to peppered moths) ...
Origin of Life
... Punctuated Equilibrium – speciation occurs during brief periods of rapid genetic change ...
... Punctuated Equilibrium – speciation occurs during brief periods of rapid genetic change ...
SBI 3U1 – EVOLUTION UNIT TEST REVIEW
... 1. State the main contributions of the following scientists to the development of thought on evolution: Buffon, Lamarck, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace, Darwin. 2. How do Lamarck’s explanations of adaptation differ from those of Darwin? 3. Define genetic bottlenecks and the founder effect. Give an example ...
... 1. State the main contributions of the following scientists to the development of thought on evolution: Buffon, Lamarck, Lyell, Malthus, Wallace, Darwin. 2. How do Lamarck’s explanations of adaptation differ from those of Darwin? 3. Define genetic bottlenecks and the founder effect. Give an example ...
Chapter 16 Study Guide answers 3
... The older the fossils, the more common skeletal features they both will have. Common Ancestor 14. If humans and cows have similar structures it means they have a common ancestor. ...
... The older the fossils, the more common skeletal features they both will have. Common Ancestor 14. If humans and cows have similar structures it means they have a common ancestor. ...
Assessment
... _____ 3. What is suggested by the similarity of early embryos of different species of vertebrates? a. no evolutionary relationship between the groups b. recent common ancestry c. similar environments in the past d. evolution from a distant common ancestor _____ 4. Some organisms that share a common ...
... _____ 3. What is suggested by the similarity of early embryos of different species of vertebrates? a. no evolutionary relationship between the groups b. recent common ancestry c. similar environments in the past d. evolution from a distant common ancestor _____ 4. Some organisms that share a common ...
here - My Haiku
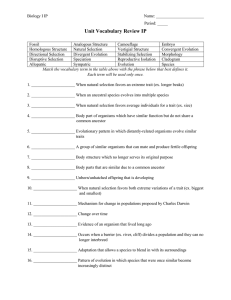
... Match the vocabulary term in the table above with the phrase below that best defines it. Each term will be used only once. 1. _____________________ When natural selection favors an extreme trait (ex. longer beaks) 2. _____________________ When an ancestral species evolves into multiple species 3. __ ...
... Match the vocabulary term in the table above with the phrase below that best defines it. Each term will be used only once. 1. _____________________ When natural selection favors an extreme trait (ex. longer beaks) 2. _____________________ When an ancestral species evolves into multiple species 3. __ ...
Natural Selection PowerPoint
... French naturalist, proposed a theory that organisms were driven by some inner force toward greater complexity. But thought that org. could pass on traits to their offspring that they acquired during their lives. (“Lamarckism”, proposed in 1809) ...
... French naturalist, proposed a theory that organisms were driven by some inner force toward greater complexity. But thought that org. could pass on traits to their offspring that they acquired during their lives. (“Lamarckism”, proposed in 1809) ...
Homology– Evidence of a Common Ancestor
... working or useful sections in other creatures. Even in human DNA, you can see the broken parts of code that were important in an organism long ago ...
... working or useful sections in other creatures. Even in human DNA, you can see the broken parts of code that were important in an organism long ago ...
created the theory of acquired traits. Darwin later explained that this
... Artificial selection – when humans choose the traits and control breeding ...
... Artificial selection – when humans choose the traits and control breeding ...
Evolution
... Structures that are different but serve the same or similar purposes An example is the torpedo body shape of porpoises and sharks ...
... Structures that are different but serve the same or similar purposes An example is the torpedo body shape of porpoises and sharks ...
Chapter 15
... b. useful support for his theory. c. interesting but unrelated to the evolution of modern species. d. evidence that traits are acquired through use or disuse. ______ 7. Molecular evidence in support of natural selection includes a. the nearly universal genetic code. b. the presence of vestigial stru ...
... b. useful support for his theory. c. interesting but unrelated to the evolution of modern species. d. evidence that traits are acquired through use or disuse. ______ 7. Molecular evidence in support of natural selection includes a. the nearly universal genetic code. b. the presence of vestigial stru ...
Applied Bio Ch. 14.2 Evidence ppt notes
... inference on which Darwin's theory of natural selection is based? • a. Variations among individuals exist in a population. b. Poorly adapted individuals never produce offspring. c. Individuals whose inherited characteristics give them advantages in their environment will generally produce more offsp ...
... inference on which Darwin's theory of natural selection is based? • a. Variations among individuals exist in a population. b. Poorly adapted individuals never produce offspring. c. Individuals whose inherited characteristics give them advantages in their environment will generally produce more offsp ...
15.2 Evidence of Evolution I. Support for Evolution
... Support for Evolution - theory of evolution states that all organisms on Earth have descended from a common ancestor a. The fossil record i. Fossils provide evidence of evolution ii. Ancient species share similarities with current species iii. Fossil record important for determining ancestry of orga ...
... Support for Evolution - theory of evolution states that all organisms on Earth have descended from a common ancestor a. The fossil record i. Fossils provide evidence of evolution ii. Ancient species share similarities with current species iii. Fossil record important for determining ancestry of orga ...
Evolution Classification Test Review
... 5. What is a vestigial structure? Traces of homologous organs that are no longer used by the modern organism. Example: appendix or whales’ femur/pelvis 6. What is a homologous structure? Body parts that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues: evidence of descent from ...
... 5. What is a vestigial structure? Traces of homologous organs that are no longer used by the modern organism. Example: appendix or whales’ femur/pelvis 6. What is a homologous structure? Body parts that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues: evidence of descent from ...
Ideas That Shaped Darwin`s Thinking
... individuals of a population produce new individuals In natural selection, traits being selected contribute to an organisms fitness (over time) NS cannot be seen directly; it can only be observed as changes in a pop. over many successive generations ...
... individuals of a population produce new individuals In natural selection, traits being selected contribute to an organisms fitness (over time) NS cannot be seen directly; it can only be observed as changes in a pop. over many successive generations ...
Vestigiality

Vestigiality refers to genetically determined structures or attributes that have apparently lost most or all of their ancestral function in a given species, but have been retained during the process of evolution. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful. Typical examples of both types occur in the loss of flying capability in island-dwelling species.