Principles of Biology ______Lake Tahoe
... 13. Explain why plants cannot extract all of the water in soil. 14. Explain how the presence of clay in soil helps prevent the leaching of mineral cations. 15. Define cation exchange, explain why it is necessary for plant nutrition, and describe how plants can stimulate the process. 16. Explain why ...
... 13. Explain why plants cannot extract all of the water in soil. 14. Explain how the presence of clay in soil helps prevent the leaching of mineral cations. 15. Define cation exchange, explain why it is necessary for plant nutrition, and describe how plants can stimulate the process. 16. Explain why ...
Estuarine and coastal ocean environments
... further accumulation - as sea level rises, marsh is inundated more frequently, and accumulation rate of sediment and peat increases. - When rate of sedimentation does not kept up with subsidence, marshland is lost. - Sea level rise due to global warming could accelerate loss of marshland. ...
... further accumulation - as sea level rises, marsh is inundated more frequently, and accumulation rate of sediment and peat increases. - When rate of sedimentation does not kept up with subsidence, marshland is lost. - Sea level rise due to global warming could accelerate loss of marshland. ...
Weathering and Erosion
... A rapid, downslope movement of a thin layer of material on a curved surface. Common on thick soils with moderate slopes and more so after it rains. e) Avalanches Landslides in mountainous areas with thick accumulations of snow. More common in early winter when snow accumulates on warm ground or due ...
... A rapid, downslope movement of a thin layer of material on a curved surface. Common on thick soils with moderate slopes and more so after it rains. e) Avalanches Landslides in mountainous areas with thick accumulations of snow. More common in early winter when snow accumulates on warm ground or due ...
Agricultural nutrient problems and the MAP IV water quality goals
... Soil organic matter maintenance within the current legislation Soil quality depends in part on a sufficient amount of soil organic matter (SOM). Therefore organic matter (OM) has to be regularly applied to the soil because crop residues are not enough to compensate for the mineralisation from SOM. T ...
... Soil organic matter maintenance within the current legislation Soil quality depends in part on a sufficient amount of soil organic matter (SOM). Therefore organic matter (OM) has to be regularly applied to the soil because crop residues are not enough to compensate for the mineralisation from SOM. T ...
Lesson 1 water - SLC Geog A Level Blog
... • The rate of infiltration of water into the soil or of percolation into rocks depends on the porosity and permeability of the material. Sand has large pores and this allows water to infiltrate quickly at a rate of about 200mm/hr whilst in clay the rate is only about 5mm/hour. Both materials are por ...
... • The rate of infiltration of water into the soil or of percolation into rocks depends on the porosity and permeability of the material. Sand has large pores and this allows water to infiltrate quickly at a rate of about 200mm/hr whilst in clay the rate is only about 5mm/hour. Both materials are por ...
Erosion and Deposits
... formations. Waves also carry small rocks and sand which only add to the effect of the waves crashing on rocks. The waves can also force water into cracks in the shore, breaking it up with more pressure. Although waves will typically erode up to 1 to 1 ½ metres of shoreline a year, storms and other f ...
... formations. Waves also carry small rocks and sand which only add to the effect of the waves crashing on rocks. The waves can also force water into cracks in the shore, breaking it up with more pressure. Although waves will typically erode up to 1 to 1 ½ metres of shoreline a year, storms and other f ...
Community Succession
... A forest is characterized by presence of herbs, shrubs, mosses, shadeloving plants and trees including decomposers. The overall changes taking place during development of successional communities are building up of substratum, shallowing of water, addition of humus and minerals, soil building and ae ...
... A forest is characterized by presence of herbs, shrubs, mosses, shadeloving plants and trees including decomposers. The overall changes taking place during development of successional communities are building up of substratum, shallowing of water, addition of humus and minerals, soil building and ae ...
File
... Habitat islands are a habitat surrounded by a different one, such as a national park surrounded by logging, mining, etc. activities. a. Habitat fragmentation leads to species vulnerability to predators, disease, etc. ...
... Habitat islands are a habitat surrounded by a different one, such as a national park surrounded by logging, mining, etc. activities. a. Habitat fragmentation leads to species vulnerability to predators, disease, etc. ...
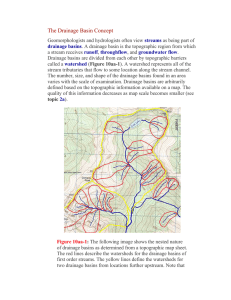
The Drainage Basin Concept
... The Drainage Basin Concept Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as being part of drainage basins. A drainage basin is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and groundwater flow. Drainage basins are divided from each other by topographic barriers cal ...
... The Drainage Basin Concept Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as being part of drainage basins. A drainage basin is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and groundwater flow. Drainage basins are divided from each other by topographic barriers cal ...
The way rocks are broken down into smaller bits and soil, either by
... grains and holds water easily. It can stick together. ...
... grains and holds water easily. It can stick together. ...
Soils 2 - Coastalzone
... Soil color isimportant for several reasons: first it is an observable measure of the orgainic content, but it may also be an indicator of drainage and aeration. To the trained eye soil color may also indicte the history of the soil. Soil color are important features and are used as part of a soil d ...
... Soil color isimportant for several reasons: first it is an observable measure of the orgainic content, but it may also be an indicator of drainage and aeration. To the trained eye soil color may also indicte the history of the soil. Soil color are important features and are used as part of a soil d ...
Agricultural Systems and Food Production
... This is a serious problem in arid and semi-arid areas and affects 7% of the world’s land area. It occurs when transpiration from plants and evaporation exceed the amount of incoming precipitation in regions where the water-table is close to the surface. The presence of salts is harmful to many p ...
... This is a serious problem in arid and semi-arid areas and affects 7% of the world’s land area. It occurs when transpiration from plants and evaporation exceed the amount of incoming precipitation in regions where the water-table is close to the surface. The presence of salts is harmful to many p ...
Mechanisms of soil erosion as affected by climatatic and
... Stabilisation of different aggregate size fractions is due to different mechanisms (micro- and macro-aggregates) - Management should have positive effect on aggregates in all size classes Climate change - changes in temporal distribution of precipitation - Challenge for soil management Helena Soinne ...
... Stabilisation of different aggregate size fractions is due to different mechanisms (micro- and macro-aggregates) - Management should have positive effect on aggregates in all size classes Climate change - changes in temporal distribution of precipitation - Challenge for soil management Helena Soinne ...
Natural Capital - World Resources Report
... ater availability is arguably the world’s most pressing resource issue. Water is essential for all living things, has shaped human societies for millennia, and is the basis of business activities such as cooling, food processing, chemical synthesis, and irrigation. Growing water scarcity and alarmin ...
... ater availability is arguably the world’s most pressing resource issue. Water is essential for all living things, has shaped human societies for millennia, and is the basis of business activities such as cooling, food processing, chemical synthesis, and irrigation. Growing water scarcity and alarmin ...
How Full is Full?
... science, permeability is defined qualitatively as the ease with which gases, liquids, or plant roots penetrate or pass through a soil mass or layer. The permeability of a small soil sample will be interpreted in this activity by measuring the amount of water traveling through the soil during a given ...
... science, permeability is defined qualitatively as the ease with which gases, liquids, or plant roots penetrate or pass through a soil mass or layer. The permeability of a small soil sample will be interpreted in this activity by measuring the amount of water traveling through the soil during a given ...
Module 2, Lesson 3 - University of Nevada Cooperative Extension
... available water to support the plants? Are your soils appropriate for growing the plants you selected? ...
... available water to support the plants? Are your soils appropriate for growing the plants you selected? ...
Every thing has its place, every species its habitat
... certain number of occupants and the other another set of occupants. The edge where the two habitats meet will have occupants from both habitats. So there will be more occupants in the edge where two habitats meet. And biodiversity will be greater in an edge environment. Habitats are quite different ...
... certain number of occupants and the other another set of occupants. The edge where the two habitats meet will have occupants from both habitats. So there will be more occupants in the edge where two habitats meet. And biodiversity will be greater in an edge environment. Habitats are quite different ...
Lab 12
... The 17 elements required by plants are obtained from the soil, water and air. Fourteen of these elements must be supplied by the soil. Six of the soil elements required by plants are needed in relatively large amounts and are usually added to the soil through fertilizer or lime. These elements are t ...
... The 17 elements required by plants are obtained from the soil, water and air. Fourteen of these elements must be supplied by the soil. Six of the soil elements required by plants are needed in relatively large amounts and are usually added to the soil through fertilizer or lime. These elements are t ...
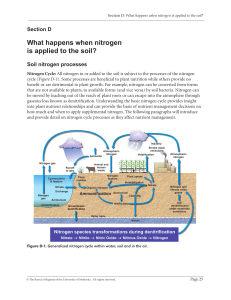
What happens when nitrogen is applied to the soil?
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
Landscape position effects on water deficit, corn growth, and gene
... 100 mg/plant, p=0.05) than toeslope plants ...
... 100 mg/plant, p=0.05) than toeslope plants ...
Bonsai Box™ Specimen Crepe Myrtle tree seed | bonsai growing
... protect the bark and branches when twisting the wire. Remove wire if it begins to cut into wood. re-potting | It is necessary to repot your bonsai when the root system becomes root bound. Crepe Myrtle need to be re-potted every 1-2 years in late winter or spring. You may use the same pot or choose a ...
... protect the bark and branches when twisting the wire. Remove wire if it begins to cut into wood. re-potting | It is necessary to repot your bonsai when the root system becomes root bound. Crepe Myrtle need to be re-potted every 1-2 years in late winter or spring. You may use the same pot or choose a ...
What is Race to the Top?
... PreK-2: Objects and materials can be sorted and described by their properties, living things are different than nonliving things, properties of objects and materials can change, water and air have specific properties that can be observed and measured. 3rd Grade Concepts The properties of air and wat ...
... PreK-2: Objects and materials can be sorted and described by their properties, living things are different than nonliving things, properties of objects and materials can change, water and air have specific properties that can be observed and measured. 3rd Grade Concepts The properties of air and wat ...
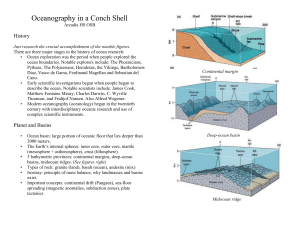
InAConchShell - some tryout study material
... Tides: waves with very long wavelengths that cause the sea level to rise and fall daily. Tidal range: vertical distance between high tide (crest) and low tide (trough). Tides can be diurnal (period: 1 day, actually 24 hr 50 min) or semidiurnal (recur twice daily, 12 hr 25 min), or mixed When tidal a ...
... Tides: waves with very long wavelengths that cause the sea level to rise and fall daily. Tidal range: vertical distance between high tide (crest) and low tide (trough). Tides can be diurnal (period: 1 day, actually 24 hr 50 min) or semidiurnal (recur twice daily, 12 hr 25 min), or mixed When tidal a ...
Weathering, Soil, and Mass Movements
... mineral composition. In nature three physical process are especially important causes of weathering: frost wedging, unloading, and biological ...
... mineral composition. In nature three physical process are especially important causes of weathering: frost wedging, unloading, and biological ...
Soil salinity control
Soil salinity control relates to controlling the problem of soil salinity and reclaiming salinized agricultural land.The aim of soil salinity control is to prevent soil degradation by salination and reclaim already salty (saline) soils. Soil reclamation is also called soil improvement, rehabilitation, remediation, recuperation, or amelioration.The primary man-made cause of salinization is irrigation. River water or groundwater used in irrigation contains salts, which remain behind in the soil after the water has evaporated.The primary method of controlling soil salinity is to permit 10-20% of the irrigation water to leach the soil, be drained and discharged through an appropriate drainage system. The salt concentration of the drainage water is normally 5 to 10 times higher than that of the irrigation water, thus salt export matches salt import and it will not accumulate.