New Results on Snow and Runoff Research
... Infiltration and the Water Table • After a storm event, water infiltrates through the unsaturated zone, and recharges the ground water reservoir • This raises the elevation of the water table, increasing the gradient and the flow of ground water away from the recharge point. This results in increas ...
... Infiltration and the Water Table • After a storm event, water infiltrates through the unsaturated zone, and recharges the ground water reservoir • This raises the elevation of the water table, increasing the gradient and the flow of ground water away from the recharge point. This results in increas ...
Lindsey`s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
... Lindsey’s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This is an extreme generalization of soil orders of Canada. More information about each order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be dif ...
Hydrologic Cycle (Water Cycle)
... the aquifer. Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. Percolation concerns the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials. The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, ...
... the aquifer. Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. Percolation concerns the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials. The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, ...
Protecting Resources
... ◦ sand- biggest grains; most space ◦ Silt- grains just large enough to see ◦ Clay- the grains too small to see; least space between particles- holds water ...
... ◦ sand- biggest grains; most space ◦ Silt- grains just large enough to see ◦ Clay- the grains too small to see; least space between particles- holds water ...
ReLecture18
... Water table: the depth at which soil is saturated. It can be variable with time and topography Soil zone: unsaturated zone of the top soil layer Zone of saturation: completely saturated zone below the water table Capillary fringe: a thin layer immediately above the water table and affected by the ca ...
... Water table: the depth at which soil is saturated. It can be variable with time and topography Soil zone: unsaturated zone of the top soil layer Zone of saturation: completely saturated zone below the water table Capillary fringe: a thin layer immediately above the water table and affected by the ca ...
Sathyabama University B.E May 2011Soil
... equal to 430 ml passed down in 10 minutes, under an effective constant head of 40 cm. On over-drying, the test specimen has mass of 498 g. Taking the specific gravity of soil solids as 2.65, calculate the seepage velocity of water during the test. (or) 14. For the soil profile shown in fig.1, determ ...
... equal to 430 ml passed down in 10 minutes, under an effective constant head of 40 cm. On over-drying, the test specimen has mass of 498 g. Taking the specific gravity of soil solids as 2.65, calculate the seepage velocity of water during the test. (or) 14. For the soil profile shown in fig.1, determ ...
SoilPaintingTemplates - Montana Soil and Water Conservation Society
... underground, and the salts go back down to where they don’t harm plants on the surface. ...
... underground, and the salts go back down to where they don’t harm plants on the surface. ...
Brandon Okafor
... S = ∫(Cl,o,r,p,t); Climate, Organisms, Relief, parent rock, time 12 soil orders, but only 3 will be important to this project ...
... S = ∫(Cl,o,r,p,t); Climate, Organisms, Relief, parent rock, time 12 soil orders, but only 3 will be important to this project ...
The Global Hydrological Cycle
... •Stream / Surface Run Off: Most water returns to the sea in the form of rivers. •Evapotranspiration: evaporation of moisture from vegetation •Ground water Flow: Some water returns to the sea as groundwater through soil and rocks. •Infiltration: The point at which rainfall seeps into soil. •Percolati ...
... •Stream / Surface Run Off: Most water returns to the sea in the form of rivers. •Evapotranspiration: evaporation of moisture from vegetation •Ground water Flow: Some water returns to the sea as groundwater through soil and rocks. •Infiltration: The point at which rainfall seeps into soil. •Percolati ...
Bloomington Community Orchard Fertility and Species Apple – also
... host of other poorly understood activities such as pollen tube growth, fruit set, etcetera. 3 oz Borax per 1000 sq. ft. is about 8 lbs borax per acre (or about 1 lb total boron). other nutrient ...
... host of other poorly understood activities such as pollen tube growth, fruit set, etcetera. 3 oz Borax per 1000 sq. ft. is about 8 lbs borax per acre (or about 1 lb total boron). other nutrient ...
Soil Unit Terminology
... Soil Unit Terminology List ____________________________________________________________________________________ Required Terms: _____________________________________________________________________________________ Acid Precipitation: ...
... Soil Unit Terminology List ____________________________________________________________________________________ Required Terms: _____________________________________________________________________________________ Acid Precipitation: ...
Earth Systems Review
... This diagram shows layers of soil and rock from below a forest floor. Which of these conclusions is best supported by the information found in this diagram? A A body of water once covered the area. B The forest was made up of oak trees. C Fish were the first animals in the area. D The area was plan ...
... This diagram shows layers of soil and rock from below a forest floor. Which of these conclusions is best supported by the information found in this diagram? A A body of water once covered the area. B The forest was made up of oak trees. C Fish were the first animals in the area. D The area was plan ...
Influence of different water saturation levels for mobility of Antimony
... These elements are released due to weathering of spent bullets. The bullet core consists of 2-5 wt% Sb for getting hard lead alloys. A potential soil remediation method is to add Febased sorbents, which are good sorbents for Antimony and other metals. This may represents a feasible stabilization of ...
... These elements are released due to weathering of spent bullets. The bullet core consists of 2-5 wt% Sb for getting hard lead alloys. A potential soil remediation method is to add Febased sorbents, which are good sorbents for Antimony and other metals. This may represents a feasible stabilization of ...
Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems
... Acid rain has increased the acidity of bodies of water – killing marine life Run off from roads that have been treated with salt increases the salt content of water – killing marine life ...
... Acid rain has increased the acidity of bodies of water – killing marine life Run off from roads that have been treated with salt increases the salt content of water – killing marine life ...
Sustainable Food Production
... orchards, vineyards, vegetable and rice production and pasture for dairy cows and sheep. Australia has the highest water storage system in the world, where 70% is used for irrigation. To support the irrigation systems, the natural landscape is changed , dams and channels are built and paddocks are l ...
... orchards, vineyards, vegetable and rice production and pasture for dairy cows and sheep. Australia has the highest water storage system in the world, where 70% is used for irrigation. To support the irrigation systems, the natural landscape is changed , dams and channels are built and paddocks are l ...
The water cycle is also affected by deforestation. Trees extract
... Shrinking forest cover lessens the landscape's capacity to intercept, retain and transpire precipitation. Instead of trapping precipitation, which then percolates to groundwater systems, deforested areas become sources of surface water runoff, which moves much faster than subsurface flows. That quic ...
... Shrinking forest cover lessens the landscape's capacity to intercept, retain and transpire precipitation. Instead of trapping precipitation, which then percolates to groundwater systems, deforested areas become sources of surface water runoff, which moves much faster than subsurface flows. That quic ...
Chemical Reactions, Chemical Equations, Electricity
... Saturated Zone – the area of permeable rock or soil that is totally filled or saturated with water Unsaturated Zone – the layer of rocks and soil above the water table, no water Aquifer – underground layer of rock or sediment that holds water and allows water to flow through it Artesian Well – water ...
... Saturated Zone – the area of permeable rock or soil that is totally filled or saturated with water Unsaturated Zone – the layer of rocks and soil above the water table, no water Aquifer – underground layer of rock or sediment that holds water and allows water to flow through it Artesian Well – water ...
Non-permeable rocks haves no spaces between the particles, so
... will tell you how much water a rock will absorb ...
... will tell you how much water a rock will absorb ...
1-20-15 About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil
... Soil - a complex plant supporting system made up of disintegrated rock, remains and wastes of organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil form ...
... Soil - a complex plant supporting system made up of disintegrated rock, remains and wastes of organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil form ...
physical geology-final exam
... 45. A “graded river” can be defined as one in which there is No Deposition-No Erosion or that Erosion is equal to Deposition 46. Braided streams are generally associated with the Delta setting 47. The distribution of sediment size in an Alluvial Fan varies from finest near the Mountain/Hill becoming ...
... 45. A “graded river” can be defined as one in which there is No Deposition-No Erosion or that Erosion is equal to Deposition 46. Braided streams are generally associated with the Delta setting 47. The distribution of sediment size in an Alluvial Fan varies from finest near the Mountain/Hill becoming ...
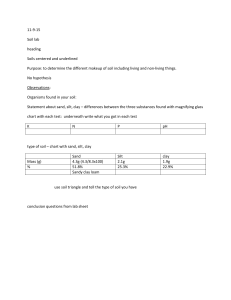
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
Lecture #3 Ways We Use and Abuse Soil
... Ways We Use and Abuse Soil • Approximately 12.5% of the earth’s land area is currently in agricultural production. – Up to four times as much could potentially be converted to agricultural use. • Much of this additional land suffers from constraints such as steep slope or poor drainage. • Global cl ...
... Ways We Use and Abuse Soil • Approximately 12.5% of the earth’s land area is currently in agricultural production. – Up to four times as much could potentially be converted to agricultural use. • Much of this additional land suffers from constraints such as steep slope or poor drainage. • Global cl ...
Soil Notes PowerPoint
... Clay - < .002 mm in size. Water clings to tiny particles holding larger soil particles together forming clumps called aggregates. Aggregates like gravel provide drainage channels for water. Water will not drain in soils with a lot of clay. Clay is easily compacted, crushing air and water pore space. ...
... Clay - < .002 mm in size. Water clings to tiny particles holding larger soil particles together forming clumps called aggregates. Aggregates like gravel provide drainage channels for water. Water will not drain in soils with a lot of clay. Clay is easily compacted, crushing air and water pore space. ...
Soil salinity control
Soil salinity control relates to controlling the problem of soil salinity and reclaiming salinized agricultural land.The aim of soil salinity control is to prevent soil degradation by salination and reclaim already salty (saline) soils. Soil reclamation is also called soil improvement, rehabilitation, remediation, recuperation, or amelioration.The primary man-made cause of salinization is irrigation. River water or groundwater used in irrigation contains salts, which remain behind in the soil after the water has evaporated.The primary method of controlling soil salinity is to permit 10-20% of the irrigation water to leach the soil, be drained and discharged through an appropriate drainage system. The salt concentration of the drainage water is normally 5 to 10 times higher than that of the irrigation water, thus salt export matches salt import and it will not accumulate.