part 2
... Other players’ types can enter into a player’s payoff function In the Cournot example, firm 1 only cares about firm 2’s type because it affects his action In some games, one player’s type can directly enter into another player’s payoff function ...
... Other players’ types can enter into a player’s payoff function In the Cournot example, firm 1 only cares about firm 2’s type because it affects his action In some games, one player’s type can directly enter into another player’s payoff function ...
Non-zero sum games: example: Hawk vs
... To be realistic we would need to consider this as an N unit (company) game, but for simplicity we can consider one company, Company A, as the row player, making their decision, considering the possible moves of the other N –1 companies, who then constitute the column player. ...
... To be realistic we would need to consider this as an N unit (company) game, but for simplicity we can consider one company, Company A, as the row player, making their decision, considering the possible moves of the other N –1 companies, who then constitute the column player. ...
SCIT1003 Chapter 3: Prisoner*s Dilemma Non
... • Traditional applications of game theory attempt to find equilibria in games. • In an equilibrium, each player is playing the strategy that is a "best response" to the strategies of the other players. No one is likely to change his strategy given the strategic choices of the others. • Equilibrium i ...
... • Traditional applications of game theory attempt to find equilibria in games. • In an equilibrium, each player is playing the strategy that is a "best response" to the strategies of the other players. No one is likely to change his strategy given the strategic choices of the others. • Equilibrium i ...
Economics for Business
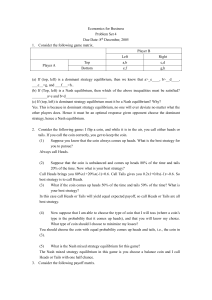
... (a) If (top, left) is a dominant strategy equilibrium, then we know that a>_e____, b>__d____, ___c__>g, and ___f___>h.. (b) If (Top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, then which of the above inequalities must be satisfied? ________a>e and b>d______________________ (c) If (top, left) is dominant strategy ...
... (a) If (top, left) is a dominant strategy equilibrium, then we know that a>_e____, b>__d____, ___c__>g, and ___f___>h.. (b) If (Top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, then which of the above inequalities must be satisfied? ________a>e and b>d______________________ (c) If (top, left) is dominant strategy ...
Note
... Theorem 30 (Nash) Every mixed extension of a finite strategic game has a Nash equilibrium. In other words, every finite strategic game has a Nash equilibrium in mixed strategies. In the case of the Matching Pennies game it is straightforward to check that ( 12 · H + 12 · T, 21 · H + 12 · T ) is suc ...
... Theorem 30 (Nash) Every mixed extension of a finite strategic game has a Nash equilibrium. In other words, every finite strategic game has a Nash equilibrium in mixed strategies. In the case of the Matching Pennies game it is straightforward to check that ( 12 · H + 12 · T, 21 · H + 12 · T ) is suc ...
Managing Expectations
... housing and privileges at each house so no child support. The child support is not for the parent, it is for the parent to provide a nearly equivalent environment as the parent’s house who is paying the child support. If one parent made more than the other, the less money earning parent would not be ...
... housing and privileges at each house so no child support. The child support is not for the parent, it is for the parent to provide a nearly equivalent environment as the parent’s house who is paying the child support. If one parent made more than the other, the less money earning parent would not be ...
Part 3.6
... Such a matrix faces 2 players with identical decisions, since a choice of strategy j by X and i by Y win aij for X, and a choice of j by Y and i by X wins the same amount aij for Y (because a ji -aij ). The optimal strategies for both players must be the same, and the expected payoff must be y *T ...
... Such a matrix faces 2 players with identical decisions, since a choice of strategy j by X and i by Y win aij for X, and a choice of j by Y and i by X wins the same amount aij for Y (because a ji -aij ). The optimal strategies for both players must be the same, and the expected payoff must be y *T ...
Game Theory
... One-Shot Advertising Game Equilibrium • Kellogg’s & General Mills want to maximize profits • Strategies consist of advertising campaigns • Simultaneous moves • One-shot interaction • Repeated interaction ...
... One-Shot Advertising Game Equilibrium • Kellogg’s & General Mills want to maximize profits • Strategies consist of advertising campaigns • Simultaneous moves • One-shot interaction • Repeated interaction ...
Nash equilibrium and its proof using Fix Point Theorems
... players, A, B, and C. Let p̄, q̄, and r̄ be their probability distributions over the action sets. And α, β, and γ are their payoff functions. P (q̄, r̄) denotes the set of best-play p̄′ s. Not hard to see P (q̄, r̄) is a convex closed set. Similarly, we define Q(r̄, p̄) and R(p̄, q̄). Define functio ...
... players, A, B, and C. Let p̄, q̄, and r̄ be their probability distributions over the action sets. And α, β, and γ are their payoff functions. P (q̄, r̄) denotes the set of best-play p̄′ s. Not hard to see P (q̄, r̄) is a convex closed set. Similarly, we define Q(r̄, p̄) and R(p̄, q̄). Define functio ...
Bayesian-Nash games ∗ Sergei Izmalkov
... The strategies depend on the procedure that is used to decide on whether to build and on contributions. For example, for the case of private voluntary contributions, each playerPcontributes ci ∈ Si = R+ . The corresponding mechanism sets mi = ci , the project is built, b = 1, only if i∈N mi ≥ c. To ...
... The strategies depend on the procedure that is used to decide on whether to build and on contributions. For example, for the case of private voluntary contributions, each playerPcontributes ci ∈ Si = R+ . The corresponding mechanism sets mi = ci , the project is built, b = 1, only if i∈N mi ≥ c. To ...
Frank Page abstract - Lunchtime
... (1992), we show that each game in the class has a Nash payoff correspondence that is a -correspondence - or equivalently, is a correspondence having the -limit property.1 We then show that if a Nash payoff correspondence has the -limit property, then its induced Nash payoff selection correspondence ...
... (1992), we show that each game in the class has a Nash payoff correspondence that is a -correspondence - or equivalently, is a correspondence having the -limit property.1 We then show that if a Nash payoff correspondence has the -limit property, then its induced Nash payoff selection correspondence ...