Blood type Antigen Antibody
... 1 RBC contains 280 million hemoglobin molecules Men- 5 million cells/mm3 Women- 4.5 million cells/mm3 Life span 100-120 days and then destroyed in spleen (RBC graveyard) ...
... 1 RBC contains 280 million hemoglobin molecules Men- 5 million cells/mm3 Women- 4.5 million cells/mm3 Life span 100-120 days and then destroyed in spleen (RBC graveyard) ...
Guide to Common Laboratory Tests for Eating Disorder Patients
... balance as well as blood sugar and blood proteins Blood sugar level at time of testing ...
... balance as well as blood sugar and blood proteins Blood sugar level at time of testing ...
all about anaemia - Kidney Health Australia
... Erythropoietin is made by the kidney and acts on the bone marrow to make red blood cells. Erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESAs) are similar to the naturally made erythropoietin and are used to treat anaemia if you have kidney disease. It is similar to people with diabetes receiving insulin to ...
... Erythropoietin is made by the kidney and acts on the bone marrow to make red blood cells. Erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESAs) are similar to the naturally made erythropoietin and are used to treat anaemia if you have kidney disease. It is similar to people with diabetes receiving insulin to ...
Know your Blood - Dubai Healthcare City
... 2014 theme for World Blood Donor Day is ‘Safe blood for saving mothers’ ...
... 2014 theme for World Blood Donor Day is ‘Safe blood for saving mothers’ ...
Dr. Tessa King, a veterinarian at Pilchuck Veterinary Hospital
... Abnormal changes on a CBC could include anemia (low red blood-cell count), leukocytosis (high white blood-cell count) or thrombocytopenia (low platelets). Anemia has a wide range of causes, and finding a low red blood-cell count, depending on the severity, usually warrants searching for a cause. The ...
... Abnormal changes on a CBC could include anemia (low red blood-cell count), leukocytosis (high white blood-cell count) or thrombocytopenia (low platelets). Anemia has a wide range of causes, and finding a low red blood-cell count, depending on the severity, usually warrants searching for a cause. The ...
Chapter 20 Blood - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... c) Enucleated- Survive 120 days in circulation, Destroyed in liver & spleen. d) Hemoglobin: (Hb) Four subunit protein. Each subunit contains 1 heme group. Each heme group contains an iron (Fe) atom which binds to oxygen. This is why we need iron in the diet! 280 million molecules of Hb in one RBC! - ...
... c) Enucleated- Survive 120 days in circulation, Destroyed in liver & spleen. d) Hemoglobin: (Hb) Four subunit protein. Each subunit contains 1 heme group. Each heme group contains an iron (Fe) atom which binds to oxygen. This is why we need iron in the diet! 280 million molecules of Hb in one RBC! - ...
INTENDED USE - Sigma
... Reticulocyte Stain reagents are for “In Vitro Diagnostic Use.” In 1949, Brecher1 introduced the new methylene blue method for identification of reticulocytes based on precipitation of ribosomal RNA by the cationic dye. This has now replaced other methods and is the recognized procedure for t ...
... Reticulocyte Stain reagents are for “In Vitro Diagnostic Use.” In 1949, Brecher1 introduced the new methylene blue method for identification of reticulocytes based on precipitation of ribosomal RNA by the cationic dye. This has now replaced other methods and is the recognized procedure for t ...
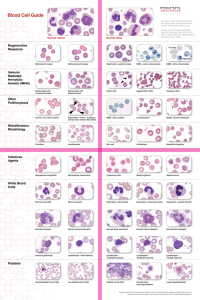
Blood Cell Guide
... cutting-edge technologies to provide you with the best hematology information available including a five-part differential and an absolute reticulocyte count. • ProCyte Dx™ Hematology Analyzer • LaserCyte® Hematology Analyzer Reference-Laboratory Hematology ...
... cutting-edge technologies to provide you with the best hematology information available including a five-part differential and an absolute reticulocyte count. • ProCyte Dx™ Hematology Analyzer • LaserCyte® Hematology Analyzer Reference-Laboratory Hematology ...
The Cardiovascular System - Waterford Public Schools
... binds four oxygen molecules so that each red blood cell carries one billion molecules of oxygen. ...
... binds four oxygen molecules so that each red blood cell carries one billion molecules of oxygen. ...
Lesson plan - Nuim Science Ed 2011
... To know that blood is made of plasma, white and red blood cells and platelets. To identify the characteristics of each blood component. To know that blood is used for transport and defence and which cells are responsible for each function. Health and safety: Oil, water, dye: ensure that noth ...
... To know that blood is made of plasma, white and red blood cells and platelets. To identify the characteristics of each blood component. To know that blood is used for transport and defence and which cells are responsible for each function. Health and safety: Oil, water, dye: ensure that noth ...
Document
... • Type O blood is known as the universal donor. At the same time because it has both A and B antibodies, individuals with Type O blood can only receive blood from other Type O donors. • Type A blood can be donated to individuals with Type A and Type AB blood. This is because Type A blood will not ...
... • Type O blood is known as the universal donor. At the same time because it has both A and B antibodies, individuals with Type O blood can only receive blood from other Type O donors. • Type A blood can be donated to individuals with Type A and Type AB blood. This is because Type A blood will not ...
Document
... • Type O blood is known as the universal donor. At the same time because it has both A and B antibodies, individuals with Type O blood can only receive blood from other Type O donors. • Type A blood can be donated to individuals with Type A and Type AB blood. This is because Type A blood will not ...
... • Type O blood is known as the universal donor. At the same time because it has both A and B antibodies, individuals with Type O blood can only receive blood from other Type O donors. • Type A blood can be donated to individuals with Type A and Type AB blood. This is because Type A blood will not ...
Blood Types
... main red blood cell groups are A, B, AB, and O. The letters stand for two antigens (chemical substances that can be targeted by one’s immune system) labeled A and B. Group A blood has only the A antigen, group B has only the B antigen, group AB has both, and group O has neither. You cannot donate ...
... main red blood cell groups are A, B, AB, and O. The letters stand for two antigens (chemical substances that can be targeted by one’s immune system) labeled A and B. Group A blood has only the A antigen, group B has only the B antigen, group AB has both, and group O has neither. You cannot donate ...
PowerPoint: Erythrocytes
... Protects the RBC from oxidative injury. Most common defect is deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6PD). If the pathway is deficient, intracellular oxidants can’t be neutralized and globin denatures then precipitates. The precipitates are referred to as Heinz bodies ...
... Protects the RBC from oxidative injury. Most common defect is deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6PD). If the pathway is deficient, intracellular oxidants can’t be neutralized and globin denatures then precipitates. The precipitates are referred to as Heinz bodies ...
Jake K. - Polycythemia Vera
... Phlebotomies are usually the first option the patient has. It involves a certain amount of blood (usually averaging one pint) to be drawn from the body. Because the blood is removed from the body, there are less red blood cells to affect the patient. Patients usually have phlebotomies more than once ...
... Phlebotomies are usually the first option the patient has. It involves a certain amount of blood (usually averaging one pint) to be drawn from the body. Because the blood is removed from the body, there are less red blood cells to affect the patient. Patients usually have phlebotomies more than once ...
Circulatory System and Blood
... to supply oxygen to the body tissues C. Reflects as red because of the iron atoms used in hemoglobin used to bond with the oxygen molecules D. Mixes with the other body fluids and bathes the cells directly ...
... to supply oxygen to the body tissues C. Reflects as red because of the iron atoms used in hemoglobin used to bond with the oxygen molecules D. Mixes with the other body fluids and bathes the cells directly ...
Annual Report 2014 - American Sickle Cell Anemia Association
... Taken daily by mouth, hydroxyurea reduces how adults disorders. often painful sickle cell crises and acute chest or disorders. Treating Pain ...
... Taken daily by mouth, hydroxyurea reduces how adults disorders. often painful sickle cell crises and acute chest or disorders. Treating Pain ...
sickle cell anemia - Sickle Cell Ministries
... In the United States with an estimated population of over 270 million, about 1,000 babies are born with sickle cell disease each year. In contrast, Nigeria, with an estimated 1997 population of 90 million, 45,000-90,000 babies with sickle cell disease are born each year. ...
... In the United States with an estimated population of over 270 million, about 1,000 babies are born with sickle cell disease each year. In contrast, Nigeria, with an estimated 1997 population of 90 million, 45,000-90,000 babies with sickle cell disease are born each year. ...
Redalyc.Spontaneous Echo Contrast in the Right Heart Chambers
... between red blood cells and auto-antibodies. The lower shear stress in the venous circulation (especially in septic shock) would contribute to SEC production in the right heart circulation. The absence of SEC in the left heart chambers would occur because the erythrocyte aggregation in “stacks of co ...
... between red blood cells and auto-antibodies. The lower shear stress in the venous circulation (especially in septic shock) would contribute to SEC production in the right heart circulation. The absence of SEC in the left heart chambers would occur because the erythrocyte aggregation in “stacks of co ...
“Just” an alcoholic hepatitis? August 2005
... Hematologic disorder? Hematology consult This patient’s anemia is likely anemia of chronic disease (low TIBC and high ferritin) or some marrow suppression in the setting of infection and inflammation. Macrocytic anemia of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency is a possibility (MCV in the upper limit ...
... Hematologic disorder? Hematology consult This patient’s anemia is likely anemia of chronic disease (low TIBC and high ferritin) or some marrow suppression in the setting of infection and inflammation. Macrocytic anemia of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency is a possibility (MCV in the upper limit ...
Blood Typing
... • A Rh negative mom may be exposed to an Rh antigen from the blood of a Rh positive baby during pregnancy or birth. • If Rh + cell enters Rh- mom the mother’s immune system will respond and produce antibodies against the Rh positive blood antigen ...
... • A Rh negative mom may be exposed to an Rh antigen from the blood of a Rh positive baby during pregnancy or birth. • If Rh + cell enters Rh- mom the mother’s immune system will respond and produce antibodies against the Rh positive blood antigen ...
RR Rr
... superscripts or subscripts (HR or B1). Since the trait is inherited from both parents, it is important to still use two ‘sets of letters’ as seen below: The allele for red hair (HR) is codominant with the allele for white hair (HW) in cattle. Cattle that have the genotypes HRHW are called roan becau ...
... superscripts or subscripts (HR or B1). Since the trait is inherited from both parents, it is important to still use two ‘sets of letters’ as seen below: The allele for red hair (HR) is codominant with the allele for white hair (HW) in cattle. Cattle that have the genotypes HRHW are called roan becau ...
Anemia

Anemia or anaemia (/əˈniːmiə/; also spelled anæmia) is usually defined as a decrease in the amount of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood. It can also be defined as a lowered ability of the blood to carry oxygen. When anemia comes on slowly the symptoms are often vague and may include: feeling tired, weakness, shortness of breath or a poor ability to exercise. Anemia that comes on quickly often has greater symptoms which may include: confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause.There are three main types of anemia: that due to blood loss, that due to decreased red blood cell production, and that due to increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes of blood loss include trauma and gastrointestinal bleeding, among others. Causes of decreased production include iron deficiency, a lack of vitamin B12, thalassemia and a number of neoplasms of the bone marrow among others. Causes of increased breakdown include a number of genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia, infections like malaria and some autoimmune diseases among others. It can also be classified based on the size of red blood cells and amount of hemoglobin in each cell. If the cells are small it is microcytic anemia, if they are large it is macrocytic anemia and if they are normal sized it is normocytic anemia. Diagnosis in men is based on a hemoglobin of less than 130 to 140 g/L (13 to 14 g/dL), while in women it must be less than 120 to 130 g/L (12 to 13 g/dL). Further testing is then required to determine the cause.Certain groups of individuals, such as pregnant women, benefit from the use of iron pills for prevention. Dietary supplementation, without determining the specific cause, is not recommended. The use of blood transfusions is typically based on a person's signs and symptoms. In those without symptoms they are not recommended unless hemoglobin levels are less than 60 to 80 g/L (6 to 8 g/dL). These recommendations may also apply to some people with acute bleeding. Erythropoiesis-stimulating medications are only recommended in those with severe anemia.Anemia is the most common disorder of the blood with it affecting about a quarter of people globally. Iron-deficiency anemia affects nearly 1 billion. In 2013 anemia due to iron deficiency resulted in about 183,000 deaths – down from 213,000 deaths in 1990. It is more common in females than males, among children, during pregnancy, and in the elderly. Anemia increases costs of medical care and lowers a person's productivity through a decreased ability to work. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀναιμία anaimia, meaning ""lack of blood"", from ἀν- an-, ""not"" + αἷμα haima, ""blood"".