
Magnetism Permanent magnetism Permanent magnets
... magnets that are randomly aligned. The magnetic field of the coil aligns these little magnets giving a larger field than that of the coil alone. We say that the nail becomes “magnetized”, but the effect is ...
... magnets that are randomly aligned. The magnetic field of the coil aligns these little magnets giving a larger field than that of the coil alone. We say that the nail becomes “magnetized”, but the effect is ...
Chapter 21 Magnetism
... • Some animals use natural magnets to detect Earth’s magnetic field to help them navigate. • Instead of using compasses, honeybees, rainbow trout, and homing pigeons have little pieces of magnetite in their bodies. ...
... • Some animals use natural magnets to detect Earth’s magnetic field to help them navigate. • Instead of using compasses, honeybees, rainbow trout, and homing pigeons have little pieces of magnetite in their bodies. ...
Lecture 4 Sea-Floor Spreading POLAR
... Rocks of the same age but on different continents give different polar positions The older the rock the further the calculated polar position is from the present position ...
... Rocks of the same age but on different continents give different polar positions The older the rock the further the calculated polar position is from the present position ...
SPH 3U(G) TEST
... The magnetic field lines inside a coil a. are straight b. point in the same direction c. are equally spaced d. all of the above e. none of the above ...
... The magnetic field lines inside a coil a. are straight b. point in the same direction c. are equally spaced d. all of the above e. none of the above ...
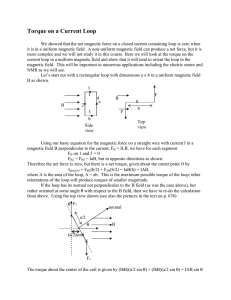
Torque on a Current Loop
... of the nucleus may depend on its local environment, since the other atoms nearby may produce small B fields themselves due to their circulating currents. NMR is so sensitive to this that it can measure a signal that tells the numbers of nuclei from atoms in different local environments. The signal l ...
... of the nucleus may depend on its local environment, since the other atoms nearby may produce small B fields themselves due to their circulating currents. NMR is so sensitive to this that it can measure a signal that tells the numbers of nuclei from atoms in different local environments. The signal l ...
The Earth is a magnet
... Atoms themselves have magnetic properties due to the spin of the atom’s electrons. Domains: Groups of atoms join so that their magnetic fields These areas of atoms are called “domains” ...
... Atoms themselves have magnetic properties due to the spin of the atom’s electrons. Domains: Groups of atoms join so that their magnetic fields These areas of atoms are called “domains” ...
Final Abstract (submitted after meeting)
... Tennessee River that did not originate from the Kingston spill. A mixing line (R2=0.85) defines the mixtures of sediment and ash from the spill in the samples. The position of each sample on this line is proportional to its concentration of magnetic material. Acid digestion of the samples yielded to ...
... Tennessee River that did not originate from the Kingston spill. A mixing line (R2=0.85) defines the mixtures of sediment and ash from the spill in the samples. The position of each sample on this line is proportional to its concentration of magnetic material. Acid digestion of the samples yielded to ...
chapter24a - Interactive Learning Toolkit
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... • some materials are naturally magnetic or can be magnetized and retain their magnetism ferromagnetic materials • other materials (iron) can be magnetized temporarily by placing them near magnets • some materials have essentially no magnetic properties copper, aluminum, plastics... • heat can de ...
... • some materials are naturally magnetic or can be magnetized and retain their magnetism ferromagnetic materials • other materials (iron) can be magnetized temporarily by placing them near magnets • some materials have essentially no magnetic properties copper, aluminum, plastics... • heat can de ...
LAB: Magnetism
... 1. Tape the measuring tape or meter stick to the table, and tape the Magnetic Field Sensor to a convenient location. The sensor should be perpendicular to the stick, with the white spot inside the rod facing along the meter stick in the direction of increasing distance. Carefully measure the locatio ...
... 1. Tape the measuring tape or meter stick to the table, and tape the Magnetic Field Sensor to a convenient location. The sensor should be perpendicular to the stick, with the white spot inside the rod facing along the meter stick in the direction of increasing distance. Carefully measure the locatio ...
Exam - Skills Commons
... C. one without magnetic flux lines D. unlike that of a permanent magnet ...
... C. one without magnetic flux lines D. unlike that of a permanent magnet ...
Magnetic stripe card
A magnetic stripe card is a type of card capable of storing data by modifying the magnetism of tiny iron-based magnetic particles on a band of magnetic material on the card. The magnetic stripe, sometimes called swipe card or magstripe, is read by swiping past a magnetic reading head. Magnetic stripe cards are commonly used in credit cards, identity cards, and transportation tickets. They may also contain an RFID tag, a transponder device and/or a microchip mostly used for business premises access control or electronic payment.Magnetic recording on steel tape and wire was invented during World War II for recording audio. In the 1950s, magnetic recording of digital computer data on plastic tape coated with iron oxide was invented. In 1960 IBM used the magnetic tape idea to develop a reliable way of securing magnetic stripes to plastic cards, under a contract with the US government for a security system. A number of International Organization for Standardization standards, ISO/IEC 7810, ISO/IEC 7811, ISO/IEC 7812, ISO/IEC 7813, ISO 8583, and ISO/IEC 4909, now define the physical properties of the card, including size, flexibility, location of the magstripe, magnetic characteristics, and data formats. They also provide the standards for financial cards, including the allocation of card number ranges to different card issuing institutions.

![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001000968_1-9cbbc8bdff99f3eeba0051a7227b6c89-300x300.png)














![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001656095_1-d86df1170441e2fe1ff7746d81978139-300x300.png)





