Nitrogen abundances in solar
... Work focus: non-LTE line formation, quantitative analysis Solar-type stars are valuable tracers of the chemical evolution of the Milky Way over cosmic history because of their longevity. They are numerous, accessible at high spectral resolution out to distances of several kpc with large telescopes, ...
... Work focus: non-LTE line formation, quantitative analysis Solar-type stars are valuable tracers of the chemical evolution of the Milky Way over cosmic history because of their longevity. They are numerous, accessible at high spectral resolution out to distances of several kpc with large telescopes, ...
Astrophysics Outline—Option E
... terms of order of magnitude. E.1.5 Describe the apparent motion of the stars/constellations over a period of a night and over a period of a year, and explain these observations in terms of the rotation and revolution of the Earth E.2 Stellar Radiation and Stellar types Assessment Statement Energy So ...
... terms of order of magnitude. E.1.5 Describe the apparent motion of the stars/constellations over a period of a night and over a period of a year, and explain these observations in terms of the rotation and revolution of the Earth E.2 Stellar Radiation and Stellar types Assessment Statement Energy So ...
26.Meikle.Supernova_2002hh
... Supernova 2002hh was discovered in the galaxy NGC 6946 in Oct. 2002. It is a type II supernova, which means that it resulted from the collapse of the core of a massive star at the end of its lifetime. The objective of the observations is to understand the nature of the explosion mechanism and the p ...
... Supernova 2002hh was discovered in the galaxy NGC 6946 in Oct. 2002. It is a type II supernova, which means that it resulted from the collapse of the core of a massive star at the end of its lifetime. The objective of the observations is to understand the nature of the explosion mechanism and the p ...
Oxygen Isotopes Anomalies in the Solar System and the G0
... Assume significant grain evolution has occurred and material fractionation has occurred (gas/ice segregation) in the disk. time this fractionation begins is a variable after fractionation begins assume that water is ...
... Assume significant grain evolution has occurred and material fractionation has occurred (gas/ice segregation) in the disk. time this fractionation begins is a variable after fractionation begins assume that water is ...
Star Formation - University of Redlands
... • Dust grains = wavelength of blue light • Dust clouds: – Opaque to blue light, UV, X-rays – Transparent to red light, IR, radio ...
... • Dust grains = wavelength of blue light • Dust clouds: – Opaque to blue light, UV, X-rays – Transparent to red light, IR, radio ...
Half Term Work On Telescopes and Lenses
... 6. “The purpose of the hyperbolic mirror in the Cassegrain reflector is to correct for spherical aberration due to the primary.” a) What do you understand by “spherical aberration” and how does this differ from “chromatic aberration. b) Why is there no chromatic aberration due to the primary mirror ...
... 6. “The purpose of the hyperbolic mirror in the Cassegrain reflector is to correct for spherical aberration due to the primary.” a) What do you understand by “spherical aberration” and how does this differ from “chromatic aberration. b) Why is there no chromatic aberration due to the primary mirror ...
Sky & Astronomy - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Babylonian, Assyrian, and Egyptian astronomers knew the approximate length of the year The Mayans of Central America developed a calendar based on the planet Venus In the British Isles, one finds spectacular monuments (such as Stonehenge) that, one now believes, were used to track the motion of the ...
... Babylonian, Assyrian, and Egyptian astronomers knew the approximate length of the year The Mayans of Central America developed a calendar based on the planet Venus In the British Isles, one finds spectacular monuments (such as Stonehenge) that, one now believes, were used to track the motion of the ...
... now-extinct radioactive isotopes. It might seem to be an odd way to make a living, studying something that no longer exists, but the payoff in understanding element formation, the formation of the Solar System, and the timing of events during its formation is well worth the effort. Robert Nichols an ...
CHAPTER 1
... 4. Phases of the Moon—the changing appearance of the Moon during its cycle—are caused by the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. 5. The phases follow the sequence of waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full Moon, waning gibbous, third (or last) quarter, waning crescent, new M ...
... 4. Phases of the Moon—the changing appearance of the Moon during its cycle—are caused by the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. 5. The phases follow the sequence of waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full Moon, waning gibbous, third (or last) quarter, waning crescent, new M ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Light elements (hydrogen, helium) formed in Big Bang • Heavier elements formed by nuclear fusion in stars and thrown into space by supernovae – Condense into new stars and planets – Elements heavier than iron form during supernovae explosions ...
... • Light elements (hydrogen, helium) formed in Big Bang • Heavier elements formed by nuclear fusion in stars and thrown into space by supernovae – Condense into new stars and planets – Elements heavier than iron form during supernovae explosions ...
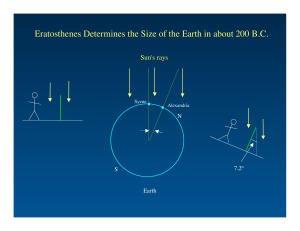
Earth
... hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silicon, magnesium and sulfur. The sun shines because it is burning hydrogen into helium in its extremely hot core. This mea ...
... hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silicon, magnesium and sulfur. The sun shines because it is burning hydrogen into helium in its extremely hot core. This mea ...
Goal: To understand how Galileo and Newton
... • It explained the reason for the motions of the planets around the sun. • Was able to derive Kepler’s Laws, and in doing so validating and verifying BOTH theories. ...
... • It explained the reason for the motions of the planets around the sun. • Was able to derive Kepler’s Laws, and in doing so validating and verifying BOTH theories. ...
holiday lights - Denver Astronomical Society
... The Angel Nebula is a dim and rarely photographed or observed emission and reflection nebula in the constellation Monoceros (the Unicorn) just off the east end of Orion’s belt. The angel figure consists of NGC 2170 and Van den Bergh 67, 68, and 69 that form the head, red heart, the wings and the flo ...
... The Angel Nebula is a dim and rarely photographed or observed emission and reflection nebula in the constellation Monoceros (the Unicorn) just off the east end of Orion’s belt. The angel figure consists of NGC 2170 and Van den Bergh 67, 68, and 69 that form the head, red heart, the wings and the flo ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... What questions might someone have about the definition? ...
... What questions might someone have about the definition? ...
Stars
... amount of energy, but there are billions of reactions per second. Each second, the Sun produces 4 × 1026 joules of energy. It would take 2,000 million nuclear power plants a whole year to produce the same amount of energy on Earth. In the Sun, and in most stars, hydrogen atoms fuse together to form ...
... amount of energy, but there are billions of reactions per second. Each second, the Sun produces 4 × 1026 joules of energy. It would take 2,000 million nuclear power plants a whole year to produce the same amount of energy on Earth. In the Sun, and in most stars, hydrogen atoms fuse together to form ...
Precession of the Earth`s Axis
... The Earth goes through one complete precession cycle in a period approximately 25,800 years. Precession of the Earth’s axis is a very slow effect, but at the level of accuracy at which astronomers work, it does need to be taken into account. The position of stars as measured in the equatorial co-ord ...
... The Earth goes through one complete precession cycle in a period approximately 25,800 years. Precession of the Earth’s axis is a very slow effect, but at the level of accuracy at which astronomers work, it does need to be taken into account. The position of stars as measured in the equatorial co-ord ...
Stellar Evolution - Harnett County High Schools Wiki
... When all the hydrogen in a star’s core is gone, star has a helium center and the outer layers have mostly hydrogen gas Some hydrogen will continue to undergo reactions in the outermost layer of the helium core; energy produced in this layer forces out layers of the star to expand and cool The star h ...
... When all the hydrogen in a star’s core is gone, star has a helium center and the outer layers have mostly hydrogen gas Some hydrogen will continue to undergo reactions in the outermost layer of the helium core; energy produced in this layer forces out layers of the star to expand and cool The star h ...
The difference between asteroids and meteorites
... coming closer to the Sun, and therefore closer to Earth. In addition to the asteroid belt, however, there have been recent discussions among astronomers about the potential existence of large number asteroids in the Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud. Asteroids are sometimes referred to as minor planets or ...
... coming closer to the Sun, and therefore closer to Earth. In addition to the asteroid belt, however, there have been recent discussions among astronomers about the potential existence of large number asteroids in the Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud. Asteroids are sometimes referred to as minor planets or ...