5.1-The process of Science - Homework
... • The duration of one rotation of the Earth, or occassionally another celestial body, on its axis. Its is measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time ...
... • The duration of one rotation of the Earth, or occassionally another celestial body, on its axis. Its is measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time ...
Earth`s Motions
... in motion is how planets were discovered. The retrograde motion of planets is more easily explained by the heliocentric model rather than the geocentric model. ...
... in motion is how planets were discovered. The retrograde motion of planets is more easily explained by the heliocentric model rather than the geocentric model. ...
Investigating the Celestial Sphere
... For the purpose of positioning and navigation, the earth is divided, horizontally and vertically into lines of latitude and longitude respectfully. Latitude is given in degrees, either decimal or DMS north or south of the equator. So here in Bury St Edmunds we are around 52° N or 52 degrees above th ...
... For the purpose of positioning and navigation, the earth is divided, horizontally and vertically into lines of latitude and longitude respectfully. Latitude is given in degrees, either decimal or DMS north or south of the equator. So here in Bury St Edmunds we are around 52° N or 52 degrees above th ...
Lecture 3
... hypothesis accordingly. But, since it was not permissible to ignore, those eight minutes pointed the road to a complete reformation in astronomy.” ...
... hypothesis accordingly. But, since it was not permissible to ignore, those eight minutes pointed the road to a complete reformation in astronomy.” ...
The Stars
... Big Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star’s nuclear fuel is depleted, it must burn out. Central Question: What are the characteristics and developmental processes of the stars? This discussion should help you to: ...
... Big Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star’s nuclear fuel is depleted, it must burn out. Central Question: What are the characteristics and developmental processes of the stars? This discussion should help you to: ...
ASTR 1010 – Spring 2016 – Study Notes Dr. Magnani
... so should be at the center of the system. Aristarchus’ arguments convinced very few people and so the idea that the Universe was geocentric became entrenched. In the second century AD, the Greek ...
... so should be at the center of the system. Aristarchus’ arguments convinced very few people and so the idea that the Universe was geocentric became entrenched. In the second century AD, the Greek ...
The History of Astronomy
... This system explains retrograde motion easily, The Earth was simply passing the by! ...
... This system explains retrograde motion easily, The Earth was simply passing the by! ...
ASTR2050 Intro A&A NAMES: ____________________ ____________________ Work sheet
... Build a scale model of the solar system, including the sizes and orbital radii of the sun and planets. Most of the data you need can be found in Kutner, Appendices B and D, and Figure 17.3. Show the units in the following lists. 1. What celestial object did you use to set the scale, and what did you ...
... Build a scale model of the solar system, including the sizes and orbital radii of the sun and planets. Most of the data you need can be found in Kutner, Appendices B and D, and Figure 17.3. Show the units in the following lists. 1. What celestial object did you use to set the scale, and what did you ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS
... gamma-rays. Thus, gamma-ray astronomy is expected to reveal astronomical objects where special conditions obtain for the acceleration of particles to high energies. The processes that lead to the production of gamma-rays in the astrophysical context are (1) nuclear excitation followed by deexcitatio ...
... gamma-rays. Thus, gamma-ray astronomy is expected to reveal astronomical objects where special conditions obtain for the acceleration of particles to high energies. The processes that lead to the production of gamma-rays in the astrophysical context are (1) nuclear excitation followed by deexcitatio ...
PowerPoint
... the right answer is, and more importantly, why it is right. – You will need to understand and be able to use any equations that have been introduced in class. Calculations using these equations will be kept simple--it is possible to do the exam without a calculator, but you can bring one if you wish ...
... the right answer is, and more importantly, why it is right. – You will need to understand and be able to use any equations that have been introduced in class. Calculations using these equations will be kept simple--it is possible to do the exam without a calculator, but you can bring one if you wish ...
ASTRONOMY 1303 Syllabus Fall 2015
... explore heavenly objects like clusters, double stars and nebulas. The date of this lab is dependent upon the weather and phase of the Moon. This fall we will also have an opportunity to view a total lunar eclipse. It is happening in the evening of the 27th of September. Weather permitting the observ ...
... explore heavenly objects like clusters, double stars and nebulas. The date of this lab is dependent upon the weather and phase of the Moon. This fall we will also have an opportunity to view a total lunar eclipse. It is happening in the evening of the 27th of September. Weather permitting the observ ...
Space – Astronomy Review
... The Universe is everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere. The study of what is beyond Earth is called Astronomy. Groups of stars that form shapes or patterns are called constellations. The Solar System consists of our Sun and all the objects that travel around it. Objects t ...
... The Universe is everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere. The study of what is beyond Earth is called Astronomy. Groups of stars that form shapes or patterns are called constellations. The Solar System consists of our Sun and all the objects that travel around it. Objects t ...
$doc.title
... collapse supernovae and long gamma-‐ray bursts is gravity, nuclear physics triggers the explosion. Neutron stars are giant nuclei in space, and short gamma-‐ray bursts are likely created when such giganBc n ...
... collapse supernovae and long gamma-‐ray bursts is gravity, nuclear physics triggers the explosion. Neutron stars are giant nuclei in space, and short gamma-‐ray bursts are likely created when such giganBc n ...
ASTRONOMICAL ERRORS
... 7. Astronomy books sometimes say that iron (specifically Fe(56)) is the most stable element. If most stable isotope means having the most binding energy per particle in the nucleus the statement that Fe(56) is the most stable isotope is false. Which isotope of which element has the highest binding e ...
... 7. Astronomy books sometimes say that iron (specifically Fe(56)) is the most stable element. If most stable isotope means having the most binding energy per particle in the nucleus the statement that Fe(56) is the most stable isotope is false. Which isotope of which element has the highest binding e ...
Astronomy Presentation WSST 2010 Final
... as much of the lecture as possible, using only what has been written in the Recall Column. This procedure helps to transfer the facts and ideas to the long term memory. • 4. Reflect. The student's own opinion is distilled from the notes. This also has the effect of training the mind to find and cate ...
... as much of the lecture as possible, using only what has been written in the Recall Column. This procedure helps to transfer the facts and ideas to the long term memory. • 4. Reflect. The student's own opinion is distilled from the notes. This also has the effect of training the mind to find and cate ...
~Crowfoot
... a) young stars still in their nursery “open cluster.” b) not physically associated, but aligned along our line of sight. c) in the nearest globular cluster to Earth. 5)2 This world is Io a) 10 AU from the sun b) Io, one of the Galilean moons of Jupiter. c) yellow due to the presence of Uranium ore o ...
... a) young stars still in their nursery “open cluster.” b) not physically associated, but aligned along our line of sight. c) in the nearest globular cluster to Earth. 5)2 This world is Io a) 10 AU from the sun b) Io, one of the Galilean moons of Jupiter. c) yellow due to the presence of Uranium ore o ...
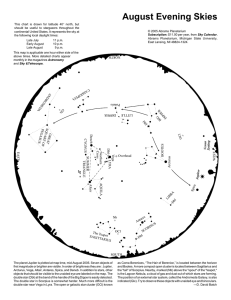
August Evening Skies
... The double star in Scorpius is somewhat harder. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
... The double star in Scorpius is somewhat harder. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. The open or galactic star cluster (OCl) known ...
Equivalent Widths and Chemical abundances Equivalent
... that we see in the Universe, its time dependence and for many of the features of galaxies that we observe. Understanding stellar evolution, the birth and death of stars and how they interact with their environments is central to understanding the evolution of galaxies. ...
... that we see in the Universe, its time dependence and for many of the features of galaxies that we observe. Understanding stellar evolution, the birth and death of stars and how they interact with their environments is central to understanding the evolution of galaxies. ...
STONEHENGE
... A circle of bluestones was commenced but the stones were dismantled after 60 had been raised. Sarsen circles and U-settings then went up, the dominant feature being the trilithon idea of a 6-ton lintel lying across pairs of 25 to 60-ton uprights. In the final stage, the bluestones were put back, som ...
... A circle of bluestones was commenced but the stones were dismantled after 60 had been raised. Sarsen circles and U-settings then went up, the dominant feature being the trilithon idea of a 6-ton lintel lying across pairs of 25 to 60-ton uprights. In the final stage, the bluestones were put back, som ...
No Slide Title
... Looking to the Future The participants in NUVA have realized with great concern that no firm plans exist to maintain an Ultraviolet observing capability for astrophysics for the future. This is despite the fact that the range of important astrophysical issues in astrophysics which require observatio ...
... Looking to the Future The participants in NUVA have realized with great concern that no firm plans exist to maintain an Ultraviolet observing capability for astrophysics for the future. This is despite the fact that the range of important astrophysical issues in astrophysics which require observatio ...
Chapter 3
... • Al-Mamun’s House of Wisdom in Baghdad was a great center of learning around A.D. 800 • With the fall of Constantinople (Istanbul) in 1453, Eastern scholars headed west to Europe, carrying knowledge that helped ignite the European Renaissance. ...
... • Al-Mamun’s House of Wisdom in Baghdad was a great center of learning around A.D. 800 • With the fall of Constantinople (Istanbul) in 1453, Eastern scholars headed west to Europe, carrying knowledge that helped ignite the European Renaissance. ...
CHAPTER 2 - THE RISE OF ASTRONOMY
... Ptolemaic and Copernican models of the solar system. Contributions of Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, and Newton and how it was when they lived. Kepler’s laws and their use. Venus phases as proof of Copernican model. Astronomy vs. Astrology. The further evolution of ideas (parallax observed, nebulae and gal ...
... Ptolemaic and Copernican models of the solar system. Contributions of Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, and Newton and how it was when they lived. Kepler’s laws and their use. Venus phases as proof of Copernican model. Astronomy vs. Astrology. The further evolution of ideas (parallax observed, nebulae and gal ...