Chapter 29 Our Solar System
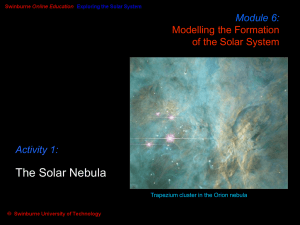
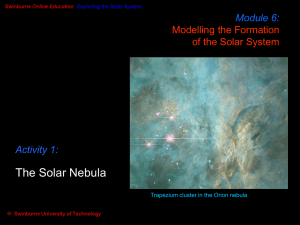
... 4. As it condenses, the cloud _____________, becomes __________ like a disk, and ______________ 5. Solar nebula: Large cloud that collapsed & formed the _______________________ a. Center _______________, ____________at edges of disk b. Temp difference caused different gases to condense in different ...
... 4. As it condenses, the cloud _____________, becomes __________ like a disk, and ______________ 5. Solar nebula: Large cloud that collapsed & formed the _______________________ a. Center _______________, ____________at edges of disk b. Temp difference caused different gases to condense in different ...
The Ionization Structure of the Irregular Galaxy NGC 4449
... ionized. H II regions characteristically include several bright, hot stars whose ultraviolet radiation is converted to visible light as described earlier. A typical H II region in our galaxy has a diameter of a few parsecs, a gas temperature of 10,000 K with a density of about 100 to 10,000 particle ...
... ionized. H II regions characteristically include several bright, hot stars whose ultraviolet radiation is converted to visible light as described earlier. A typical H II region in our galaxy has a diameter of a few parsecs, a gas temperature of 10,000 K with a density of about 100 to 10,000 particle ...
COMETS - Mount Holyoke College
... radiation pressure. Since the net force of radiation pressure relative to solar gravity depends on the ratio of the dust particle's cross section/mass, the smallest particles will have the highest velocity and the particles will spread out in the tail according to their size. Large particles are le ...
... radiation pressure. Since the net force of radiation pressure relative to solar gravity depends on the ratio of the dust particle's cross section/mass, the smallest particles will have the highest velocity and the particles will spread out in the tail according to their size. Large particles are le ...
Helioseismology - University of Warwick
... Examples are Global Oscillations at Low Frequencies (GOLF), Variability of solar IRradiance and Gravity Oscillations (VIRGO), and the Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) on the SOlar and Heliosepheric Observatory (SOHO) spacecraft, which was launched in 1995. Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) on the ...
... Examples are Global Oscillations at Low Frequencies (GOLF), Variability of solar IRradiance and Gravity Oscillations (VIRGO), and the Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) on the SOlar and Heliosepheric Observatory (SOHO) spacecraft, which was launched in 1995. Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) on the ...
Conceptual steps towards exploring the fundamental nature of our Sun
... All aspects of solar activity (Ellerman Bombs, Bright Points, flares, particle acceleration etc.) are self-similar and their statistical behavior follows well-defined power laws. This last point reinforces the belief that the solar atmosphere is coupled, through the magnetic field, with the convecti ...
... All aspects of solar activity (Ellerman Bombs, Bright Points, flares, particle acceleration etc.) are self-similar and their statistical behavior follows well-defined power laws. This last point reinforces the belief that the solar atmosphere is coupled, through the magnetic field, with the convecti ...
cosmic-ray neon, wolf-rayet stars, and the superbubble origin of
... material of solar system composition and accelerated by subsequent SN shocks within the superbubble to provide the bulk of the GCRs. The calculations of Schaller et al. (1992) and Woosley & Weaver (1995) are used to estimate the yields of 20 Ne and 22 Ne from W-R stars and core-collapse SNe, and fro ...
... material of solar system composition and accelerated by subsequent SN shocks within the superbubble to provide the bulk of the GCRs. The calculations of Schaller et al. (1992) and Woosley & Weaver (1995) are used to estimate the yields of 20 Ne and 22 Ne from W-R stars and core-collapse SNe, and fro ...
tremaine_lecture_1
... Unknowns include: • smaller asteroids and Kuiper belt beyond Neptune • mass loss from Sun • drag of solar wind on planetary magnetospheres • tidal forces from the Milky Way • passing stars (highly unlikely) • errors in planetary masses or initial conditions ...
... Unknowns include: • smaller asteroids and Kuiper belt beyond Neptune • mass loss from Sun • drag of solar wind on planetary magnetospheres • tidal forces from the Milky Way • passing stars (highly unlikely) • errors in planetary masses or initial conditions ...
The Astrophysical Origins of the Short
... separate this way (e.g., Simon et al. 2002) 4. Production of 26Al or 41Ca at meteoritic levels will overproduce 10Be, using best-case scenario [Gounelle et al. (2001)] and new measured reaction rate for 3He(24Mg,p)26Al [Fitoussi et al. (2004)], especially if most 10Be is inherited [Desch et al. (200 ...
... separate this way (e.g., Simon et al. 2002) 4. Production of 26Al or 41Ca at meteoritic levels will overproduce 10Be, using best-case scenario [Gounelle et al. (2001)] and new measured reaction rate for 3He(24Mg,p)26Al [Fitoussi et al. (2004)], especially if most 10Be is inherited [Desch et al. (200 ...
The Lyman-alpha telescope of the Extreme Ultraviolet Imager
... the spacecraft to observe one specific area for much longer time than possible from an orbit close to Earth. Solar Orbiter is a three-axis stabilized spacecraft equipped with instruments for both in-situ measurements and remote-sensing observations from a highly elliptical orbit approaching the Sun ...
... the spacecraft to observe one specific area for much longer time than possible from an orbit close to Earth. Solar Orbiter is a three-axis stabilized spacecraft equipped with instruments for both in-situ measurements and remote-sensing observations from a highly elliptical orbit approaching the Sun ...
Hard X-Ray Polarization – a Diagnostic of Electron
... Backscatter Polarization – Unpolarized Primary ...
... Backscatter Polarization – Unpolarized Primary ...
Obliquity and precession of the equinoxes The angle ε between the
... (1) Kepler’s Laws state that a planet moves more quickly when it is closer to the Sun in its elliptical orbit (Earth reaches perihelion [Gr. peri + helios = around + Sun], its point of closest approach, in early January, and aphelion [Gr.apo + helios = away from + Sun] in early July). Consequently, ...
... (1) Kepler’s Laws state that a planet moves more quickly when it is closer to the Sun in its elliptical orbit (Earth reaches perihelion [Gr. peri + helios = around + Sun], its point of closest approach, in early January, and aphelion [Gr.apo + helios = away from + Sun] in early July). Consequently, ...
Chapter 16 The Sun
... • Number of sunspots varies in an 11-year cycle • Large solar ejection events: prominences, flares, and coronal ejections • Observations of solar neutrinos show deficit, due to peculiar neutrino behavior (class: explain what that behavior is) ...
... • Number of sunspots varies in an 11-year cycle • Large solar ejection events: prominences, flares, and coronal ejections • Observations of solar neutrinos show deficit, due to peculiar neutrino behavior (class: explain what that behavior is) ...
ES_CH3_L1 - AFJROTC Ar/Ld 4
... The Nuclear Fusion Power of the Sun An atom’s nucleus is made up of protons, positively charged particles; and neutrons, particles with no electrical charge In nuclear fusion, two nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus. They “fuse.” Primary source of the Sun’s energy is a series of nuclear fusi ...
... The Nuclear Fusion Power of the Sun An atom’s nucleus is made up of protons, positively charged particles; and neutrons, particles with no electrical charge In nuclear fusion, two nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus. They “fuse.” Primary source of the Sun’s energy is a series of nuclear fusi ...
Advanced Composition Explorer

Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) is a NASA Explorers program Solar and space exploration mission to study matter comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources. Real-time data from ACE is used by the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center to improve forecasts and warnings of solar storms. The ACE robotic spacecraft was launched August 25, 1997 and entered a Lissajous orbit close to the L1 Lagrangian point (which lies between the Sun and the Earth at a distance of some 1.5 million km from the latter) on December 12, 1997. The spacecraft is currently operating at that orbit. Because ACE is in a non-Keplerian orbit, and has regular station-keeping maneuvers, the orbital parameters at right are only approximate. The spacecraft is still in generally good condition in 2015, and is projected to have enough fuel to maintain its orbit until 2024. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center managed the development and integration of the ACE spacecraft.