Testosterone and breast cancer prevention
... in psychological symptoms (depressive mood, irritability, anxiety, physical and mental exhaustion), somatic symptoms (hot flashes, heart discomfort, sleep problems, pain) and urogenital symptoms including sexual desire, activity, satisfaction, vaginal dryness and bladder problems (Fig. 2). There were ...
... in psychological symptoms (depressive mood, irritability, anxiety, physical and mental exhaustion), somatic symptoms (hot flashes, heart discomfort, sleep problems, pain) and urogenital symptoms including sexual desire, activity, satisfaction, vaginal dryness and bladder problems (Fig. 2). There were ...
Ocular toxicity of systemic anticancer chemotherapy
... A quarter of a century ago, the aim of cancer care was simply to cure the patient with little concern about the side effects of the treatment.4 The increased use of chemotherapeutic agents has resulted in longer patient survival; consequently the ophthalmologist is seeing more patients with adverse ...
... A quarter of a century ago, the aim of cancer care was simply to cure the patient with little concern about the side effects of the treatment.4 The increased use of chemotherapeutic agents has resulted in longer patient survival; consequently the ophthalmologist is seeing more patients with adverse ...
ANS - Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics
... most PS ganglia lie on or within the organ they innervate. On the otherhand, the diagram also shows the important paravertebral sympathetic ganglion chain which forms a network with few ‘external way stations’ such as the coeliac and superior and inferior mesenteric ganglia. The left side diagrams i ...
... most PS ganglia lie on or within the organ they innervate. On the otherhand, the diagram also shows the important paravertebral sympathetic ganglion chain which forms a network with few ‘external way stations’ such as the coeliac and superior and inferior mesenteric ganglia. The left side diagrams i ...
SAS Software for Log-linear Models
... operated in log-linear model mode through the combined use of the MODEL statement and a new REPEATED statement, coupled with a new keyword, _RESPONSE_. In this example, TRTMNT*ATELECT on the left-hand side of the model equation specifies that r = 6 response categories are to be constructed from all ...
... operated in log-linear model mode through the combined use of the MODEL statement and a new REPEATED statement, coupled with a new keyword, _RESPONSE_. In this example, TRTMNT*ATELECT on the left-hand side of the model equation specifies that r = 6 response categories are to be constructed from all ...
Zofran Lawsuits | FAQs
... What is Zofran? Zofran (odansetron) is an anti-nausea/vomiting medication. It is classified as a Serotonin-3 Receptor Antogonist. The Food & Drug Administration originally approved it in 1998. What is it used for? Zofran was approved for and is prescribed to treat cancer patients suffering from naus ...
... What is Zofran? Zofran (odansetron) is an anti-nausea/vomiting medication. It is classified as a Serotonin-3 Receptor Antogonist. The Food & Drug Administration originally approved it in 1998. What is it used for? Zofran was approved for and is prescribed to treat cancer patients suffering from naus ...
Glucocorticoid Increases Angiotensin II Type 1
... FIG 2. Bar graph shows time course for the effect of dexamethasone on relative Increase in numbers of angiotensin II type 1 (AT,) receptors. Vascular smooth muscle cells were Incubated for the Indicated time periods with 1 ^mol/L dexamethasone. AT, receptor density was calculated from Scatchard plot ...
... FIG 2. Bar graph shows time course for the effect of dexamethasone on relative Increase in numbers of angiotensin II type 1 (AT,) receptors. Vascular smooth muscle cells were Incubated for the Indicated time periods with 1 ^mol/L dexamethasone. AT, receptor density was calculated from Scatchard plot ...
Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) - GB non
... Risk assessments consider only the risks posed by a species. They do not consider the practicalities, impacts or other issues relating to the management of the species. They therefore cannot on their own be used to determine what, if any, management response should be undertaken. Risk assessment ...
... Risk assessments consider only the risks posed by a species. They do not consider the practicalities, impacts or other issues relating to the management of the species. They therefore cannot on their own be used to determine what, if any, management response should be undertaken. Risk assessment ...
CARDIAC TOXICITY OF CANCER THERAPEUTIC AGENTS
... • Capecitabine is metabolized to fluorouracil, preferentially in tumor cells and is less toxic. ...
... • Capecitabine is metabolized to fluorouracil, preferentially in tumor cells and is less toxic. ...
CARDIAC TOXICITY OF CANCER THERAPEUTIC AGENTS
... • Capecitabine is metabolized to fluorouracil, preferentially in tumor cells and is less toxic. ...
... • Capecitabine is metabolized to fluorouracil, preferentially in tumor cells and is less toxic. ...
adrenergic agents - NC State Veterinary Medicine
... occurs within 2 hours following administration and is maintained for 6 to 24 hours, depending upon formulation, due to suppression of AH production by 24%. Acetazolamide is highly protein-bound in humans, which necessitates relatively large doses to result in sufficient levels of the unbound, un-ion ...
... occurs within 2 hours following administration and is maintained for 6 to 24 hours, depending upon formulation, due to suppression of AH production by 24%. Acetazolamide is highly protein-bound in humans, which necessitates relatively large doses to result in sufficient levels of the unbound, un-ion ...
Premarin®
... through cell membranes, distribute themselves throughout the cell, and bind to and activate the nuclear estrogen receptor, a DNA-binding protein which is found in estrogen-responsive tissues. The activated estrogen receptor binds to specific DNA sequences, or hormone-response elements, which enhance ...
... through cell membranes, distribute themselves throughout the cell, and bind to and activate the nuclear estrogen receptor, a DNA-binding protein which is found in estrogen-responsive tissues. The activated estrogen receptor binds to specific DNA sequences, or hormone-response elements, which enhance ...
Lecture 6
... Short acting, reversible • Drugs as Edrophonium • Alcohol • forms weak hydrogen bond with cholinesterase Intermediate acting, reversible • Carbamates esters • binds to two sites of cholinesterase enzyme • All polar except physostigmine – Physostigmine – Pyridostigmine – Neostigmine ...
... Short acting, reversible • Drugs as Edrophonium • Alcohol • forms weak hydrogen bond with cholinesterase Intermediate acting, reversible • Carbamates esters • binds to two sites of cholinesterase enzyme • All polar except physostigmine – Physostigmine – Pyridostigmine – Neostigmine ...
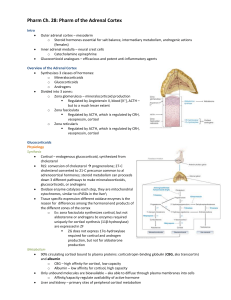
Pharm of the Adrenal Cortex
... Cortisol binds to cytosolic receptor and forms hormone-receptor complex, transported to nucleus o Dimerized hormone-receptor complex binds to gene promoter elements (aka glucocorticoid response elements – GREs), which either enhance/inhibit expression of certain genes o Cortisol – profound effect ...
... Cortisol binds to cytosolic receptor and forms hormone-receptor complex, transported to nucleus o Dimerized hormone-receptor complex binds to gene promoter elements (aka glucocorticoid response elements – GREs), which either enhance/inhibit expression of certain genes o Cortisol – profound effect ...
Precambrian - Cambrian Eukaryotes
... What causes extinction? • Old explanations: – Maladaptation organisms evolved poorly-adapted features – Racial senescence species became “weak over time” – Discuss the likelihood of these explanations with your table ...
... What causes extinction? • Old explanations: – Maladaptation organisms evolved poorly-adapted features – Racial senescence species became “weak over time” – Discuss the likelihood of these explanations with your table ...
PDF - Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science
... leads to a decrease in the synthesis of various prostaglandins and thromboxanes. The main mechanism of action of NSAIDs was clarified by Sir John Vane in 1971. He noted the inhibition by aspirin, of prostaglandin synthesis. Around 1972, the mechanism of action of NSAIDs was proposed that it works by ...
... leads to a decrease in the synthesis of various prostaglandins and thromboxanes. The main mechanism of action of NSAIDs was clarified by Sir John Vane in 1971. He noted the inhibition by aspirin, of prostaglandin synthesis. Around 1972, the mechanism of action of NSAIDs was proposed that it works by ...
Internal Medicine Morning Report
... • Maintains blood glucose levels between meals and fasting periods – Initiates glycogenolysis – Increase the transport of amino acids in the liver – gluconeogenesis – Activates adipose cell lipase – makes fatty acids available for energy ...
... • Maintains blood glucose levels between meals and fasting periods – Initiates glycogenolysis – Increase the transport of amino acids in the liver – gluconeogenesis – Activates adipose cell lipase – makes fatty acids available for energy ...
cardiovascular drugs and autacoids
... - drugs in this class inhibit the converting enzyme peptidyl dipeptidase that hydrolyzes angiotensin I to angiotensin II - (under the name plasma kininase) inactivates bradykinin, a potent vasodilator, which works by stimulating release of nitric oxide and prostacyclin The hypotensive activity of ca ...
... - drugs in this class inhibit the converting enzyme peptidyl dipeptidase that hydrolyzes angiotensin I to angiotensin II - (under the name plasma kininase) inactivates bradykinin, a potent vasodilator, which works by stimulating release of nitric oxide and prostacyclin The hypotensive activity of ca ...
Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System
... increase (angiotensin, and acetylcholine via a nicotinic receptor) and decrease (dopamine, histamine, serotonin, adenosine, PGD2, PGE2 and acetylcholine via a muscarinic receptor) norepinephrine release in selected tissues. Released catecholamines may a) be retaken up into the neuron (norepinephrine ...
... increase (angiotensin, and acetylcholine via a nicotinic receptor) and decrease (dopamine, histamine, serotonin, adenosine, PGD2, PGE2 and acetylcholine via a muscarinic receptor) norepinephrine release in selected tissues. Released catecholamines may a) be retaken up into the neuron (norepinephrine ...
peptic ulcer2011-09-11 10:543.4 MB
... Mechanism of action Irreversible inhibition of proton pump (H+/ K+ ATPase) that is responsible for final step in gastric acid secretion from the parietal cell. PP inhibitors include: Omperazole Lansoprazole Pantoprazole ...
... Mechanism of action Irreversible inhibition of proton pump (H+/ K+ ATPase) that is responsible for final step in gastric acid secretion from the parietal cell. PP inhibitors include: Omperazole Lansoprazole Pantoprazole ...
FSC402H Forensic Toxicology of Common Pharmaceuticals
... Pharmaceutical Drugs Shown to Have Impairing Effects with respect to Driving ...
... Pharmaceutical Drugs Shown to Have Impairing Effects with respect to Driving ...
Strategies for In Vitro Metabolic Stability Testing
... Damage to metabolic enzymes during tissue handling Extra hepatic metabolism (gut CYP3A4) Non-specific binding to microsomal lipids and cellular components in the incubation Hepatic drug uptake transporters (concentration in liver > plasma concentration). Measured in hepatocytes by “media loss” assay ...
... Damage to metabolic enzymes during tissue handling Extra hepatic metabolism (gut CYP3A4) Non-specific binding to microsomal lipids and cellular components in the incubation Hepatic drug uptake transporters (concentration in liver > plasma concentration). Measured in hepatocytes by “media loss” assay ...
Opioids
... Tolerance and Dependence • Maintenance of normal sensitivity of receptors requires reactivation by endocytosis and recycling. • activation of receptors by endogenous ligands results in endocytosis followed by resensitization and recycling of the receptor to the plasma membrane. • But morphine fails ...
... Tolerance and Dependence • Maintenance of normal sensitivity of receptors requires reactivation by endocytosis and recycling. • activation of receptors by endogenous ligands results in endocytosis followed by resensitization and recycling of the receptor to the plasma membrane. • But morphine fails ...
The Niche
... 5. An organism’s niche describes the organisms role (job) in the environment where it lives. In other words, an organism’s niche includes not only the physical and biological aspects of its environment, but also the way in which the organism uses them to survive and reproduce. ...
... 5. An organism’s niche describes the organisms role (job) in the environment where it lives. In other words, an organism’s niche includes not only the physical and biological aspects of its environment, but also the way in which the organism uses them to survive and reproduce. ...
Toxicodynamics

Toxicodynamics, termed pharmacodynamics in pharmacology, describes the dynamic interactions of a toxicant with a biological target and its biological effects. A biological target, also known as the site of action, can be binding proteins, ion channels, DNA, or a variety of other receptors. When a toxicant enters an organism, it can interact with these receptors and produce structural or functional alterations. The mechanism of action of the toxicant, as determined by a toxicant’s chemical properties, will determine what receptors are targeted and the overall toxic effect at the cellular level and organismal level.Toxicants have been grouped together according to their chemical properties by way of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs), which allows prediction of toxic action based on these properties. endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and carcinogens are examples of classes of toxicants that can act as QSARs. EDCs mimic or block transcriptional activation normally caused by natural steroid hormones. These types of chemicals can act on androgen receptors, estrogen receptors and thyroid hormone receptors. This mechanism can include such toxicants as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDE) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Another class of chemicals, carcinogens, are substances that cause cancer and can be classified as genotoxic or nongenotoxic carcinogens. These categories include toxicants such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). The process of toxicodynamics can be useful for application in environmental risk assessment by implementing toxicokinetic-toxicodynamic (TKTD) models. TKTD models include phenomenas such as time-varying exposure, carry-over toxicity, organism recovery time, effects of mixtures, and extrapolation to untested chemicals and species. Due to their advantages, these types of models may be more applicable for risk assessment than traditional modeling approaches.