Policy and procedures for Bone Conduction Implantable Devices
... Bone conduction implantable devices are used in cases of conductive hearing loss, mixed hearing loss and single sided deafness, when conventional hearing aids do not provide sufficient access to sound or are contraindicated due to anatomical or chronic middle ear conditions. Information generated th ...
... Bone conduction implantable devices are used in cases of conductive hearing loss, mixed hearing loss and single sided deafness, when conventional hearing aids do not provide sufficient access to sound or are contraindicated due to anatomical or chronic middle ear conditions. Information generated th ...
Fostering auditory development of a child with auditory neuropathy
... Learn to Talk by Nancy Rushmer They learn to talk through listening with their hearing aids. Because hearing aids do not restore hearing, several adjustments can be used to help them: Adults should refrain from asking the child to say words. Once a while, it is okay to do that. Language is cau ...
... Learn to Talk by Nancy Rushmer They learn to talk through listening with their hearing aids. Because hearing aids do not restore hearing, several adjustments can be used to help them: Adults should refrain from asking the child to say words. Once a while, it is okay to do that. Language is cau ...
1) Department of Otolaryngology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear
... (CI) users over 65 years of age have different surgical and audiological outcomes when compared to younger adult CI users and 2) identify reasons for these possible differences. Study Design: Retrospective single institution study Methods: Records of 113 post-lingually deafened adults with unilatera ...
... (CI) users over 65 years of age have different surgical and audiological outcomes when compared to younger adult CI users and 2) identify reasons for these possible differences. Study Design: Retrospective single institution study Methods: Records of 113 post-lingually deafened adults with unilatera ...
Optimising Hearing Aid Settings to Maximise Speech Audibility
... performed best with a wide-band amplification. In high levels of noise, patients did not improve with wide-band amplification, although fortunately scores did not decrease either. Clinically, this suggests that providing gain into the high-frequency dead region is at least as good, and often better, ...
... performed best with a wide-band amplification. In high levels of noise, patients did not improve with wide-band amplification, although fortunately scores did not decrease either. Clinically, this suggests that providing gain into the high-frequency dead region is at least as good, and often better, ...
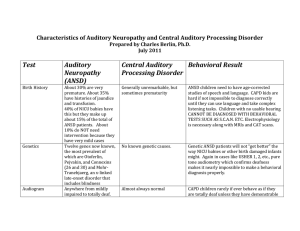
Characteristics of Auditory Neuropathy and Central Auditory
... Generally unremarkable, but sometimes prematurity ...
... Generally unremarkable, but sometimes prematurity ...
CHANGING TIMES Deaf/HH Services in the Schools
... • Spontaneously alert to name half of time by 6 months of device use • Alert spontaneously to a few environmental sounds after 6 months of use • Performance in booth consistent with real life by 9 months post-CI • Evidence of meaning derived from sound after 12 months of use • Major jump in language ...
... • Spontaneously alert to name half of time by 6 months of device use • Alert spontaneously to a few environmental sounds after 6 months of use • Performance in booth consistent with real life by 9 months post-CI • Evidence of meaning derived from sound after 12 months of use • Major jump in language ...
psychoacoustics and the effects of hearing loss
... hearing ear, ears with hearing loss may also have reduced frequency resolution ability (pitch discrimination) and reduced temporal resolution ability (eg, tracking the rapid changes in phonemes within words) while processing acoustically amplified sound. There may also be reduced ability to localise ...
... hearing ear, ears with hearing loss may also have reduced frequency resolution ability (pitch discrimination) and reduced temporal resolution ability (eg, tracking the rapid changes in phonemes within words) while processing acoustically amplified sound. There may also be reduced ability to localise ...
Speech perception

Speech perception is the process by which the sounds of language are heard, interpreted and understood. The study of speech perception is closely linked to the fields of phonology and phonetics in linguistics and cognitive psychology and perception in psychology. Research in speech perception seeks to understand how human listeners recognize speech sounds and use this information to understand spoken language. Speech perception research has applications in building computer systems that can recognize speech, in improving speech recognition for hearing- and language-impaired listeners, and in foreign-language teaching.