
BIOL 252 - American University of Beirut
... Course description This is an introductory course in ecology that covers most of the basic concepts in this field namely, environmental factors, the main physiological, morphological and behavioral adaptations of various organisms to these factors, populations, their structures, dynamics and positiv ...
... Course description This is an introductory course in ecology that covers most of the basic concepts in this field namely, environmental factors, the main physiological, morphological and behavioral adaptations of various organisms to these factors, populations, their structures, dynamics and positiv ...
4.LECTURE-Systems of the Earth [Compatibility Mode]
... The total estimated global mass of living biological organisms is the biomass, and it ranges from 2.4 × 1012 tons to 1 × 1013 tons of dry matter, the largest part of which is phytomass (phytoplankton, trees, grasses), whereas the amount of zoomass is estimated from 2 to 10 % of the total biomass. Th ...
... The total estimated global mass of living biological organisms is the biomass, and it ranges from 2.4 × 1012 tons to 1 × 1013 tons of dry matter, the largest part of which is phytomass (phytoplankton, trees, grasses), whereas the amount of zoomass is estimated from 2 to 10 % of the total biomass. Th ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... provided by your teacher, For those words you do not know, set them to the side, you will learn them by the end of the period. ...
... provided by your teacher, For those words you do not know, set them to the side, you will learn them by the end of the period. ...
Name - MIT OpenCourseWare
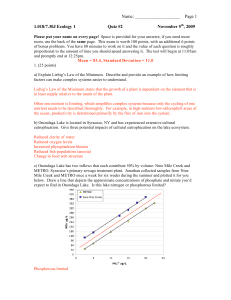
... of bonus problems. You have 80 minutes to work on it and the value of each question is roughly proportional to the amount of time you should spend answering it. The test will begin at 11:05am and promptly end at 12:25pm. Mean = 83.4, Standard Deviation = 11.0 1. (25 points) a) Explain Liebig’s Law o ...
... of bonus problems. You have 80 minutes to work on it and the value of each question is roughly proportional to the amount of time you should spend answering it. The test will begin at 11:05am and promptly end at 12:25pm. Mean = 83.4, Standard Deviation = 11.0 1. (25 points) a) Explain Liebig’s Law o ...
Essential Questions and Answers
... relationship because the bacteria get a place to live and an energy source and the plants get nitrogen. Other soil bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. Why do living things need phosphorus? Phosphorus is essential to living organisms because it is a component of DNA and RNA which form our ge ...
... relationship because the bacteria get a place to live and an energy source and the plants get nitrogen. Other soil bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. Why do living things need phosphorus? Phosphorus is essential to living organisms because it is a component of DNA and RNA which form our ge ...
Matcuk-Grischow Biology 2014-09-01
... • Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g., food chains, food webs, energy pyramids). • Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem (e.g., competition, predation, symbiosis). • Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e., water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen ...
... • Describe how energy flows through an ecosystem (e.g., food chains, food webs, energy pyramids). • Describe biotic interactions in an ecosystem (e.g., competition, predation, symbiosis). • Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e., water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen ...
APES FINAL EXAM REVIEW: TOP TEN LISTS
... 2) Carbon entering any “pools” such as the ocean or large forests is always naturally balanced out by carbon leaving the pools until the Industrial Revolution when human activities began to distort the cycle. Example: Carbon used in photosynthesis ends up in the soil, where decomposers then release ...
... 2) Carbon entering any “pools” such as the ocean or large forests is always naturally balanced out by carbon leaving the pools until the Industrial Revolution when human activities began to distort the cycle. Example: Carbon used in photosynthesis ends up in the soil, where decomposers then release ...
1.1 Biomes Factors That Influence the Characteristics and
... Ecosystems can take up many hectares of land or can be small, such as a tide pool or a rotting log. A ___________is where an organism lives. ...
... Ecosystems can take up many hectares of land or can be small, such as a tide pool or a rotting log. A ___________is where an organism lives. ...
Factors That Affect Climate
... – Ecologists used to think that succession in a given area always proceeds through the same stages to produce a specific and stable climax community. – Recent studies, however, have shown that succession doesn’t always follow the same path, and that climax communities are not always uniform and stab ...
... – Ecologists used to think that succession in a given area always proceeds through the same stages to produce a specific and stable climax community. – Recent studies, however, have shown that succession doesn’t always follow the same path, and that climax communities are not always uniform and stab ...
The rainforest ecosystem - Environmental Systems and Societies
... many as 1500 species of flowering plants, 750 species of trees, 125 species of mammals, 400 species of birds, 100 species of reptiles, 60 species of amphibians, and 150 species of butterflies. ...
... many as 1500 species of flowering plants, 750 species of trees, 125 species of mammals, 400 species of birds, 100 species of reptiles, 60 species of amphibians, and 150 species of butterflies. ...
Provincial Exam Review: Ecosystems Biomes Identify each of the
... C. Grasses of the grassland biome have deep roots that form dense mats to collect water when it is available. D. Plants in the desert biome produce chemicals that protect them from being eaten by animals. 30. No trees grow above the tree line in the tundra biome of northern Canada. Which combination ...
... C. Grasses of the grassland biome have deep roots that form dense mats to collect water when it is available. D. Plants in the desert biome produce chemicals that protect them from being eaten by animals. 30. No trees grow above the tree line in the tundra biome of northern Canada. Which combination ...
Food Chains
... Sea otter; there are no arrows point from the sea otter to another species, meaning that nothing eats the sea otter 15. Explain the consequences if the abalones were removed from the food web. ↓ in population of Sea urchins and smaller herbivores fishes/invertebrates (sea stars increased predation p ...
... Sea otter; there are no arrows point from the sea otter to another species, meaning that nothing eats the sea otter 15. Explain the consequences if the abalones were removed from the food web. ↓ in population of Sea urchins and smaller herbivores fishes/invertebrates (sea stars increased predation p ...
Ecology and the Environment - Mrs. Nicolai's Science Class
... that restricts (limits) the number of individuals in a population. Examples of limiting factors: amount of food, water, living space, mates, and nesting sites. ...
... that restricts (limits) the number of individuals in a population. Examples of limiting factors: amount of food, water, living space, mates, and nesting sites. ...

![4.LECTURE-Systems of the Earth [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014265275_1-c3f0353eb192762d4742baddbdbd9cf1-300x300.png)



















![Populations – Limits to Growth[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008135102_1-595d6a50892f69171ad3bc47138eaf45-300x300.png)
