Рубежный контроль № 2 Профессионально ориентированный
... II. kills its host III. cannot reproduce outside its host A. I and III only B. II only C. I only D. II and III only E. I, II, and III 64. An organism that feeds at several trophic levels is A. an omnivore B. a carnivore C. a primary consumer D. an herbivore E. a primary producer 65. Yeast are cultur ...
... II. kills its host III. cannot reproduce outside its host A. I and III only B. II only C. I only D. II and III only E. I, II, and III 64. An organism that feeds at several trophic levels is A. an omnivore B. a carnivore C. a primary consumer D. an herbivore E. a primary producer 65. Yeast are cultur ...
IMCC Yr12 Integrated Science Course Outline
... differences in geographical and physical conditions result in a wide variety of ecosystems ...
... differences in geographical and physical conditions result in a wide variety of ecosystems ...
dependance
... patterns of abundance factors that determine the range of environments that organisms occupy and that determine how abundant organisms are within those ranges ...
... patterns of abundance factors that determine the range of environments that organisms occupy and that determine how abundant organisms are within those ranges ...
eco chpt 3
... i. The space, food, and other conditions and organism needs to survive and reproduce are part of its niche ii. It also includes how the specie affects its environment C. Two species can't exist for ling if their niches are the same i. one of the species will gain control and the other specie will ei ...
... i. The space, food, and other conditions and organism needs to survive and reproduce are part of its niche ii. It also includes how the specie affects its environment C. Two species can't exist for ling if their niches are the same i. one of the species will gain control and the other specie will ei ...
fish species ecology in spanish freshwater ecosystems
... Feeding is at four trophic levels: detritus, phytoberithos, benthonic macroinvertebrates, and emergent forms. Exploitation is sometimes at a single level (Chondr-ostoma-detritus) and sometimes at several levels (Bar-hz1.s-niacroinvertebrates, phytobenthos, drift). There can even be an ontogenic vari ...
... Feeding is at four trophic levels: detritus, phytoberithos, benthonic macroinvertebrates, and emergent forms. Exploitation is sometimes at a single level (Chondr-ostoma-detritus) and sometimes at several levels (Bar-hz1.s-niacroinvertebrates, phytobenthos, drift). There can even be an ontogenic vari ...
Available
... b. The community-unit hypothesis/ integrated hypothesis formulated by F E Clements ...
... b. The community-unit hypothesis/ integrated hypothesis formulated by F E Clements ...
Essential terms to know in Ecology
... Biome: A collection of ecosystems sharing a similar climate; i.e. tundra, tropical rainforest, desert. Biosphere: That part of the Earth inhabited by organisms, that is, the narrow zone (a few km thick) in which plants and animals exist. It extends from the upper part of the atmosphere (where birds, ...
... Biome: A collection of ecosystems sharing a similar climate; i.e. tundra, tropical rainforest, desert. Biosphere: That part of the Earth inhabited by organisms, that is, the narrow zone (a few km thick) in which plants and animals exist. It extends from the upper part of the atmosphere (where birds, ...
Energy Webs and Chains
... Population: All of the members of the same species, living in the same ecosystem or habitat. Community: The collection of all populations of all the species in an ecosystem or habitat. Energy -All organisms need energy to live: to grow, to run, to reproduce, etc. -A major part of ecology is the stud ...
... Population: All of the members of the same species, living in the same ecosystem or habitat. Community: The collection of all populations of all the species in an ecosystem or habitat. Energy -All organisms need energy to live: to grow, to run, to reproduce, etc. -A major part of ecology is the stud ...
Ecology and Food
... It refers to the predators being of high trophic level and sitting “on top” of the food chain or the trophic pyramid. Give an example of how there might be few individual autotrophs but many individuals that feed on it. You might have a few large trees in an ecosystem, or you could have many small i ...
... It refers to the predators being of high trophic level and sitting “on top” of the food chain or the trophic pyramid. Give an example of how there might be few individual autotrophs but many individuals that feed on it. You might have a few large trees in an ecosystem, or you could have many small i ...
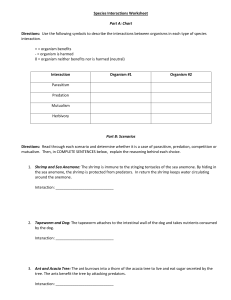
Species Interaction Worksheet
... 1. Shrimp and Sea Anemone: The shrimp is immune to the stinging tentacles of the sea anemone. By hiding in the sea anemone, the shrimp is protected from predators. In return the shrimp keeps water circulating around the anemone. Interaction: ____________________________ ...
... 1. Shrimp and Sea Anemone: The shrimp is immune to the stinging tentacles of the sea anemone. By hiding in the sea anemone, the shrimp is protected from predators. In return the shrimp keeps water circulating around the anemone. Interaction: ____________________________ ...
Ecology Note packet
... 8. All energy in an ecosystem originates with the _______________. 9. The total energy transfer form one tropic level to the next is only about _______%, the other ______% is lost in the form of heat. 10. A tick feeds on the blood of a rabbit. What type of symbiosis is this? ________________ 11. A s ...
... 8. All energy in an ecosystem originates with the _______________. 9. The total energy transfer form one tropic level to the next is only about _______%, the other ______% is lost in the form of heat. 10. A tick feeds on the blood of a rabbit. What type of symbiosis is this? ________________ 11. A s ...
Geo yr 12 - ecosystems - Homework 1
... The hydrosphere incorporates all the water cycles on Earth, and is closely linked to the atmosphere. The atmosphere determines the nature of the water cycle in a particular ecosystem, for example the polar biome consists of cold deserts with very low annual rainfall, resulting in little available fr ...
... The hydrosphere incorporates all the water cycles on Earth, and is closely linked to the atmosphere. The atmosphere determines the nature of the water cycle in a particular ecosystem, for example the polar biome consists of cold deserts with very low annual rainfall, resulting in little available fr ...
NOAA PROJECTS RESEARCH AND DATA NEEDS FOR THE
... have investigated the impact of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita on the Pontchartrain Basin, including at least habitat and water quality. These studies need to be complied into a single report so that a complete picture can be defined of the short term impacts and the expected long term effects on the ...
... have investigated the impact of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita on the Pontchartrain Basin, including at least habitat and water quality. These studies need to be complied into a single report so that a complete picture can be defined of the short term impacts and the expected long term effects on the ...
Unit 15 vocabulary
... Environment: all of the abiotic and biotic factors within the same geographic location. Niche: a role an organism plays in its environment. Limiting factor: a biotic or abiotic factor needed as a resource for survival; depletion prevents growth or expansion of the population. 10) Interdependence: to ...
... Environment: all of the abiotic and biotic factors within the same geographic location. Niche: a role an organism plays in its environment. Limiting factor: a biotic or abiotic factor needed as a resource for survival; depletion prevents growth or expansion of the population. 10) Interdependence: to ...
In one sentence, define the following terms:
... Bottom-up= Lower trophic level organisms (primary producers) control/have a limiting effect on higher trophic level organisms’ populations. ii. example of top-down: Killer whale ...
... Bottom-up= Lower trophic level organisms (primary producers) control/have a limiting effect on higher trophic level organisms’ populations. ii. example of top-down: Killer whale ...
Topic 1 - Interactions Within Ecosystems
... [ Find out more ] http://www.cws-scf.ec.gc.ca/hww-fap/hww-fap.cfm?ID_species=32&lang=e Knowing what effects you are having on the environment (or will likely have) will help you make decisions. The use of DDT (a chemical pesticide) was found to have a negative effect on Peregrine Falcons. It wasn’t ...
... [ Find out more ] http://www.cws-scf.ec.gc.ca/hww-fap/hww-fap.cfm?ID_species=32&lang=e Knowing what effects you are having on the environment (or will likely have) will help you make decisions. The use of DDT (a chemical pesticide) was found to have a negative effect on Peregrine Falcons. It wasn’t ...
sci 10 exam review b.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... species, this means we are overpopulated. What could happen to the human race? Give specific reasons for this. 21. Why has the human population tripled? 22. Give a reason why monocultures are good. Give a reason why monocultures are not good. 23. Where does all of our energy come from? 24. Draw a fo ...
... species, this means we are overpopulated. What could happen to the human race? Give specific reasons for this. 21. Why has the human population tripled? 22. Give a reason why monocultures are good. Give a reason why monocultures are not good. 23. Where does all of our energy come from? 24. Draw a fo ...
Letter to Pond Owners - Pender Islands Farmers Institute
... threaten indigenous ecosystems, habitats and native species. They eat everything from ducklings, hummingbirds and ground-nesting birds to fish and other frogs, and can radically alter local biodiversity. Ignoring the problem will only allow it to worsen. You can help. The Pender Islands Farmers’ Ins ...
... threaten indigenous ecosystems, habitats and native species. They eat everything from ducklings, hummingbirds and ground-nesting birds to fish and other frogs, and can radically alter local biodiversity. Ignoring the problem will only allow it to worsen. You can help. The Pender Islands Farmers’ Ins ...
Reading Plants - The Huntington
... internal structure. Can you infer why the leaves have their structure? o Desert plants generally have waxy coverings on their leaves to reduce water loss through the leaf surface. These leaves may be almost spherical to reduce surface area, again to reduce water loss. These leaves are often light gr ...
... internal structure. Can you infer why the leaves have their structure? o Desert plants generally have waxy coverings on their leaves to reduce water loss through the leaf surface. These leaves may be almost spherical to reduce surface area, again to reduce water loss. These leaves are often light gr ...
Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factor activity
... giraffes could not all survive-there would not be enough food. No matter how much shelter, water and other resources there were, the population would not grow much larger than 10 giraffes. The largest population that an area can support is called its carrying capacity. The carrying capacity of this ...
... giraffes could not all survive-there would not be enough food. No matter how much shelter, water and other resources there were, the population would not grow much larger than 10 giraffes. The largest population that an area can support is called its carrying capacity. The carrying capacity of this ...