Grade 3 - NewportCurriculum
... Where does the energy in food come from and they need for body repair and growth what is it used for? and the energy they need to maintain How much water can be found in different places body warmth and for motion. on Earth? Nearly all of the Earth’s available water is What are the chief sou ...
... Where does the energy in food come from and they need for body repair and growth what is it used for? and the energy they need to maintain How much water can be found in different places body warmth and for motion. on Earth? Nearly all of the Earth’s available water is What are the chief sou ...
Fish - WVU Division of Forestry and Natural Resources
... – Teays R was the major N-W flowing river Ice sheets dams caused it to flow S through the small Mississippi R. Melt water cut through central highlands making Mississippi R the major river ...
... – Teays R was the major N-W flowing river Ice sheets dams caused it to flow S through the small Mississippi R. Melt water cut through central highlands making Mississippi R the major river ...
CHAPTER 55 CONSERVATION BIOLOGY AND GLOBAL CHANGE
... Biodiversity • Conservation biology is a goal-oriented science that seeks to counter the biodiversity crisis, the current rapid decrease in Earth’s variety of life. • Extinction is a natural phenomenon that has been occurring since life evolved on earth. – The current rate of extinction is what und ...
... Biodiversity • Conservation biology is a goal-oriented science that seeks to counter the biodiversity crisis, the current rapid decrease in Earth’s variety of life. • Extinction is a natural phenomenon that has been occurring since life evolved on earth. – The current rate of extinction is what und ...
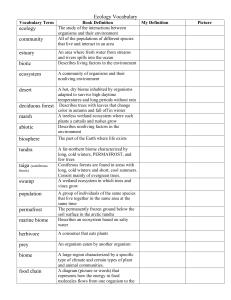
Ecosystems Vocabulary - Brandywine School District
... A grouping of the same species in a certain area ...
... A grouping of the same species in a certain area ...
Document
... Biodiversity – the degree of variation of life. Variety of organisms present in different ecosystems. ...
... Biodiversity – the degree of variation of life. Variety of organisms present in different ecosystems. ...
Temporal Community Development (Succession) Communities in
... Aquatic communities: 1) barren (oligotrophic) 2) plankton, settle to form much on bottom ---phyto leads to zoo 3) support fish, insects etc. meanwhile terrestrial runnoff etc are providing increased nutrients (eutrophication) 4) Muck provides substrate for aquatic plants which consolidate bottom, ad ...
... Aquatic communities: 1) barren (oligotrophic) 2) plankton, settle to form much on bottom ---phyto leads to zoo 3) support fish, insects etc. meanwhile terrestrial runnoff etc are providing increased nutrients (eutrophication) 4) Muck provides substrate for aquatic plants which consolidate bottom, ad ...
Ecosystems
... that ecosystem (plants, animals, microorganism) Ecosystems can be large, like a coastal Douglas Fir forest, or small like a tide pool. Within each ecosystem is a habitat and a habitat is the place in which organisms that can be found in that ecosystem live. A specific example would be the sculpin fi ...
... that ecosystem (plants, animals, microorganism) Ecosystems can be large, like a coastal Douglas Fir forest, or small like a tide pool. Within each ecosystem is a habitat and a habitat is the place in which organisms that can be found in that ecosystem live. A specific example would be the sculpin fi ...
study guide for first semester final exam 2013
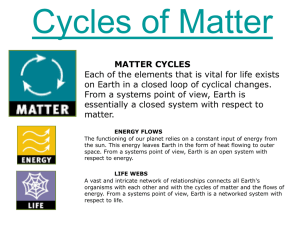
... Where is carbon stored in the ecosystem? Pg 132-33; carbon is stored in the bones of animals as well as the other molecules in their bodies; when these animals die and are fossilized, they form fossil fuels; carbon is also stored in carbon sinks—limestone rock and the ocean are both carbon sinks, bu ...
... Where is carbon stored in the ecosystem? Pg 132-33; carbon is stored in the bones of animals as well as the other molecules in their bodies; when these animals die and are fossilized, they form fossil fuels; carbon is also stored in carbon sinks—limestone rock and the ocean are both carbon sinks, bu ...
Ecology Notes
... o Unlimited environment refers to available space, food, and favorable conditions; o It is a sum of the specific growth rate of all the individuals in the population (The more individuals there are in the population the faster they will breed) o Results in a J-shaped growth curve showing exponential ...
... o Unlimited environment refers to available space, food, and favorable conditions; o It is a sum of the specific growth rate of all the individuals in the population (The more individuals there are in the population the faster they will breed) o Results in a J-shaped growth curve showing exponential ...
Attachment 4
... On these hard surfaces, organisms find refuge, feed, and reproduce. Some important features of these natural and artificial reefs include the fish and invertebrate communities inhabiting them, the structural complexity, depth, temperature, sunlight reaching the ocean floor, the amount of disturbance ...
... On these hard surfaces, organisms find refuge, feed, and reproduce. Some important features of these natural and artificial reefs include the fish and invertebrate communities inhabiting them, the structural complexity, depth, temperature, sunlight reaching the ocean floor, the amount of disturbance ...
Ecology Biomes - Peterson Science
... a diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web ...
... a diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web ...
Lesson 2: Inherited Traits and Adaptive Characteristics
... biome: one of the six major land areas of the world that is home to specific plant and animal populations and is defined by its ...
... biome: one of the six major land areas of the world that is home to specific plant and animal populations and is defined by its ...
Apr14
... Graphs suggest that limits may be related to variation in: – Temperature – Radiation – Moisture – Nutrients (depending on the system) In reality, primary productivity is limited by a succession of factors over the course of a year. Trophic Cascades Focus on primary productivity is “bottom-up” explan ...
... Graphs suggest that limits may be related to variation in: – Temperature – Radiation – Moisture – Nutrients (depending on the system) In reality, primary productivity is limited by a succession of factors over the course of a year. Trophic Cascades Focus on primary productivity is “bottom-up” explan ...
Ecology
... own food for energy by capturing sunlight or other chemicals Heterotrophs can not make their own food for energy & must obtain it by feeding on another organism ...
... own food for energy by capturing sunlight or other chemicals Heterotrophs can not make their own food for energy & must obtain it by feeding on another organism ...