Ch.15 star formation
... suggest that radiation pressure limits how massive a star can be without blowing itself apart • Observations have not found stars more massive than about 150MSun ...
... suggest that radiation pressure limits how massive a star can be without blowing itself apart • Observations have not found stars more massive than about 150MSun ...
Stellarium is a simple and easy way to look at the
... years – and show what positio the stars were or are going to b in. ...
... years – and show what positio the stars were or are going to b in. ...
Geochemistry & Lab
... Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. A plot of luminosity (absolute magnitude) against the colour of the stars ranging from the high-temperature blue-white stars on the left side of the diagram to the low temperature red stars on the right side. "This diagram below is a plot of 22000 stars from the Hipparc ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. A plot of luminosity (absolute magnitude) against the colour of the stars ranging from the high-temperature blue-white stars on the left side of the diagram to the low temperature red stars on the right side. "This diagram below is a plot of 22000 stars from the Hipparc ...
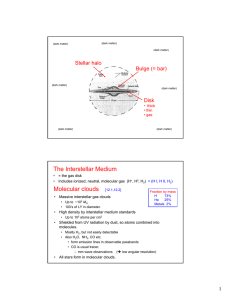
The Interstellar Medium Molecular clouds Stellar halo Bulge (= bar)
... • Photons from very luminous O stars heat and blow away surrounding gas. • So slightly older clusters no longer shrouded by dusty gas • Compression of gas further inside cloud causes inward wave of star formation (“triggered” star formation). ...
... • Photons from very luminous O stars heat and blow away surrounding gas. • So slightly older clusters no longer shrouded by dusty gas • Compression of gas further inside cloud causes inward wave of star formation (“triggered” star formation). ...
Time Domain Astrophysics in South Africa 2
... A good start to astero-seismology is in determining these for as many modes as possible ...
... A good start to astero-seismology is in determining these for as many modes as possible ...
Lesson 2 | The Sun and Other Stars
... 7. two stars that orbit each other 8. apparent surface of a star 9. charged particles that stream away from the Sun 10. large ball of gas held together by gravity with an extremely hot core ...
... 7. two stars that orbit each other 8. apparent surface of a star 9. charged particles that stream away from the Sun 10. large ball of gas held together by gravity with an extremely hot core ...
June 2008 - Otterbein University
... • Deep Sky Objects – Star Clusters (Open and Globular) – Bright and Dark Nebulae – Galaxies (used to be called nebulae also) ...
... • Deep Sky Objects – Star Clusters (Open and Globular) – Bright and Dark Nebulae – Galaxies (used to be called nebulae also) ...
Astroparticle physics 1. stellar astrophysics and solar neutrinos
... Ia: luminous supergiants Ib: less luminous... II: bright giants. III: normal giants. IV: subgiants. V: main sequence (dwarfs). • VI,sd: subdwarfs • D: white dwarfs. ...
... Ia: luminous supergiants Ib: less luminous... II: bright giants. III: normal giants. IV: subgiants. V: main sequence (dwarfs). • VI,sd: subdwarfs • D: white dwarfs. ...
Lecture 3
... system that made predictions of the planetary positions on the sky to the limits of all available observations ● The observational accuracy with which planetary positions were measured (until Tycho Brahe) was 10' ● Based on compositions of circular motion on circular motion (epicycles, deferents, et ...
... system that made predictions of the planetary positions on the sky to the limits of all available observations ● The observational accuracy with which planetary positions were measured (until Tycho Brahe) was 10' ● Based on compositions of circular motion on circular motion (epicycles, deferents, et ...
Components of the Milky Way
... Empirically, more massive stars are more luminous. Very roughly: ...
... Empirically, more massive stars are more luminous. Very roughly: ...
Evolution of High Mass Stars
... • A star’s mass determines its entire life story because it determines its core temperature • High-mass stars with >8MSun have short lives, eventually becoming hot enough to make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbo ...
... • A star’s mass determines its entire life story because it determines its core temperature • High-mass stars with >8MSun have short lives, eventually becoming hot enough to make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbo ...
The age–metallicity distribution of earth-harbouring stars
... Selection of the solar stars sample • Our sample is based on a compilation of several surveys of chromospheric activity and Strömgren photometry among solartype stars. A total of 1188 stars were selected. • Stars were binned according to age and metallicity. Several corrections to account for ...
... Selection of the solar stars sample • Our sample is based on a compilation of several surveys of chromospheric activity and Strömgren photometry among solartype stars. A total of 1188 stars were selected. • Stars were binned according to age and metallicity. Several corrections to account for ...
Morphological characteristics of OB spectra and environments
... The Antennae, at a distance of about 20 Mpc, constitute the nearest major merger and are thus a key system for understanding this phenomenon, which is ubiquitous at greater distances in the earlier Universe. Accordingly, it has been the subject of intensive investigation. With HST imaging, [26] have ...
... The Antennae, at a distance of about 20 Mpc, constitute the nearest major merger and are thus a key system for understanding this phenomenon, which is ubiquitous at greater distances in the earlier Universe. Accordingly, it has been the subject of intensive investigation. With HST imaging, [26] have ...
Review for Midterm 1
... What affect does the corona have on passing objects? Is the sun a star? How bright is it compared to other stars? What kind of threat do coronal mass ejections pose to the earth? 2. Spectroscopy: How are emission, absorption, and continuous spectra created? What can the spectrum of a star tell us ab ...
... What affect does the corona have on passing objects? Is the sun a star? How bright is it compared to other stars? What kind of threat do coronal mass ejections pose to the earth? 2. Spectroscopy: How are emission, absorption, and continuous spectra created? What can the spectrum of a star tell us ab ...
Name
... Stars are born, grow, and die in a certain pattern. This page will show you some images of each of these steps. Skip down to Step a.) of the page (where you see the pictures). 3. List the steps of stellar evolution in order, according to the left hand side of the page. Examine the pictures. 1st ____ ...
... Stars are born, grow, and die in a certain pattern. This page will show you some images of each of these steps. Skip down to Step a.) of the page (where you see the pictures). 3. List the steps of stellar evolution in order, according to the left hand side of the page. Examine the pictures. 1st ____ ...
The HLCO Project - High Legh Community Observatory
... found within a comparable environment, that is capable of supporting the full range of interests from the casual observer, to the dedicated ‘professional’ ...
... found within a comparable environment, that is capable of supporting the full range of interests from the casual observer, to the dedicated ‘professional’ ...
WOMEN-ASTRONOMERS OF FORMER USSR L.V. RYKHLOVA
... astronomical education. The indicator of professional level is for women often higher then for men at this stage of career. Unfortunately this level remains the limit for most women-astronomers, because the possibility of farther promotion and higher position depends on family-status, home-life, hav ...
... astronomical education. The indicator of professional level is for women often higher then for men at this stage of career. Unfortunately this level remains the limit for most women-astronomers, because the possibility of farther promotion and higher position depends on family-status, home-life, hav ...
A Tale of Star and Planet Formation
... Our Sun is a single star, but half of all Sun-like stars are found to be in multiple systems (twins, triplets, quads). Models of star formation have trouble predicting exactly how these systems are made. ...
... Our Sun is a single star, but half of all Sun-like stars are found to be in multiple systems (twins, triplets, quads). Models of star formation have trouble predicting exactly how these systems are made. ...
Astronomy
... telescope being released by the Space Shuttle. Why would an ultraviolet telescope need to be in space? Earth’s atmosphere blocks ultraviolet radiation. ...
... telescope being released by the Space Shuttle. Why would an ultraviolet telescope need to be in space? Earth’s atmosphere blocks ultraviolet radiation. ...
Star Life
... a. It allows for water to be formed inside of the star b. It fuses together to make radioactive uranium and releases energy used to fuel the star c. It has only one neutron which allows neutron star to be born d. It fuses together to form helium and releases energy used to fuel the star 18) The temp ...
... a. It allows for water to be formed inside of the star b. It fuses together to make radioactive uranium and releases energy used to fuel the star c. It has only one neutron which allows neutron star to be born d. It fuses together to form helium and releases energy used to fuel the star 18) The temp ...
PRESENTATION: Evolution of the elements through the lifecycles of
... -C-O. 800Mill K. At this points our star is about done. It will expand into a red giant and consume Mercury and Venus. Once it reaches this size it will collapse upon itself and form a white dwarf. 1/millionth its normal size, becoming ~ the size of earth. -Stars that have 1-4 times our suns solar m ...
... -C-O. 800Mill K. At this points our star is about done. It will expand into a red giant and consume Mercury and Venus. Once it reaches this size it will collapse upon itself and form a white dwarf. 1/millionth its normal size, becoming ~ the size of earth. -Stars that have 1-4 times our suns solar m ...
Formation of the Universe
... to and it becomes a white dwarf. After it cools, which takes billions of years, a white dwarf becomes a black dwarf. In larger stars, when fuel runs out and the material contracts a huge explosion occurs. Depending on the size of the star, this explosion is called a nova or supernova. These explosio ...
... to and it becomes a white dwarf. After it cools, which takes billions of years, a white dwarf becomes a black dwarf. In larger stars, when fuel runs out and the material contracts a huge explosion occurs. Depending on the size of the star, this explosion is called a nova or supernova. These explosio ...
Planetary nebula

A planetary nebula, often abbreviated as PN or plural PNe, is a kind of emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from old red giant stars late in their lives. The word ""nebula"" is Latin for mist or cloud and the term ""planetary nebula"" is a misnomer that originated in the 1780s with astronomer William Herschel because when viewed through his telescope, these objects appeared to him to resemble the rounded shapes of planets. Herschel's name for these objects was popularly adopted and has not been changed. They are a relatively short-lived phenomenon, lasting a few tens of thousands of years, compared to a typical stellar lifetime of several billion years.A mechanism for formation of most planetary nebulae is thought to be the following: at the end of the star's life, during the red giant phase, the outer layers of the star are expelled by strong stellar winds. Eventually, after most of the red giant's atmosphere is dissipated, the exposed hot, luminous core emits ultraviolet radiation to ionize the ejected outer layers of the star. Absorbed ultraviolet light energises the shell of nebulous gas around the central star, appearing as a bright coloured planetary nebula at several discrete visible wavelengths.Planetary nebulae may play a crucial role in the chemical evolution of the Milky Way, returning material to the interstellar medium from stars where elements, the products of nucleosynthesis (such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and neon), have been created. Planetary nebulae are also observed in more distant galaxies, yielding useful information about their chemical abundances.In recent years, Hubble Space Telescope images have revealed many planetary nebulae to have extremely complex and varied morphologies. About one-fifth are roughly spherical, but the majority are not spherically symmetric. The mechanisms which produce such a wide variety of shapes and features are not yet well understood, but binary central stars, stellar winds and magnetic fields may play a role.