How Does Earth Work?
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely silica (45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, C ...
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely silica (45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, C ...
Chromite - NSW Resources and Energy
... all world production coming from such deposits. Podiform and vein deposits tend to be smaller than the cumulate type, and are less important commercially. South Africa accounts for 46% of world production. Only minor production of chromite, from small podiform deposits, has occurred in Australia. Al ...
... all world production coming from such deposits. Podiform and vein deposits tend to be smaller than the cumulate type, and are less important commercially. South Africa accounts for 46% of world production. Only minor production of chromite, from small podiform deposits, has occurred in Australia. Al ...
Mineral
... Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Other Properties – Specific gravity (*excellent clue to mineral’s identity) Specific Gravity – Attraction to magnets – Bending of light ...
... Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Other Properties – Specific gravity (*excellent clue to mineral’s identity) Specific Gravity – Attraction to magnets – Bending of light ...
PC Minerals
... Many chemical changes continue to occur to a sedimentary rock even long after the rock is formed. Changes in temperature, pressure and chemistry of ground water permeating the rock formation produce new minerals. Minerals formed earlier may be replaced chemically. New minerals may also form in the i ...
... Many chemical changes continue to occur to a sedimentary rock even long after the rock is formed. Changes in temperature, pressure and chemistry of ground water permeating the rock formation produce new minerals. Minerals formed earlier may be replaced chemically. New minerals may also form in the i ...
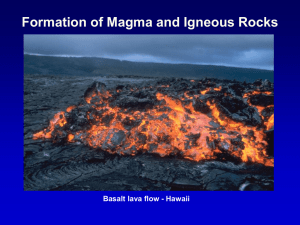
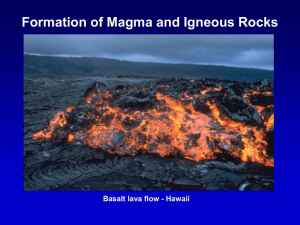
Formation of Magma and Igneous Rocks Basalt
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely SiO2 (~45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, Ca ...
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely SiO2 (~45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, Ca ...
Chapter 5
... Cold deep-ocean waters are under high pressure and contain more dissolved carbon dioxide than shallower waters. ...
... Cold deep-ocean waters are under high pressure and contain more dissolved carbon dioxide than shallower waters. ...
Glass-grade calcite resources of Borra area
... industries depending on its grade. High-grade limestone (>52 CaO %) is commonly used as raw material in various industries like glass, ceramics, iron & steel, chemical, fertilizer, foundry and sugar industries. In general the term limestone is applied to any calcareous sedimentary rock consisting es ...
... industries depending on its grade. High-grade limestone (>52 CaO %) is commonly used as raw material in various industries like glass, ceramics, iron & steel, chemical, fertilizer, foundry and sugar industries. In general the term limestone is applied to any calcareous sedimentary rock consisting es ...
The World of Rocks and Minerals - Everything You Need to Succeed
... Igneous rock formed beneath Earth’s surface forms rock such as granite. Large crystals of quartz, feldspar, and mica are found in granite. Gabbro and diorite are two other rocks that form from magma when it slowly cools. Igneous rocks are very hard, which gives them many practical uses. Granite is p ...
... Igneous rock formed beneath Earth’s surface forms rock such as granite. Large crystals of quartz, feldspar, and mica are found in granite. Gabbro and diorite are two other rocks that form from magma when it slowly cools. Igneous rocks are very hard, which gives them many practical uses. Granite is p ...
rock - Ms. Pinkstaff
... When magma reaches Earth’s surface and flows from volcanoes, it is called lava. As magma cools, atoms and compounds in the liquid rearrange themselves into new crystals called mineral grains. ...
... When magma reaches Earth’s surface and flows from volcanoes, it is called lava. As magma cools, atoms and compounds in the liquid rearrange themselves into new crystals called mineral grains. ...
Grade: 3rd Activity #: 1 Activity Title: Studying Rocks and Minerals
... also be the least useful in identifying a mineral. Most minerals occur in more than one color. The other properties, such as hardness, cleavage, and luster, must be used instead. For some minerals, color can be characteristic and serve as a means of identification. Malichite is always green, azurite ...
... also be the least useful in identifying a mineral. Most minerals occur in more than one color. The other properties, such as hardness, cleavage, and luster, must be used instead. For some minerals, color can be characteristic and serve as a means of identification. Malichite is always green, azurite ...
Chapter -13 Principles of Metallurgy
... Extraction of Platinum: 1) Platinum is rarely found on its own, but in combination with other base & precious metals. 2) The extraction process of platinum is quite complex, which includes milling the ore and smelting it at high temperatures. This removes base metals notably the concentrate PGM (pla ...
... Extraction of Platinum: 1) Platinum is rarely found on its own, but in combination with other base & precious metals. 2) The extraction process of platinum is quite complex, which includes milling the ore and smelting it at high temperatures. This removes base metals notably the concentrate PGM (pla ...
Formation of Sedimentary Rocks
... During lithification, parts of an organism can be replaced by minerals and turned into rock, such as shells that have been mineralized. ...
... During lithification, parts of an organism can be replaced by minerals and turned into rock, such as shells that have been mineralized. ...
Geological Society, London, Special Publications
... springs are common. Rarely economic, these vein deposits may or may not be genetically or temporally linked to their host rocks. Thus, many of them are hosted in igneous rocks (varying from basalt to rhyolite) which might possibly supply the ore solutions. O'Reilly (1992) inferred that the vein-type ...
... springs are common. Rarely economic, these vein deposits may or may not be genetically or temporally linked to their host rocks. Thus, many of them are hosted in igneous rocks (varying from basalt to rhyolite) which might possibly supply the ore solutions. O'Reilly (1992) inferred that the vein-type ...
Eastern Klamath Mountains - College of the Siskiyous
... of the geologic features we’ll see today during our field trip through the eastern Klamath Mountains. The mileages given are approximate and begin at College of the Siskiyous in Weed. 0.0 mi. Enter I-5 and drive south. From the campus loop road turn left onto Siskiyou Way and then right on South Wee ...
... of the geologic features we’ll see today during our field trip through the eastern Klamath Mountains. The mileages given are approximate and begin at College of the Siskiyous in Weed. 0.0 mi. Enter I-5 and drive south. From the campus loop road turn left onto Siskiyou Way and then right on South Wee ...
3. Overview of Stratigraphy and Depositional Systems
... Present is the key to the past, the observable processes operating today are the key to interpreting the geologic record ...
... Present is the key to the past, the observable processes operating today are the key to interpreting the geologic record ...
Rocks - Macmillan Learning
... Rocks formed by the consolidation of fragments of previously existing rock ...
... Rocks formed by the consolidation of fragments of previously existing rock ...
Rocks Outline - MrLaneScience
... Origin of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks come from volcanoes or volcanic processes. a. Magma Magma is rock material melted by heat and pressure. Magma will rise in the Earth. When magma reaches the Earth’s surface, it will flow as lava. b. Intrusive Rocks Intrusive rocks form below the Earth’s surface. ...
... Origin of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks come from volcanoes or volcanic processes. a. Magma Magma is rock material melted by heat and pressure. Magma will rise in the Earth. When magma reaches the Earth’s surface, it will flow as lava. b. Intrusive Rocks Intrusive rocks form below the Earth’s surface. ...
Chapter 5—The Sedimentary Archives
... laminae are usually at inclinations of less than 30 degrees and may be either straight or concave. delta (82): Transitional environments (between marine and non-marine) form deltas when streams enter bodies of standing water, undergo an abrupt loss of velocity, and drop their load of sediment. disch ...
... laminae are usually at inclinations of less than 30 degrees and may be either straight or concave. delta (82): Transitional environments (between marine and non-marine) form deltas when streams enter bodies of standing water, undergo an abrupt loss of velocity, and drop their load of sediment. disch ...
Chapter 5: Mineral Resources of the Midwestern US
... to the location of ore bodies. The occurrence of minerals in the Earth’s crust is due to the geologic processes that formed certain rock types in a given area. An understanding of the environments in which minerals form, the minerals that make up different rocks, and the geologic history of an area, ...
... to the location of ore bodies. The occurrence of minerals in the Earth’s crust is due to the geologic processes that formed certain rock types in a given area. An understanding of the environments in which minerals form, the minerals that make up different rocks, and the geologic history of an area, ...
Carlin-Type Gold Deposits in Nevada: Critical Geologic
... Carlin-type Au deposits in Nevada have huge Au endowments that have made the state, and the United States, one of the leading Au producers in the world. Forty years of mining and numerous studies have provided a detailed geologic picture of the deposits, yet a comprehensive and widely accepted genet ...
... Carlin-type Au deposits in Nevada have huge Au endowments that have made the state, and the United States, one of the leading Au producers in the world. Forty years of mining and numerous studies have provided a detailed geologic picture of the deposits, yet a comprehensive and widely accepted genet ...
Note Packet
... The scale is from _________ to __________ ( _________________ is the hardest mineral) Larger values will scratch mineral of lower or equal value! Hardness is due to the ______________________________________________________ ...
... The scale is from _________ to __________ ( _________________ is the hardest mineral) Larger values will scratch mineral of lower or equal value! Hardness is due to the ______________________________________________________ ...
Save 0 - Science Lec | Home
... away by running water, wind, glaciers, and gravity to lower elevations where they collect and deposit physically, chemically or biologically. These loose, unconsolidated particles are referred collectively by sediment. When the sediment is lithified and cemented together and form new consolidated ma ...
... away by running water, wind, glaciers, and gravity to lower elevations where they collect and deposit physically, chemically or biologically. These loose, unconsolidated particles are referred collectively by sediment. When the sediment is lithified and cemented together and form new consolidated ma ...
Part I. Earth`s Internal Structure and composition
... Igneous rocks form from a cooling magma. The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar. These rocks include Granite and Rhyolite. 2. Mafic Rocks: ...
... Igneous rocks form from a cooling magma. The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar. These rocks include Granite and Rhyolite. 2. Mafic Rocks: ...
Presentation1__ULTRAMAFICS
... ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS & REGOLITH • ALKALI-RICH ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS PROVIDE EXCELLENT BALANCE NUTRIENTS TO THE SOILS; PERIDOTITE & SERPENTINITE HAVE HIGH RATIO OF MAGNESIUM TO CALCIUM BUT DEFICIENT IN POTASSIUM & PHOSPORUS; CONTAIN TOXIC AMOUNTS OF CHROMIUM & NICKEL • ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS CREATE UNIQUE VEGETA ...
... ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS & REGOLITH • ALKALI-RICH ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS PROVIDE EXCELLENT BALANCE NUTRIENTS TO THE SOILS; PERIDOTITE & SERPENTINITE HAVE HIGH RATIO OF MAGNESIUM TO CALCIUM BUT DEFICIENT IN POTASSIUM & PHOSPORUS; CONTAIN TOXIC AMOUNTS OF CHROMIUM & NICKEL • ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS CREATE UNIQUE VEGETA ...
Shirbatu Granite Dimension Stone, Bamyan Province
... The Shirbatu Granite Complex (SGC) outcrops over a surface area of 164km2 and formed during the Phase II intrusion of granites and granodiorites. There are also some veins and stocks of alaskite granites and granosyenites. At this locality, the complex intruded limestones of Upper Permian age (Figur ...
... The Shirbatu Granite Complex (SGC) outcrops over a surface area of 164km2 and formed during the Phase II intrusion of granites and granodiorites. There are also some veins and stocks of alaskite granites and granosyenites. At this locality, the complex intruded limestones of Upper Permian age (Figur ...
Ore genesis

The various theories of ore genesis explain how the various types of mineral deposits form within the Earth's crust. Ore genesis theories are dependent on the mineral or commodity.Ore genesis theories generally involve three components: source, transport or conduit, and trap. This also applies to the petroleum industry, which was first to use this methodology. Source is required because metal must come from somewhere, and be liberated by some process Transport is required first to move the metal-bearing fluids or solid minerals into the right position, and refers to the act of physically moving the metal, as well as chemical or physical phenomenon which encourage movement Trapping is required to concentrate the metal via some physical, chemical or geological mechanism into a concentration which forms mineable oreThe biggest deposits are formed when the source is large, the transport mechanism is efficient, and the trap is active and ready at the right time.