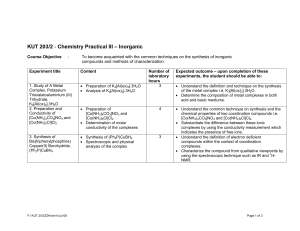
Structural Geology 1
... Elastic deformation – The rock returns to original size and shape when stress removed. When the (strength) of a rock is surpassed, it either flows (ductile deformation) or fractures (brittle deformation). Brittle behavior occurs in the shallow crust; ductile in the deeper crust. Stephen Marshak ...
... Elastic deformation – The rock returns to original size and shape when stress removed. When the (strength) of a rock is surpassed, it either flows (ductile deformation) or fractures (brittle deformation). Brittle behavior occurs in the shallow crust; ductile in the deeper crust. Stephen Marshak ...
3 Paleozoic Geology Homework c
... 9) In the Paleozoic, the single largest source of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere was: a) deposition of large amounts of organic matter. b) volcanic activity during sea-floor. spreading and subduction. c) widespread limestone production. d) abundant vegetation on the land surface. 10) In the late ...
... 9) In the Paleozoic, the single largest source of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere was: a) deposition of large amounts of organic matter. b) volcanic activity during sea-floor. spreading and subduction. c) widespread limestone production. d) abundant vegetation on the land surface. 10) In the late ...
Chapters 19 & 20
... cations with a configuration of the noble gas from the preceding period Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form anins with a configuration of the noble gas in the same period ...
... cations with a configuration of the noble gas from the preceding period Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form anins with a configuration of the noble gas in the same period ...
Plate tectonics - Brogranoni-GEO1
... The earth is made up of 4 distinct layers: 1. The inner core is in the centre of the earth and is the hottest part of the earth. The inner core is solid. It is made up of iron and nickel with temperatures of up to 5500°C. With its immense heat energy, the inner core is like the engine room of the Ea ...
... The earth is made up of 4 distinct layers: 1. The inner core is in the centre of the earth and is the hottest part of the earth. The inner core is solid. It is made up of iron and nickel with temperatures of up to 5500°C. With its immense heat energy, the inner core is like the engine room of the Ea ...
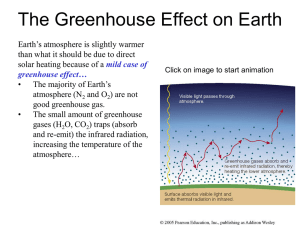
The Greenhouse Effect on Earth
... • Erosion by wind Particles of sand are transported close to the surface. finer particles of silt and clay can be transported great ...
... • Erosion by wind Particles of sand are transported close to the surface. finer particles of silt and clay can be transported great ...
Chapter 4
... In a titration a solution of accurately known concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. Equivalence point – the point at which the reaction is complete Indicator – substance that changes colo ...
... In a titration a solution of accurately known concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. Equivalence point – the point at which the reaction is complete Indicator – substance that changes colo ...
summerpp_4
... In a titration a solution of accurately known concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. Equivalence point – the point at which the reaction is complete Indicator – substance that changes colo ...
... In a titration a solution of accurately known concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. Equivalence point – the point at which the reaction is complete Indicator – substance that changes colo ...
Chapter 6 Section 3
... • Features such as grooves, striations, or polished surfaces called slickensides also show where rocks have moved. • Fault offset is often obvious for faults that have lengths of many kilometers. • A landform or manmade objects may be offset. • Streams commonly change their direction of flow at a fa ...
... • Features such as grooves, striations, or polished surfaces called slickensides also show where rocks have moved. • Fault offset is often obvious for faults that have lengths of many kilometers. • A landform or manmade objects may be offset. • Streams commonly change their direction of flow at a fa ...
Word - LEARNZ
... predict when earthquakes would strike, people could be told to move out until the danger was over). Most earthquakes are caused by sudden movement along natural fractures in the rocks, called faults. Explain that we are going to model how forces acting in the Earth can build up stresses, which are s ...
... predict when earthquakes would strike, people could be told to move out until the danger was over). Most earthquakes are caused by sudden movement along natural fractures in the rocks, called faults. Explain that we are going to model how forces acting in the Earth can build up stresses, which are s ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 10. According to ocean drilling evidence, what happens to the age of the ocean floor as a ship travels from the continental margin to the midocean ridge crest? ...
... 10. According to ocean drilling evidence, what happens to the age of the ocean floor as a ship travels from the continental margin to the midocean ridge crest? ...
crust
... • The hot material (magma) in the mantle rises to the top of the mantle, cools, then sinks, reheats, and rises again. These convection currents cause changes in the Earth’s surface ...
... • The hot material (magma) in the mantle rises to the top of the mantle, cools, then sinks, reheats, and rises again. These convection currents cause changes in the Earth’s surface ...
PPT - George Mason University
... Boron-Nitrogen compounds are similar in structure to elemental Carbon and some of its organic compounds Size, Ionization Energy, Electronegativity of Carbon is between Boron & Nitrogen Ethane & Amine – Borane have the same number & electron configuration ...
... Boron-Nitrogen compounds are similar in structure to elemental Carbon and some of its organic compounds Size, Ionization Energy, Electronegativity of Carbon is between Boron & Nitrogen Ethane & Amine – Borane have the same number & electron configuration ...
Ocean Features Objectives and HW
... D. spreading of new crust created by volcanic activity near a mid-ocean ridge ...
... D. spreading of new crust created by volcanic activity near a mid-ocean ridge ...
Continental Drift Powerpoint
... In 1912, a German scientist (he was an explorer, astronomer, and meteorologist) proposed that at one time all of the continents had been joined together to form one huge continent His name was Alfred Wegener He called this supercontinent Pangaea (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (millions ...
... In 1912, a German scientist (he was an explorer, astronomer, and meteorologist) proposed that at one time all of the continents had been joined together to form one huge continent His name was Alfred Wegener He called this supercontinent Pangaea (it means “all Earth”) And, over time (millions ...
earth`s history practice test
... 35. Which of the following statements best summarizes the history of life on Earth? a. Living organisms on Earth have become increasingly complex over time b. Earth has been populated by living organisms for most of its history c. The end of each Era saw an extinction of all life on the planet d. Oc ...
... 35. Which of the following statements best summarizes the history of life on Earth? a. Living organisms on Earth have become increasingly complex over time b. Earth has been populated by living organisms for most of its history c. The end of each Era saw an extinction of all life on the planet d. Oc ...
Inside Earth: Layers of the Earth
... Seismic waves change speed as they move through different materials. This causes them to bend. Some seismic waves do not travel through liquids or gases. Scientists use all of this information to understand what makes up the Earth’s interior. The properties of seismic waves allow scientists to under ...
... Seismic waves change speed as they move through different materials. This causes them to bend. Some seismic waves do not travel through liquids or gases. Scientists use all of this information to understand what makes up the Earth’s interior. The properties of seismic waves allow scientists to under ...
C1a Revision notes - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... Advantages and disadvantages of various building materials Limestone, cement and mortar slowly react with carbon dioxide dissolved in rainwater, and wear away. This damages walls made from limestone, and it leaves gaps between bricks in buildings. These gaps must be filled in or “pointed”. Pollution ...
... Advantages and disadvantages of various building materials Limestone, cement and mortar slowly react with carbon dioxide dissolved in rainwater, and wear away. This damages walls made from limestone, and it leaves gaps between bricks in buildings. These gaps must be filled in or “pointed”. Pollution ...
Ocean Basin Physiography
... Submarine canyons are steep-walled, V-shaped valleys that incise into continental shelves and slopes and open out at depth onto the continental rise. Most submarine canyons are associated with the mouths of large rivers. Although their origin is still debated, submarine canyons are important here be ...
... Submarine canyons are steep-walled, V-shaped valleys that incise into continental shelves and slopes and open out at depth onto the continental rise. Most submarine canyons are associated with the mouths of large rivers. Although their origin is still debated, submarine canyons are important here be ...
Name
... III. The Theory of Plate Tectonics: The Earth’s lithosphere is made of a number of solid pieces , called ____________ which move in relation to each other. These plates are “riding” on a more “plastic molten” layer below. This layer is called the ASTHENOSPHERE. The evidence shows that approximately ...
... III. The Theory of Plate Tectonics: The Earth’s lithosphere is made of a number of solid pieces , called ____________ which move in relation to each other. These plates are “riding” on a more “plastic molten” layer below. This layer is called the ASTHENOSPHERE. The evidence shows that approximately ...
RHV_Margins_Mini_Lesson.v8
... Earth’s crust, to a maximum of about 12 km in continental crust and 5 km in oceanic crust. Drilling has not reached the mantle. Although drilling samples only the outermost part of the Earth, many important Earth processes can be investigated, for example, we can find out: What is delivered to a ...
... Earth’s crust, to a maximum of about 12 km in continental crust and 5 km in oceanic crust. Drilling has not reached the mantle. Although drilling samples only the outermost part of the Earth, many important Earth processes can be investigated, for example, we can find out: What is delivered to a ...