pHeT – Plate Tectonics
... 1. Observe the Oceanic Crust on your left and the continental crust on your right. Which type of crust is thicker? ________________________ 2. You can change the crust in the middle of the simulator by adjusting the temperature, composition and thickness. Grab and move the Density gauge and thermome ...
... 1. Observe the Oceanic Crust on your left and the continental crust on your right. Which type of crust is thicker? ________________________ 2. You can change the crust in the middle of the simulator by adjusting the temperature, composition and thickness. Grab and move the Density gauge and thermome ...
CHEMISTRY REVISION GUIDE for CIE IGCSE Coordinated Science
... grams (molar mass, Mm) as its formula mass. For example the Mr of water is 18.02 so the Mm of water is 18.02g; the Mr of decane is 142.34 so the Mm of decane is 142.34g. Importantly this means that 18.02 g of water and 142.34g decane contains the same number of molecules. ...
... grams (molar mass, Mm) as its formula mass. For example the Mr of water is 18.02 so the Mm of water is 18.02g; the Mr of decane is 142.34 so the Mm of decane is 142.34g. Importantly this means that 18.02 g of water and 142.34g decane contains the same number of molecules. ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... 1. The Theory of Plate Tectonics combines Continental Drift with the processes of ____________________ & ____________________. 2. Lithospheric Plates includes the two types of crust (______________ or _______________) and the upper rigid part of the mantle. 3. Oceanic Crust is ______________________ ...
... 1. The Theory of Plate Tectonics combines Continental Drift with the processes of ____________________ & ____________________. 2. Lithospheric Plates includes the two types of crust (______________ or _______________) and the upper rigid part of the mantle. 3. Oceanic Crust is ______________________ ...
File
... solid, when otherwise they would melt from the intense heat. When hot rocks rise to shallow depths, the pressure is finally released & the minerals can melt. Composition – Sometimes fluids enter a rock that is close to its melting point. When these fluids combine with the rock, they can lower the me ...
... solid, when otherwise they would melt from the intense heat. When hot rocks rise to shallow depths, the pressure is finally released & the minerals can melt. Composition – Sometimes fluids enter a rock that is close to its melting point. When these fluids combine with the rock, they can lower the me ...
Landforms depend on types of crust that meet
... • Two plates colliding • Landforms depend on types of crust that meet • Mountain ranges: ...
... • Two plates colliding • Landforms depend on types of crust that meet • Mountain ranges: ...
1 UNIT 10 Plate Tectonics Study Guide Chapters 1, 2, 9, and most of
... - Biodiversity Similar plant and animal species within one large ecosystem will become rapidly become dissimilar from previously identical species when their ecosystem becomes isolated ecosystem from the large system. (This is true especially if those ecosystems are separated by land masses or ocean ...
... - Biodiversity Similar plant and animal species within one large ecosystem will become rapidly become dissimilar from previously identical species when their ecosystem becomes isolated ecosystem from the large system. (This is true especially if those ecosystems are separated by land masses or ocean ...
Chapter 7: Weathering & Soil
... Chemical Weathering Chemical reactions dissolve the minerals in rocks or change them to different minerals Changes the chemical composition of the rock Naturally occurring acids, such as carbonic acid, react with calcite in limestone The acid weathers away the limestone to form caves Kaolin ...
... Chemical Weathering Chemical reactions dissolve the minerals in rocks or change them to different minerals Changes the chemical composition of the rock Naturally occurring acids, such as carbonic acid, react with calcite in limestone The acid weathers away the limestone to form caves Kaolin ...
Evolution of Earth`s Atmosphere
... The internal structure of the Earth is layered in spherical shells, like an onion (Fig. 1.2). These layers can be defined by either their chemical or their theological properties. Earth has an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous mantle, a liquid outer core that is much less viscous than the ...
... The internal structure of the Earth is layered in spherical shells, like an onion (Fig. 1.2). These layers can be defined by either their chemical or their theological properties. Earth has an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous mantle, a liquid outer core that is much less viscous than the ...
MINERAL RESOURCES
... Nonrenewable Resource • Resource that exists in a fixed amount in various places in the Earth’s crust and has the potential for renewal only by geological, physical and chemical processes taking place over hundreds of millions of years. • Mineral Resources – naturally occurring, inorganic solid ...
... Nonrenewable Resource • Resource that exists in a fixed amount in various places in the Earth’s crust and has the potential for renewal only by geological, physical and chemical processes taking place over hundreds of millions of years. • Mineral Resources – naturally occurring, inorganic solid ...
Name
... minerals make up rocks. Describe how rocks and minerals are formed and/or classified. Indicator 1: Describe the rock cycle and explain that there are sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks that have distinct properties (e.g., color, texture) and are formed in different ways. Indicator 2: Explain ...
... minerals make up rocks. Describe how rocks and minerals are formed and/or classified. Indicator 1: Describe the rock cycle and explain that there are sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks that have distinct properties (e.g., color, texture) and are formed in different ways. Indicator 2: Explain ...
Plate Tectonics
... often forms island arc-volcanoes which erupt through the overriding plate as the descending plate melts below it Ex. Aleutian Islands of Alaska ...
... often forms island arc-volcanoes which erupt through the overriding plate as the descending plate melts below it Ex. Aleutian Islands of Alaska ...
Indian Journal of Chemistry
... branched alcohols have been measured as a function of composition at 298.15 K. The branched alcohol includes 2– propanol, 2-methyl-1-propanol, 3-methyl-1-butanol, and 2-methyl-2-propanol. The VmE for each of the mixtures studied are negative over the whole composition range. From the experimental da ...
... branched alcohols have been measured as a function of composition at 298.15 K. The branched alcohol includes 2– propanol, 2-methyl-1-propanol, 3-methyl-1-butanol, and 2-methyl-2-propanol. The VmE for each of the mixtures studied are negative over the whole composition range. From the experimental da ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... heat into space. As a result, the rocks of Earth’s surface are hard and brittle. The cold outer layer of our planet, which holds together as a rigid shell, is not made of one solid piece. Instead, this shell is broken into separate pieces, or tectonic plates (lithosphere), that slide on top of the m ...
... heat into space. As a result, the rocks of Earth’s surface are hard and brittle. The cold outer layer of our planet, which holds together as a rigid shell, is not made of one solid piece. Instead, this shell is broken into separate pieces, or tectonic plates (lithosphere), that slide on top of the m ...
Continental Drift
... century yet the validity of continental drift was not generally recognized until the late 1960’s” It took ocean floor data to solidify ideas and convince scientific community! The oceans rule! ...
... century yet the validity of continental drift was not generally recognized until the late 1960’s” It took ocean floor data to solidify ideas and convince scientific community! The oceans rule! ...
Geochemistry and Origin of Middle Miocene Volcanic Rocks from
... A knowledge of the chemical composition of the volcanic rocks may provide a better understanding of the specific tectonic environment of their magma genesis. The chemical characterization of these lavas will aid also in the correlation between different volcanic areas. This information would be usef ...
... A knowledge of the chemical composition of the volcanic rocks may provide a better understanding of the specific tectonic environment of their magma genesis. The chemical characterization of these lavas will aid also in the correlation between different volcanic areas. This information would be usef ...
Science
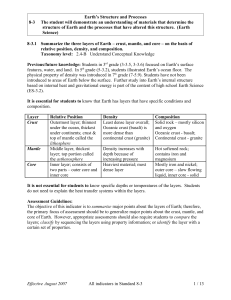
... Previous/future knowledge: Students in 3rd grade (3-3.5, 3-3.6) focused on Earth’s surface features, water, and land. In 5th grade (5-3.2), students illustrated Earth’s ocean floor. The physical property of density was introduced in 7th grade (7-5.9). Students have not been introduced to areas of Ea ...
... Previous/future knowledge: Students in 3rd grade (3-3.5, 3-3.6) focused on Earth’s surface features, water, and land. In 5th grade (5-3.2), students illustrated Earth’s ocean floor. The physical property of density was introduced in 7th grade (7-5.9). Students have not been introduced to areas of Ea ...
Plate Tectonics - Duplin County Schools
... • Plate tectonics – Theory that the lithosphere is made up of plates that float on the asthenosphere and that the plates possibly are moved by convection currents. ...
... • Plate tectonics – Theory that the lithosphere is made up of plates that float on the asthenosphere and that the plates possibly are moved by convection currents. ...
Summary from Previous Class
... P,T, density variation in the earth’s interior Transition Zone, Two-layered vs. whole mantle convection Plate tectonics, Plumes, Wilson Cycle, and recent hypotheses by Anderson and Larson ...
... P,T, density variation in the earth’s interior Transition Zone, Two-layered vs. whole mantle convection Plate tectonics, Plumes, Wilson Cycle, and recent hypotheses by Anderson and Larson ...
File
... explains these movements is called "plate tectonics." It was developed in the mid 1960s by geophysicists. The term "plate" refers to large rigid blocks of the Earth's surface which appear to move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ...
... explains these movements is called "plate tectonics." It was developed in the mid 1960s by geophysicists. The term "plate" refers to large rigid blocks of the Earth's surface which appear to move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ...
Do Now - North Thurston Public Schools
... plates pull AWAY from each other 2. Convergent- Crust is being destroyed or uplifted and the plates move TOWARDS each other 3. Transform- where crust is neither created or destroyed and the plates that slide horizontally past each other ...
... plates pull AWAY from each other 2. Convergent- Crust is being destroyed or uplifted and the plates move TOWARDS each other 3. Transform- where crust is neither created or destroyed and the plates that slide horizontally past each other ...
Hydrogen, Alkalis, and Alkaline Earths
... The Hydrogen Economy Hydrogen is an attractive fuel because of its high heat of combustion and zero pollution ...
... The Hydrogen Economy Hydrogen is an attractive fuel because of its high heat of combustion and zero pollution ...
Plate Tectonics
... down into the mantle. The slab of oceanic rock melts when the endges get to a depth which is hot enough. This process is called subduction. Molten material produced in a subduction zone can rise to the earth’s surface and cause mountains, and islands. ...
... down into the mantle. The slab of oceanic rock melts when the endges get to a depth which is hot enough. This process is called subduction. Molten material produced in a subduction zone can rise to the earth’s surface and cause mountains, and islands. ...