Earthquakes
... Earthquakes An earthquake is the shaking or trembling of the earth caused by the _Sudden_ movement of the earth’s crust. They usually occur where rocks that have been fractured suddenly _Shift___. ...
... Earthquakes An earthquake is the shaking or trembling of the earth caused by the _Sudden_ movement of the earth’s crust. They usually occur where rocks that have been fractured suddenly _Shift___. ...
Review Mid-Term Exam
... In time EARTH’S interior accumulated heat New atmosphere created by volcanic outgassing and delivery of gases and water by ice-covered comets. ...
... In time EARTH’S interior accumulated heat New atmosphere created by volcanic outgassing and delivery of gases and water by ice-covered comets. ...
review list 2013
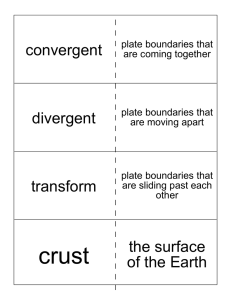
... Plate movement causes earthquakes (and makes mountains, volcanoes and new ocean crust), therefore these things occur mostly along active plate boundaries. There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, transform. Convergent: Subduction happens if it is ocean and continental ...
... Plate movement causes earthquakes (and makes mountains, volcanoes and new ocean crust), therefore these things occur mostly along active plate boundaries. There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, transform. Convergent: Subduction happens if it is ocean and continental ...
103-04-RocksIntrod-2006(Lesson08)
... Pyroxene (=dark Fe, Mg, & Ca-rich Al silicates) Na & Ca feldspars abundant (instead of K-feldspars of granite) No quartz comparison with continental crust: ...
... Pyroxene (=dark Fe, Mg, & Ca-rich Al silicates) Na & Ca feldspars abundant (instead of K-feldspars of granite) No quartz comparison with continental crust: ...
There are 4 main layers – the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and
... is thought to be responsible for protecting our atmosphere from getting blown away by the Sun's solar wind! ...
... is thought to be responsible for protecting our atmosphere from getting blown away by the Sun's solar wind! ...
Fortune Teller
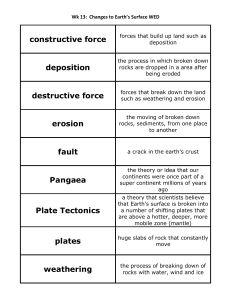
... 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the boundary of plates (faults). 2. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks chemically and physically. 3. Erosion causes weathered rocks and soil to be washed away. 4. Sedimentary – layers of sediment cemented together Igneous – melting and ...
... 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the boundary of plates (faults). 2. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks chemically and physically. 3. Erosion causes weathered rocks and soil to be washed away. 4. Sedimentary – layers of sediment cemented together Igneous – melting and ...
GUIDED NOTES – IGNEOUS ROCKS Name Date
... 2. _____________________: (FIH shurz), large cracks in Earth’s crust, can open up. ...
... 2. _____________________: (FIH shurz), large cracks in Earth’s crust, can open up. ...
Types of Weathering
... absorbs sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides. Through a series of chemical reactions these pollutants are converted into acids that are a cause of acid precipitation. ...
... absorbs sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides. Through a series of chemical reactions these pollutants are converted into acids that are a cause of acid precipitation. ...
Earth Science: Unit 1
... The Earth’s Surface (C-38 to C-43) • Vocabulary: landforms, plateau, plains, volcano, lava, magma, crust, mantle, core, deposition, Pangea, tectonic plates, geologist • Highlight sheets: “Landforms”, “The Earth’s Interior” ...
... The Earth’s Surface (C-38 to C-43) • Vocabulary: landforms, plateau, plains, volcano, lava, magma, crust, mantle, core, deposition, Pangea, tectonic plates, geologist • Highlight sheets: “Landforms”, “The Earth’s Interior” ...
ocks in the lithosphere
... The Lithosphere is made up of a large variety of minerals. These minerals are all composed of the chemical elements. Element ...
... The Lithosphere is made up of a large variety of minerals. These minerals are all composed of the chemical elements. Element ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Mountain ranges pushed up at the margins of colliding plates. - When an oceanic plate collides with a continental landmass, the continental plate will ride up over the seafloor and the oceanic plate will subduct down into the mantle. Deep ocean trenches mark subduction zones. ...
... Mountain ranges pushed up at the margins of colliding plates. - When an oceanic plate collides with a continental landmass, the continental plate will ride up over the seafloor and the oceanic plate will subduct down into the mantle. Deep ocean trenches mark subduction zones. ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
Review Sheet for Exam 1
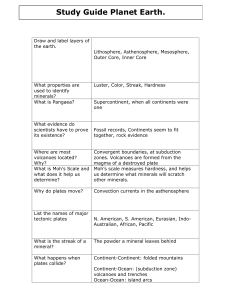
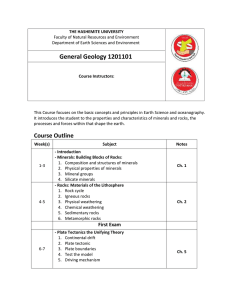
... What is the structure of an atom and what are its characteristics? (i.e., atomic mass, atomic number, etc.) What the four types of chemical bonds are What silicate minerals are & what they are primarily composed of The seven physical properties of minerals Moh’s Hardness Scale How minera ...
... What is the structure of an atom and what are its characteristics? (i.e., atomic mass, atomic number, etc.) What the four types of chemical bonds are What silicate minerals are & what they are primarily composed of The seven physical properties of minerals Moh’s Hardness Scale How minera ...
Time - Research School of Earth Sciences
... How are relative ages of rocks classified? Fossils (remnants of prehistoric life ...
... How are relative ages of rocks classified? Fossils (remnants of prehistoric life ...