Appalachian Mountains - Brief Geologic History The Earth is
... have been the source of high-purity minerals (such as feldspar,quartz,& mica) and gemstones (such as emeralds & beryl). When continental masses collided with the edge of ancestral North America, rocks were subjected to intense pressure and heat. Where the temperature was high but below the melting p ...
... have been the source of high-purity minerals (such as feldspar,quartz,& mica) and gemstones (such as emeralds & beryl). When continental masses collided with the edge of ancestral North America, rocks were subjected to intense pressure and heat. Where the temperature was high but below the melting p ...
PLATE MOVEMENT AND CONTINENTAL GROWTH
... they move horizontally and cool. The cool material sinks. All of this rising and sinking make the crust bulge, buckle and crack. Unscramble the letters in parentheses, and write in the space provided what else you think the molten material might cause the crust to do. (tshecrt) (rpemcul) ...
... they move horizontally and cool. The cool material sinks. All of this rising and sinking make the crust bulge, buckle and crack. Unscramble the letters in parentheses, and write in the space provided what else you think the molten material might cause the crust to do. (tshecrt) (rpemcul) ...
Geology and Earth Resources
... 3. Why are there so many volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis along the “ring of fire” that rims the Pacific Ocean? 4. Define mineral and rock. 5. Describe the rock cycle and name the three main rock types that it produces. ...
... 3. Why are there so many volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis along the “ring of fire” that rims the Pacific Ocean? 4. Define mineral and rock. 5. Describe the rock cycle and name the three main rock types that it produces. ...
Directed Reading C14.1 and C14.2
... 22. A rock that contains a large amount of a particular mineral, often a metal, to make it profitable for mining and processing is called a _________________________________________. 23. Name 5 commonly mined metallic minerals. ...
... 22. A rock that contains a large amount of a particular mineral, often a metal, to make it profitable for mining and processing is called a _________________________________________. 23. Name 5 commonly mined metallic minerals. ...
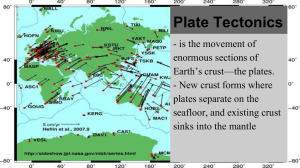
Plate Tectonics
... How is metamorphic rock formed? - The weight of the ground presses down on rocks that are deep under the surface. Metamorphic rocks are made when underground rocks are pressed and heated. -They are not hot enough to melt and turn into magma, but they are heated enough to change them from sedimentar ...
... How is metamorphic rock formed? - The weight of the ground presses down on rocks that are deep under the surface. Metamorphic rocks are made when underground rocks are pressed and heated. -They are not hot enough to melt and turn into magma, but they are heated enough to change them from sedimentar ...
Geological Past - Government of New Brunswick
... New Brunswick geology forms a rich tapestry of rock types and landscapes. In several areas of the province, the rocks are quarried for commercial purposes or contain valuable mineral deposits. Some of the deposits are being mined today, whereas others remain to be discovered. But how and when did th ...
... New Brunswick geology forms a rich tapestry of rock types and landscapes. In several areas of the province, the rocks are quarried for commercial purposes or contain valuable mineral deposits. Some of the deposits are being mined today, whereas others remain to be discovered. But how and when did th ...
Petrology
... formed by the cooling of melted materials, such as magma inside the earth and lava about the ground. ...
... formed by the cooling of melted materials, such as magma inside the earth and lava about the ground. ...
Earth`s Moving Plates
... the ideas of continental drift and ocean floor spreading and explains how the earth has evolved over time. Explains the formation, movement, collisions and destruction of the Earth’s crust. ...
... the ideas of continental drift and ocean floor spreading and explains how the earth has evolved over time. Explains the formation, movement, collisions and destruction of the Earth’s crust. ...
Earth Revealed #10: Geologic Time
... 2. How many varieties of minerals exist? Of these minerals, how many common minerals exist? ...
... 2. How many varieties of minerals exist? Of these minerals, how many common minerals exist? ...
BOOK REVIEWS 179 background information on the Data
... makes reference to plate tectonics, the lithosphere and asthenosphere, subduction, heat flow within the Earth, geothermal gradients, pressure within the Earth, magmatism on other planets, etc., and yet somehow fails to explain how igneous rocks are produced by partial fusion (this is explained in Ch ...
... makes reference to plate tectonics, the lithosphere and asthenosphere, subduction, heat flow within the Earth, geothermal gradients, pressure within the Earth, magmatism on other planets, etc., and yet somehow fails to explain how igneous rocks are produced by partial fusion (this is explained in Ch ...
inner core
... • IGNEOUS ROCKS are formed by the cooling and crystallization of hot, molten rock – magma. The word igneous means “formed by fire”. Igneous rocks make up about 95% of the Earth crust. Basalt and granite are common igneous rocks. • SEDIMENTARY ROCKS are formed from pieces of other rocks (sediments) c ...
... • IGNEOUS ROCKS are formed by the cooling and crystallization of hot, molten rock – magma. The word igneous means “formed by fire”. Igneous rocks make up about 95% of the Earth crust. Basalt and granite are common igneous rocks. • SEDIMENTARY ROCKS are formed from pieces of other rocks (sediments) c ...
PPT
... SPI 0707.7.3 Identify the major processes that drive the rock cycle. SPI 0707.7.4 Differentiate among the characteristics of the earth’s three layers. SPI 0707.7.5 Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year. SPI 0707.7.6 ...
... SPI 0707.7.3 Identify the major processes that drive the rock cycle. SPI 0707.7.4 Differentiate among the characteristics of the earth’s three layers. SPI 0707.7.5 Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year. SPI 0707.7.6 ...
Minerals
... Sediment is transported from one place to another by gravity, wind, water, and ice. Moving sediment from one place to another is called either erosion or mass wasting. Eventually, sediment is deposited into lakes, river valleys and oceans. ...
... Sediment is transported from one place to another by gravity, wind, water, and ice. Moving sediment from one place to another is called either erosion or mass wasting. Eventually, sediment is deposited into lakes, river valleys and oceans. ...
Rocks, Rock Cycle and Layers of the Earth Review
... Rocks, Rock Cycle and Layers of the Earth Review ...
... Rocks, Rock Cycle and Layers of the Earth Review ...
Lecture 5 - Plate Tectonics and Rocks
... Intermediate (chemically) igneous rocks are commonly formed at convergent boundaries Partial melting of basaltic oceanic crust produces intermediate magmas ...
... Intermediate (chemically) igneous rocks are commonly formed at convergent boundaries Partial melting of basaltic oceanic crust produces intermediate magmas ...
Physical Earth Science Semester 1 Mid
... more than 4500 degrees Celsius. The inner core is solid due to intense pressure, made of iron and nickel and more than 5000 degrees Celsius. 53. In the early Paleozoic, where was life restricted to? The seas 54. What is an ion? An atom that loses or gains electrons 55. On a topographic map, contour ...
... more than 4500 degrees Celsius. The inner core is solid due to intense pressure, made of iron and nickel and more than 5000 degrees Celsius. 53. In the early Paleozoic, where was life restricted to? The seas 54. What is an ion? An atom that loses or gains electrons 55. On a topographic map, contour ...
UNIT TITLE: Readers Theater
... The rock cycle shows how rocks are formed and how they change over time. (You should know how to read the rock cycle below!) ...
... The rock cycle shows how rocks are formed and how they change over time. (You should know how to read the rock cycle below!) ...
Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... Metamorphism is due to solid-state reactions between minerals due to change in temperature and pressure ...
... Metamorphism is due to solid-state reactions between minerals due to change in temperature and pressure ...
Review Questions For Earth crust (answers)
... 7. Explain how the Atlantic Ocean is becoming 3 cm wider each year. There is a place in the Atlantic Ocean where two Giant Plates meet. This plate boundary is called the Mid Atlantic Ridge and is where the two plates separate from each other. Magma from the Mantle rises up between the two plates and ...
... 7. Explain how the Atlantic Ocean is becoming 3 cm wider each year. There is a place in the Atlantic Ocean where two Giant Plates meet. This plate boundary is called the Mid Atlantic Ridge and is where the two plates separate from each other. Magma from the Mantle rises up between the two plates and ...
REVISED EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE – PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
... a. Along the mid-ocean ridges b. Around the Pacific Ring of Fire c. In California d. In the Appalachians ...
... a. Along the mid-ocean ridges b. Around the Pacific Ring of Fire c. In California d. In the Appalachians ...