Geology Test
... a. Precipitated rocks. b. Igneous rocks. c. Sedimentary rocks. d. Metamorphic rocks. 3. Rocks altered by heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface are a. Intrusive igneous rocks b. Extrusive sedimentary rocks c. Metamorphic rocks d. Igneous rocks 4. The Earth’s magnetic field is generated in a. ...
... a. Precipitated rocks. b. Igneous rocks. c. Sedimentary rocks. d. Metamorphic rocks. 3. Rocks altered by heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface are a. Intrusive igneous rocks b. Extrusive sedimentary rocks c. Metamorphic rocks d. Igneous rocks 4. The Earth’s magnetic field is generated in a. ...
magma
... What happens after they erupt? a. The magma explodes through a main vent in the volcano. b. A deep hole called a crater is often left on top of the volcano. c. The erupting magma is called lava. d. Gases, volcanic bombs, ash, and melted rock also burst from inside the volcano. e. The lava layers an ...
... What happens after they erupt? a. The magma explodes through a main vent in the volcano. b. A deep hole called a crater is often left on top of the volcano. c. The erupting magma is called lava. d. Gases, volcanic bombs, ash, and melted rock also burst from inside the volcano. e. The lava layers an ...
Bal Bharati Public School Class – 7 Subject
... 2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior of the earth, are called endogenic forces. The forces which act on the surface of the earth are called enogenic forces. 3. What is a volcano ? A volcano is a vent in the earth’s crust through which the molten material er ...
... 2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior of the earth, are called endogenic forces. The forces which act on the surface of the earth are called enogenic forces. 3. What is a volcano ? A volcano is a vent in the earth’s crust through which the molten material er ...
Ch 14 Notes - OCPS TeacherPress
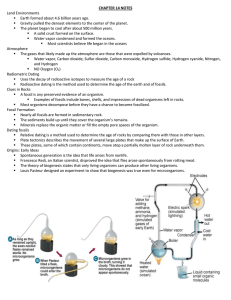
... Spontaneous generation is the idea that life arises from nonlife. Francesco Redi, an Italian scientist, disproved the idea that flies arose spontaneously from rotting meat. The theory of biogenesis states that only living organisms can produce other living organisms. Louis Pasteur designed a ...
... Spontaneous generation is the idea that life arises from nonlife. Francesco Redi, an Italian scientist, disproved the idea that flies arose spontaneously from rotting meat. The theory of biogenesis states that only living organisms can produce other living organisms. Louis Pasteur designed a ...
Igneous Petrology
... Petrology has two aspects: Petrography--the descriptive part of the science (modes, mineral compositions, textures, bulk composition (major & trace elements, isotopes…). [Check “Supplemental Material” on website for details on methods of characterizing ...
... Petrology has two aspects: Petrography--the descriptive part of the science (modes, mineral compositions, textures, bulk composition (major & trace elements, isotopes…). [Check “Supplemental Material” on website for details on methods of characterizing ...
Felsic
... A rock mass that forms when magma cools inside Earth’s interior. Also called a pluton Reaches Earth’s surface only after uplift and/or erosion. 1. Sills - A sheet of igneous rock that lies parallel to the layer it intrudes. Forced between rock layers. 2. Dikes - A sheet of igneous rock that cuts ...
... A rock mass that forms when magma cools inside Earth’s interior. Also called a pluton Reaches Earth’s surface only after uplift and/or erosion. 1. Sills - A sheet of igneous rock that lies parallel to the layer it intrudes. Forced between rock layers. 2. Dikes - A sheet of igneous rock that cuts ...
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY
... The oldest Olympic rock is basalt that originally formed from lava erupting out of crustal fissures into water at the bottom of the ocean. The other Olympic rocks were sediments deposited on the ocean floor, buried, and then hardened into sandstone and shale. Later, they were jammed against the basa ...
... The oldest Olympic rock is basalt that originally formed from lava erupting out of crustal fissures into water at the bottom of the ocean. The other Olympic rocks were sediments deposited on the ocean floor, buried, and then hardened into sandstone and shale. Later, they were jammed against the basa ...
Document
... Derived from weathered or fragmented rocks (clasts) In order of decreasing grain size, resultant rocks include conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone and shale Chemical sedimentary rocks Formed from dissolved minerals, transported in solution and precipitated from that solution. The most common example ...
... Derived from weathered or fragmented rocks (clasts) In order of decreasing grain size, resultant rocks include conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone and shale Chemical sedimentary rocks Formed from dissolved minerals, transported in solution and precipitated from that solution. The most common example ...
E.S. SOL Facts
... 1. The Earth consists of a solid inner core made of Fe and Ni (iron and Nickel); A liquid outer core made of Fe and Ni (iron and nickel) ; a plastic-like mantle made of Si, O, Fe, and Ni (silicon, oxygen, iron, and nickel); and a thin rocky crust made of Si and O (silicon and oxygen). 2. The lithosp ...
... 1. The Earth consists of a solid inner core made of Fe and Ni (iron and Nickel); A liquid outer core made of Fe and Ni (iron and nickel) ; a plastic-like mantle made of Si, O, Fe, and Ni (silicon, oxygen, iron, and nickel); and a thin rocky crust made of Si and O (silicon and oxygen). 2. The lithosp ...
A review sheet
... much study, you determine that there is a considerable span of time for which no sedimentary rock layer exists at the site. You have just discovered a(n) ___(B)_____. a. angular unconformity b. disconformity c. nonconformity 54. Mass wasting is most likely to occur (omit, B) a. in bedrock b. in an a ...
... much study, you determine that there is a considerable span of time for which no sedimentary rock layer exists at the site. You have just discovered a(n) ___(B)_____. a. angular unconformity b. disconformity c. nonconformity 54. Mass wasting is most likely to occur (omit, B) a. in bedrock b. in an a ...
The changing Earth. - Concord High School
... Literacy: A.L.A.R.M; Remember I.D.E.A and stop at the verb provided Identify: Name and Define Describe: Differentiate and distinguish by providing characteristics, features and properties Explain: Cause and effect = LINK purpose or function of EACH feature or characteristic listed above (Use linking ...
... Literacy: A.L.A.R.M; Remember I.D.E.A and stop at the verb provided Identify: Name and Define Describe: Differentiate and distinguish by providing characteristics, features and properties Explain: Cause and effect = LINK purpose or function of EACH feature or characteristic listed above (Use linking ...
Evolution of Life and Mass Extinctions
... formed during the hot and humid conditions of the Carboniferous Period) Deposits of salt and gypsum are found in western NYS because old oceans that covered the state evaporated during the hot and dry Silurian Period (noted on reference tables) ...
... formed during the hot and humid conditions of the Carboniferous Period) Deposits of salt and gypsum are found in western NYS because old oceans that covered the state evaporated during the hot and dry Silurian Period (noted on reference tables) ...
Chapter 9: Earth`s Changing Surface
... c. The deeper part of the mantle is made of solid rock and is under very high pressure with temperatures ranging from 900°C to 2,200°C. 1. Slow convection currents move the rock in the mantle. Cooler rock flows down and hotter rock flows up. d. The core is at the center of Earth and is made mostly o ...
... c. The deeper part of the mantle is made of solid rock and is under very high pressure with temperatures ranging from 900°C to 2,200°C. 1. Slow convection currents move the rock in the mantle. Cooler rock flows down and hotter rock flows up. d. The core is at the center of Earth and is made mostly o ...
Name Date
... 4. All rocks contain minerals formed by compression and cementation. 12. ______The crystal characteristics of quartz shown in the accompanying diagram are the result of the (1) internal arrangement of the elements from which quartz is formed (2) shape of the other rock crystals in the area where the ...
... 4. All rocks contain minerals formed by compression and cementation. 12. ______The crystal characteristics of quartz shown in the accompanying diagram are the result of the (1) internal arrangement of the elements from which quartz is formed (2) shape of the other rock crystals in the area where the ...
Mineral Resources
... Eight chemical elements make up 98.3% of Earth’s crust. O – 46.6% Al – 8.1% ...
... Eight chemical elements make up 98.3% of Earth’s crust. O – 46.6% Al – 8.1% ...
Chapter 8 Test Review Notes
... boundary, and the rocks are old. The rocks are cold and dense. The greater density causes the seafloor to be deeper. As it plunges into a deep-sea trench, the seafloor reaches its greatest depths of anywhere in the ocean basin. ...
... boundary, and the rocks are old. The rocks are cold and dense. The greater density causes the seafloor to be deeper. As it plunges into a deep-sea trench, the seafloor reaches its greatest depths of anywhere in the ocean basin. ...
Study Guide Exam #4
... What evidence indicates that the outer core is liquid? What evidence indicates that the core is composed mostly of iron and Earth’s magnetic field generated? Chapters 12 & 13 Plate Tectonics: How do continental crust and oceanic crust differ in density, composition, thickness, and relative age? What ...
... What evidence indicates that the outer core is liquid? What evidence indicates that the core is composed mostly of iron and Earth’s magnetic field generated? Chapters 12 & 13 Plate Tectonics: How do continental crust and oceanic crust differ in density, composition, thickness, and relative age? What ...
1: How does the process of mountain building begin
... 9: What happens once the elastic limit or strength of the rock is exceeded? ...
... 9: What happens once the elastic limit or strength of the rock is exceeded? ...
GLCE Inside the Ea
... Describe layers of the Earth as a lithosphere (crust & upper mantle). convecting mantle, and dense metallic core (E.SE.06.53) Describe the Earth as a magnet and compare the magnetic properties of the Earth to that of a natural or man-made magnet (E.SE.06.61) Explain how a compass works using the mag ...
... Describe layers of the Earth as a lithosphere (crust & upper mantle). convecting mantle, and dense metallic core (E.SE.06.53) Describe the Earth as a magnet and compare the magnetic properties of the Earth to that of a natural or man-made magnet (E.SE.06.61) Explain how a compass works using the mag ...