Chapter 18- Volcanoes - Independence High School
... – molten material rises and mixes with overlying silica and water rich continental crust – high viscosity – very explosive eruptions – highest silica content – thick, slow moving lava – melted granite ...
... – molten material rises and mixes with overlying silica and water rich continental crust – high viscosity – very explosive eruptions – highest silica content – thick, slow moving lava – melted granite ...
Earth`s Interior Information- Core-Innermost layer Inner Core
... Asthenosphere-Not liquid, but there is melted rock, carries the lithosphere, moves slowly Lithosphere-broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. The pieces move a little bit each year. They slide on a somewhat liquid asthenosphere Crust-Layer of rock that forms Earth’s ou ...
... Asthenosphere-Not liquid, but there is melted rock, carries the lithosphere, moves slowly Lithosphere-broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. The pieces move a little bit each year. They slide on a somewhat liquid asthenosphere Crust-Layer of rock that forms Earth’s ou ...
Rock - My CCSD
... fossils some rocks contain also provide clues about lifeforms that lived billions of years ago, long before dinosaurs walked the Earth. ...
... fossils some rocks contain also provide clues about lifeforms that lived billions of years ago, long before dinosaurs walked the Earth. ...
Name date
... cuts across another rock layer is _______________ than the ones being cut (dykes) Absolute Ages of Rocks A. Atoms and Isotopes 1. Atoms are made of _______________, _______________, and _______________ 2. Isotopes of an atom have the same number of _______________, but different number of __________ ...
... cuts across another rock layer is _______________ than the ones being cut (dykes) Absolute Ages of Rocks A. Atoms and Isotopes 1. Atoms are made of _______________, _______________, and _______________ 2. Isotopes of an atom have the same number of _______________, but different number of __________ ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... Resulting Question: Are all of the oceans getting bigger? • Suggested Answer: Ocean floors do not keep spreading. Parts of the oceanic crust get plunged into deep-ocean trenches due to the process of subduction. ...
... Resulting Question: Are all of the oceans getting bigger? • Suggested Answer: Ocean floors do not keep spreading. Parts of the oceanic crust get plunged into deep-ocean trenches due to the process of subduction. ...
final_exam - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth but Swaves can. This results in a P-wave shadow on the side of the Earth opposite an earthquake. 11. To reach its dew point temperature, a packet of unsaturated air must usually be [ heated / cooled ]. (circl ...
... 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth but Swaves can. This results in a P-wave shadow on the side of the Earth opposite an earthquake. 11. To reach its dew point temperature, a packet of unsaturated air must usually be [ heated / cooled ]. (circl ...
geology exam is - Spring Branch ISD
... 1. Name one mineral that you can scratch with your fingernail. 2. Which mineral can scratch anything? ...
... 1. Name one mineral that you can scratch with your fingernail. 2. Which mineral can scratch anything? ...
Review Topics for Test I
... may exhibit foliation (alignment of minerals or apparent “layers” of minerals) due to stress on the parent rock Sedimentary: Formed from existing rock as solid rocks weather mechanically. Pieces are buried, compacted and cemented to form a new rock. Also formed from chemical weathering where mineral ...
... may exhibit foliation (alignment of minerals or apparent “layers” of minerals) due to stress on the parent rock Sedimentary: Formed from existing rock as solid rocks weather mechanically. Pieces are buried, compacted and cemented to form a new rock. Also formed from chemical weathering where mineral ...
Intrusive Activity Earth Science Notes Chapter 18.3
... Draw an illustration that includes the following features: Batholiths Dike Laccolith Sill Stock ...
... Draw an illustration that includes the following features: Batholiths Dike Laccolith Sill Stock ...
The Interior of Earth
... Continents are made of granite, a low density rock Submerged parts of continents are made of basalt (higher density) Interior o Core – iron (iron porous silicates) and nickel – most dense Inner (solid) core Outer (molten) core o Mantel – silicate rocks and iron (iron rich silicates) – lower dens ...
... Continents are made of granite, a low density rock Submerged parts of continents are made of basalt (higher density) Interior o Core – iron (iron porous silicates) and nickel – most dense Inner (solid) core Outer (molten) core o Mantel – silicate rocks and iron (iron rich silicates) – lower dens ...
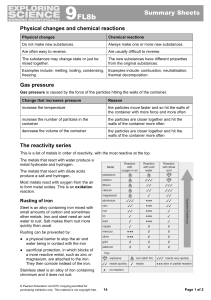
9F Reactivity - Parrs Wood High School
... These substances contain hydrogen and carbon only. They burn in a plentiful supply of air to form carbon dioxide and water: hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water The test for oxygen is that it relights a glowing splint. An input of energy from a flame or spark is needed to start the combusti ...
... These substances contain hydrogen and carbon only. They burn in a plentiful supply of air to form carbon dioxide and water: hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water The test for oxygen is that it relights a glowing splint. An input of energy from a flame or spark is needed to start the combusti ...
section 1 - image identification
... "Tsunami" is the correct term for what hit the Indian Ocean on December 26, 2004 and which we mistakenly call ________. Is Kilauea an excellent example of a regularly erupting volcano? Is weathering is the breaking up and removal of earth materials? Can dams be used indefinitely? What happ ...
... "Tsunami" is the correct term for what hit the Indian Ocean on December 26, 2004 and which we mistakenly call ________. Is Kilauea an excellent example of a regularly erupting volcano? Is weathering is the breaking up and removal of earth materials? Can dams be used indefinitely? What happ ...
weathering_and_erosion
... also form where there is stretching and thinning of the Earth's crust (called "non-hotspot intraplate volcanism"), such as in the African Rift Valley, the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and the Rio Grande Rift in North America and the European Rhine Graben with its Eifel volcanoes. Volcanoes c ...
... also form where there is stretching and thinning of the Earth's crust (called "non-hotspot intraplate volcanism"), such as in the African Rift Valley, the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and the Rio Grande Rift in North America and the European Rhine Graben with its Eifel volcanoes. Volcanoes c ...
Igneous Rock
... makes its way to Earth's surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above the surface as lava, and then cools forming rock. Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks ...
... makes its way to Earth's surface. The molten rock erupts or flows above the surface as lava, and then cools forming rock. Most extrusive (volcanic) rocks ...
Chapter 21 Planet Earth
... easy to see as those of physical weathering, but chemical weathering can have a great effect on the landscape over millions of years. Carbon dioxide can cause chemical weathering ...
... easy to see as those of physical weathering, but chemical weathering can have a great effect on the landscape over millions of years. Carbon dioxide can cause chemical weathering ...
Summary notes - Kelso High School
... Acids and pH The word ACID means sour. We often say that a sour liquid tastes acid. Examples of sour liquids that you will find in the home are vinegar, lemon juice, grapefruit juice and sour milk. You can find out if a substance is an acid or and alkali by dissolving it in water and adding an indi ...
... Acids and pH The word ACID means sour. We often say that a sour liquid tastes acid. Examples of sour liquids that you will find in the home are vinegar, lemon juice, grapefruit juice and sour milk. You can find out if a substance is an acid or and alkali by dissolving it in water and adding an indi ...
Earth`s internal structure
... lava and magma). It is the only region of the planet that we can investigate directly by boring into it and taking samples. In continental areas, the crust's average thickness is 36 km but may be anything from 10 km to 80 km depending on the last movement of the tectonic plates in that area. The cru ...
... lava and magma). It is the only region of the planet that we can investigate directly by boring into it and taking samples. In continental areas, the crust's average thickness is 36 km but may be anything from 10 km to 80 km depending on the last movement of the tectonic plates in that area. The cru ...
controls (practical/laboratory) work, abstract
... rock by heat, pressure, or other natural agency B- denoting or relating to rock that has undergone transformation by heat, pressure, or other natural agencies, e.g. in the folding of strata or the nearby intrusion of igneous rocks C-is the solid mineral material forming part of the surface of the ea ...
... rock by heat, pressure, or other natural agency B- denoting or relating to rock that has undergone transformation by heat, pressure, or other natural agencies, e.g. in the folding of strata or the nearby intrusion of igneous rocks C-is the solid mineral material forming part of the surface of the ea ...
Our Dynamic Earth
... Atmosphere- includes all the gases around Earth. Hydrosphere- all of Earth’s water. Crust- rocky layer of Earth. Mantle- Earth’s interior below the crust. Inner Core- deep inside Earth; made of solid metals. ...
... Atmosphere- includes all the gases around Earth. Hydrosphere- all of Earth’s water. Crust- rocky layer of Earth. Mantle- Earth’s interior below the crust. Inner Core- deep inside Earth; made of solid metals. ...
Mineral – Naturally formed solids that are not made from living
... by wind or water. Shape & appearance change BUT NOT composition. Chemical Weathering – Process in which chemicals break down the composition of a rock into new materials. Ex: Acid rain & rusting. 2. Erosion – Process by which sediment is removed from its source (mountains) by wind, H2O, ice or heat. ...
... by wind or water. Shape & appearance change BUT NOT composition. Chemical Weathering – Process in which chemicals break down the composition of a rock into new materials. Ex: Acid rain & rusting. 2. Erosion – Process by which sediment is removed from its source (mountains) by wind, H2O, ice or heat. ...