The Theory of Plate Tectonics Homework
... 4. Describe what happens when (a) two plates carrying oceanic crust collide, (b) two plates carrying continental crust collide, and (c) a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. 5. Explain what force caused the movement of the continents from one supercontinent ...
... 4. Describe what happens when (a) two plates carrying oceanic crust collide, (b) two plates carrying continental crust collide, and (c) a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. 5. Explain what force caused the movement of the continents from one supercontinent ...
4 - Devon County Council
... constituents. The tourmalinisation has affected not only the contact hornfels but also the outer parts of the intrusion, reddening the granite especially adjacent to joints. The 'shales' at the contact zone demonstrate both the chemical exchanges consequent upon intrusion and the effects upon the gr ...
... constituents. The tourmalinisation has affected not only the contact hornfels but also the outer parts of the intrusion, reddening the granite especially adjacent to joints. The 'shales' at the contact zone demonstrate both the chemical exchanges consequent upon intrusion and the effects upon the gr ...
Geologic Resources at Golden Gate
... wildlife that live upon them, it benefits all park staff to have a basic understanding of the earth beneath our feet! ...
... wildlife that live upon them, it benefits all park staff to have a basic understanding of the earth beneath our feet! ...
File
... together as Pangaea. ……..a supercontinent. 200 million years ago Pangaea began to break apart. Pangaea divided into Laurasia and Gondwanaland… They further divided into the continents we know today…. ...
... together as Pangaea. ……..a supercontinent. 200 million years ago Pangaea began to break apart. Pangaea divided into Laurasia and Gondwanaland… They further divided into the continents we know today…. ...
Gabbro Igneous rock containing coarse, iron
... is a notable exception to the rather arbitrary division between layered and unlayered gabbro complexes. The lower part of this mass has the average composition of an olivine gabbro but is strongly banded. The upper portion is a comparatively homogeneous feldspathic gabbro, not sharply banded. Althou ...
... is a notable exception to the rather arbitrary division between layered and unlayered gabbro complexes. The lower part of this mass has the average composition of an olivine gabbro but is strongly banded. The upper portion is a comparatively homogeneous feldspathic gabbro, not sharply banded. Althou ...
ch07 - earthjay science
... Which of the following is paleoclimatological evidence for continental drift? a. Magnetic reversals b. Lack of annual tree rings in fossilized trees c. Orientation of mountain ranges d. The fit of the continental margins e. Apparent polar wandering ...
... Which of the following is paleoclimatological evidence for continental drift? a. Magnetic reversals b. Lack of annual tree rings in fossilized trees c. Orientation of mountain ranges d. The fit of the continental margins e. Apparent polar wandering ...
6th Grade Earth Science – Inside Earth Vocabulary 1. crust – the
... 8. Earth as a magnet – the Earth acts like a magnet because of the liquid outer core made of iron and nickel which spins as the earth rotates and creates a magnetic field and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is ...
... 8. Earth as a magnet – the Earth acts like a magnet because of the liquid outer core made of iron and nickel which spins as the earth rotates and creates a magnetic field and the north & south poles on earth 9. compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is ...
Origin of the earth – Earth`s crust – Composition Origin of earth Earth
... nebula which once encircled the Sun. The outer planets formed first, followed by Mars, the Earth, Venus, and Mercury. This hypothesis suggests a sequential origin from outermost planet to innermost. As per this hypothesis, Mars evolved earlier than the Earth. This hypothesis is widely accepted to ex ...
... nebula which once encircled the Sun. The outer planets formed first, followed by Mars, the Earth, Venus, and Mercury. This hypothesis suggests a sequential origin from outermost planet to innermost. As per this hypothesis, Mars evolved earlier than the Earth. This hypothesis is widely accepted to ex ...
Chapter 19
... consists of a gentle continental shelf, a steep continental slope, and at the base of the slope the continental rise. The youngest part of the ocean basins are at divergent boundaries called spreading centers. Here the oceanic plates are moving apart and magma rises from the mantle to form brand new ...
... consists of a gentle continental shelf, a steep continental slope, and at the base of the slope the continental rise. The youngest part of the ocean basins are at divergent boundaries called spreading centers. Here the oceanic plates are moving apart and magma rises from the mantle to form brand new ...
Lithosphere #2
... Core- Made mostly of metals, iron and nickel; consists of 2 parts, outer core (molten) and inner core (solid); movement of outer core creates magnetic field, and is composed of iron. ...
... Core- Made mostly of metals, iron and nickel; consists of 2 parts, outer core (molten) and inner core (solid); movement of outer core creates magnetic field, and is composed of iron. ...
Lesson 1: Earth Energy Lesson
... phenomenon that One: that reasoned are difficult to All the all of the explain: continents 1)That the continents look like giant used be must to have pieces of a puzzle. joined together been joined 2) Fossils of the same in one large together at non-swimming organisms found on piece somecalled past ...
... phenomenon that One: that reasoned are difficult to All the all of the explain: continents 1)That the continents look like giant used be must to have pieces of a puzzle. joined together been joined 2) Fossils of the same in one large together at non-swimming organisms found on piece somecalled past ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes!
... – Normal faults: form where rocks are angled with each other; one block or rock lies below the other – Reverse faults: are like normal faults but move in the opposite direction – Strike-slip faults: form when rocks slide past each other ...
... – Normal faults: form where rocks are angled with each other; one block or rock lies below the other – Reverse faults: are like normal faults but move in the opposite direction – Strike-slip faults: form when rocks slide past each other ...
File
... kilometer network of volcanoes, generates new oceanic crust at the rate of 17 km3 per year, covering the ocean floor with an igneous rock called basalt. Hawaii and Iceland are two examples of the accumulation of basalt islands. ...
... kilometer network of volcanoes, generates new oceanic crust at the rate of 17 km3 per year, covering the ocean floor with an igneous rock called basalt. Hawaii and Iceland are two examples of the accumulation of basalt islands. ...
(>8.0 magnitude, past 100 yrs) Active Volcanoes
... 1. The crust and the upper mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rock called the: ...
... 1. The crust and the upper mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rock called the: ...
Wet Corrosion Conditions for Wet Corrosion Just as we live in an
... 1. There must be two dissimilar metals. Metals of different chemistry provide the obvious example, such as using steel nails to secure a copper sheet. Not as obvious is that, even with the same chemistry, differences in grain size or different amounts of cold working can drive electrochemical attack ...
... 1. There must be two dissimilar metals. Metals of different chemistry provide the obvious example, such as using steel nails to secure a copper sheet. Not as obvious is that, even with the same chemistry, differences in grain size or different amounts of cold working can drive electrochemical attack ...
Chapter 22.1: Earth`s Structure
... 3. The asthenosphere – which is in the mantle 4. The core 5. The crust 5. Oceanic crust is denser (but thinner) 6. The upper mantle (and the crust make up the ...
... 3. The asthenosphere – which is in the mantle 4. The core 5. The crust 5. Oceanic crust is denser (but thinner) 6. The upper mantle (and the crust make up the ...
Inside Earth Worksheet
... 1. Draw and label a model of the Earth’s layers. Be sure to label both the compositional layers and physical properties layers. You may draw two separate models for each “type” of layers or just one. ...
... 1. Draw and label a model of the Earth’s layers. Be sure to label both the compositional layers and physical properties layers. You may draw two separate models for each “type” of layers or just one. ...
Chapter 10-2 - Seafloor Spreading
... Example of a drilling rig at sea. What did the scientists find? Well the research concluded that the age of the rocks become much older in samples found farther from the ridges. This is evidence for seafloor spreading. ...
... Example of a drilling rig at sea. What did the scientists find? Well the research concluded that the age of the rocks become much older in samples found farther from the ridges. This is evidence for seafloor spreading. ...
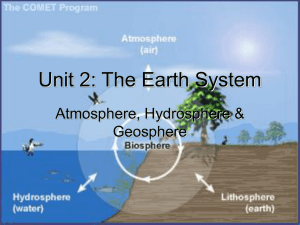
Earth System PP slides
... atmosphere, climate changes, new crust • Plate movements causing crust to be recycled including elements that accumulate such as carbon and “salt” • Provides varied topography on which both dry and wet land creatures dwell • Weathers to form soil from which land ...
... atmosphere, climate changes, new crust • Plate movements causing crust to be recycled including elements that accumulate such as carbon and “salt” • Provides varied topography on which both dry and wet land creatures dwell • Weathers to form soil from which land ...
Inside Earth - bms8thgradescience
... 11. Why was the continental drift hypothesis rejected by scientists at first (pg. 22)? Because Wegener could not explain how continents could move…he could not provide a satisfactory explanation for the force that pushes and pulls continents. Sea-Floor Spreading and Subduction (Section 1.4): 12. Com ...
... 11. Why was the continental drift hypothesis rejected by scientists at first (pg. 22)? Because Wegener could not explain how continents could move…he could not provide a satisfactory explanation for the force that pushes and pulls continents. Sea-Floor Spreading and Subduction (Section 1.4): 12. Com ...
EARTH, ATMOSPHERIC, OCEAN AND PLANETARY SCIENCES
... 2. it will have an adverse effect on bio-diversity. 3. plants may become extinct followed by animals and humans 4. The pH of the rain water will increase. ...
... 2. it will have an adverse effect on bio-diversity. 3. plants may become extinct followed by animals and humans 4. The pH of the rain water will increase. ...